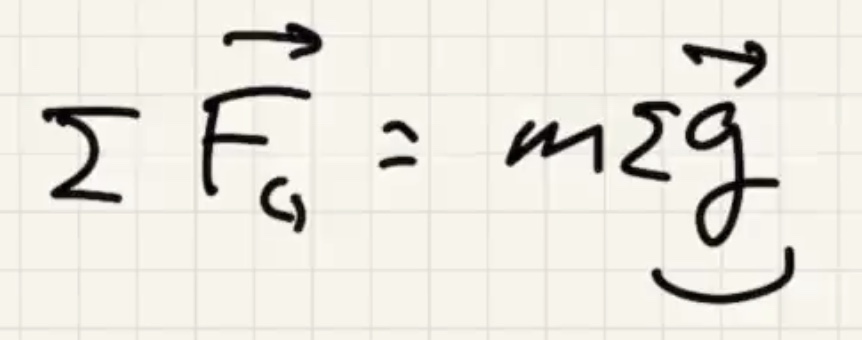Announcements #
- HW 13 Ch 6 due tomorrow
- Quiz 7 due 4/14
- Lab due tomorrow
- New lab today
- Revised schedule posted
- Office hour tomorrow @ 11am

Today #

Clicker questions #
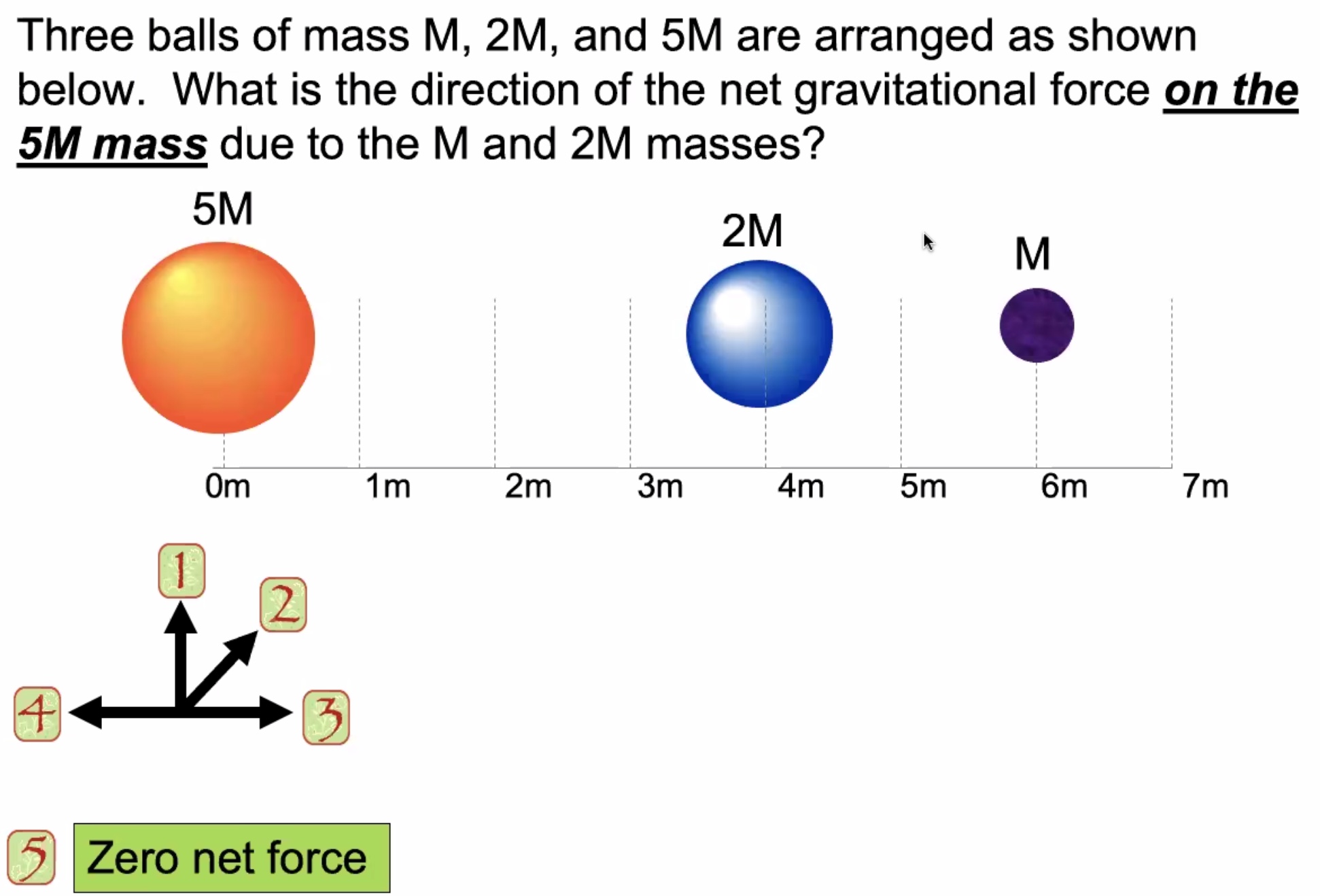
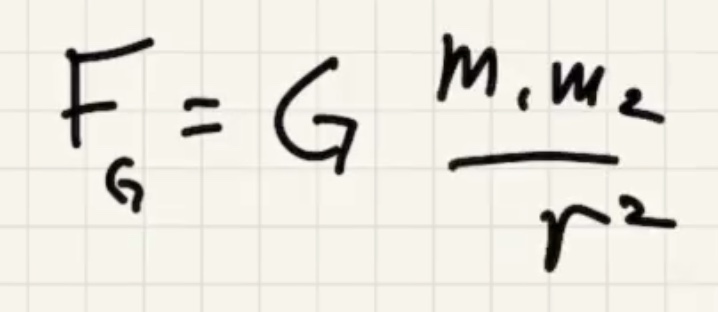
Gravitational force is always attractive.
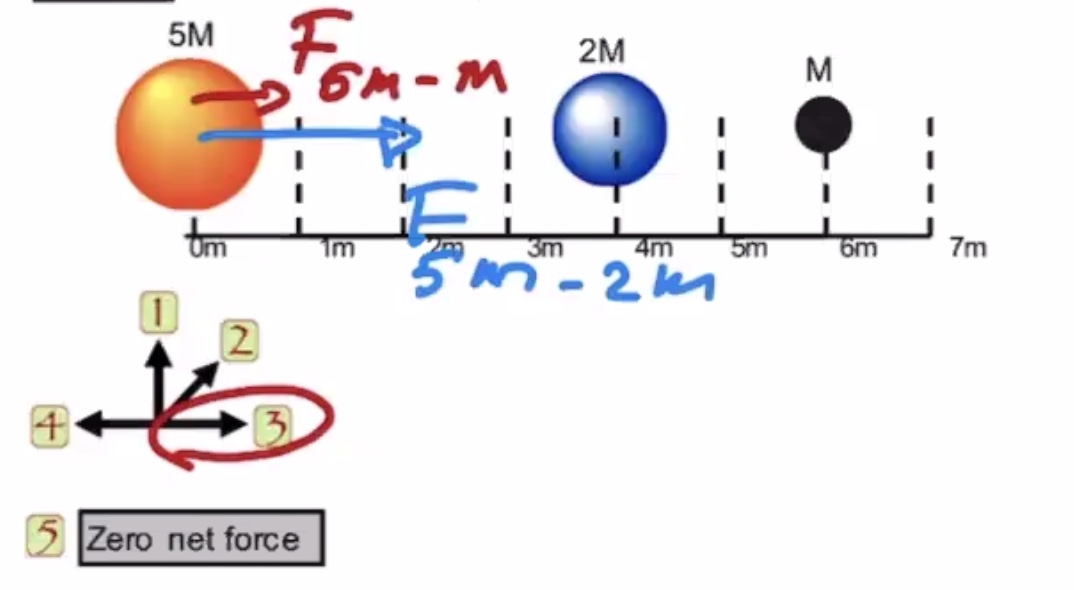
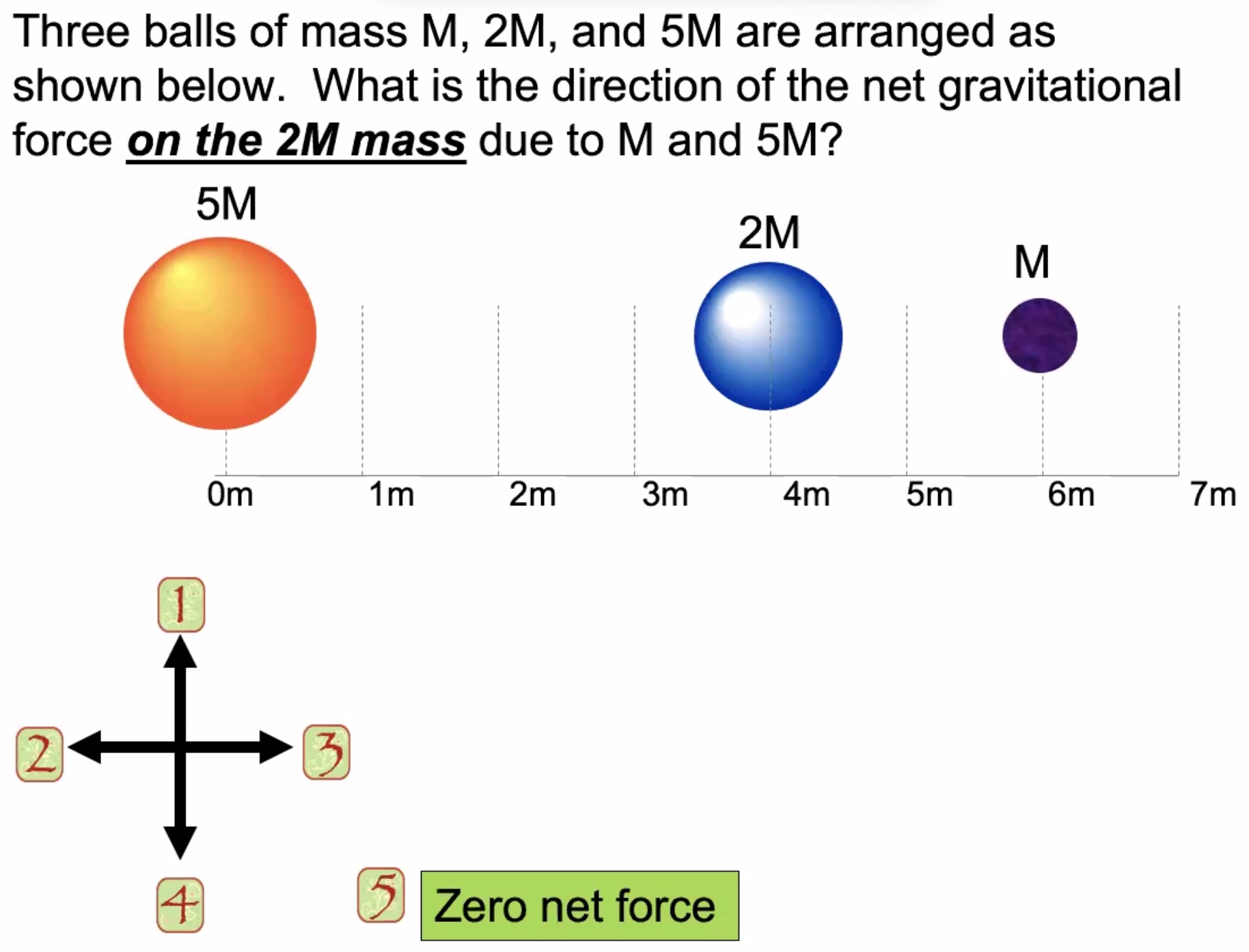
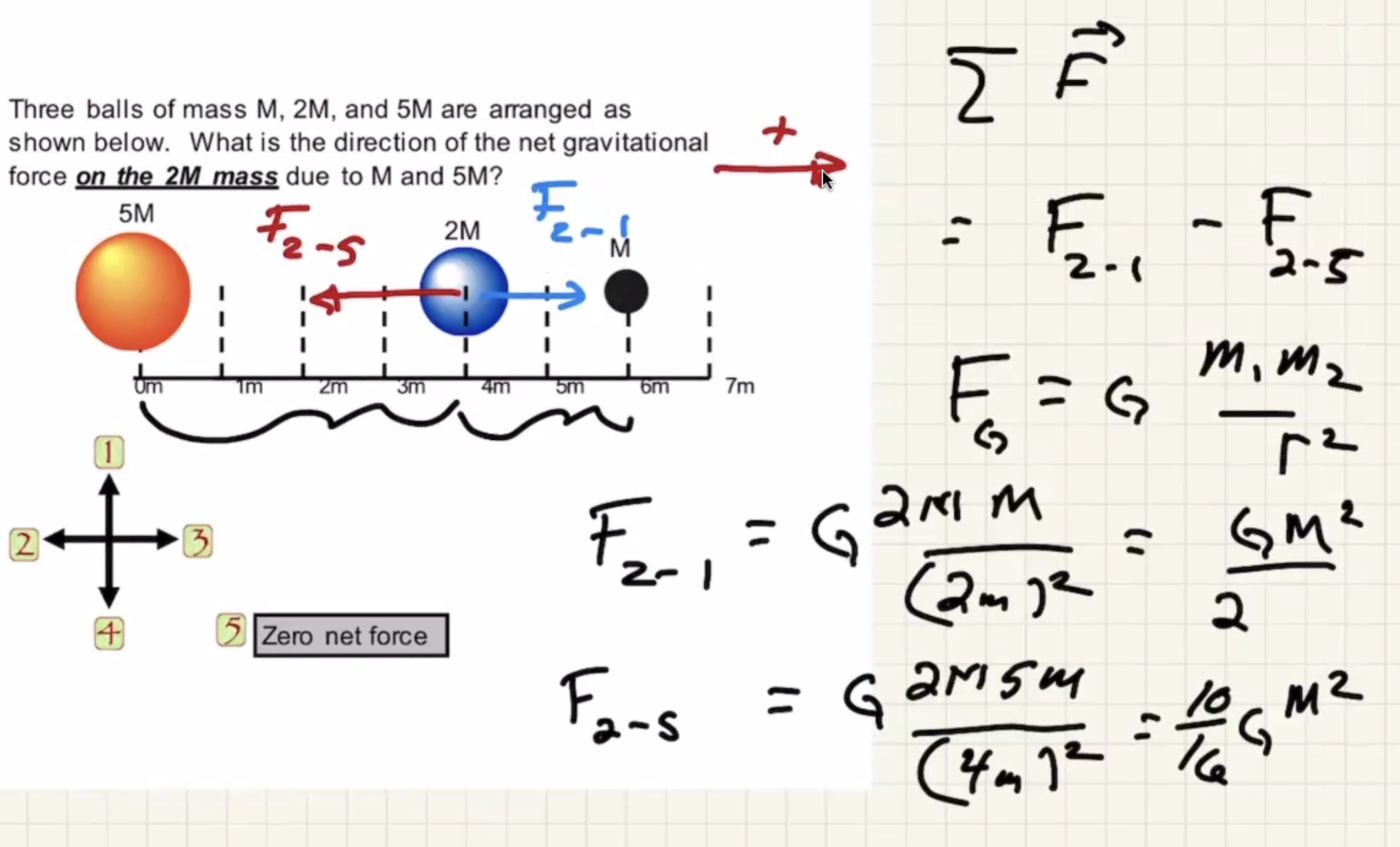
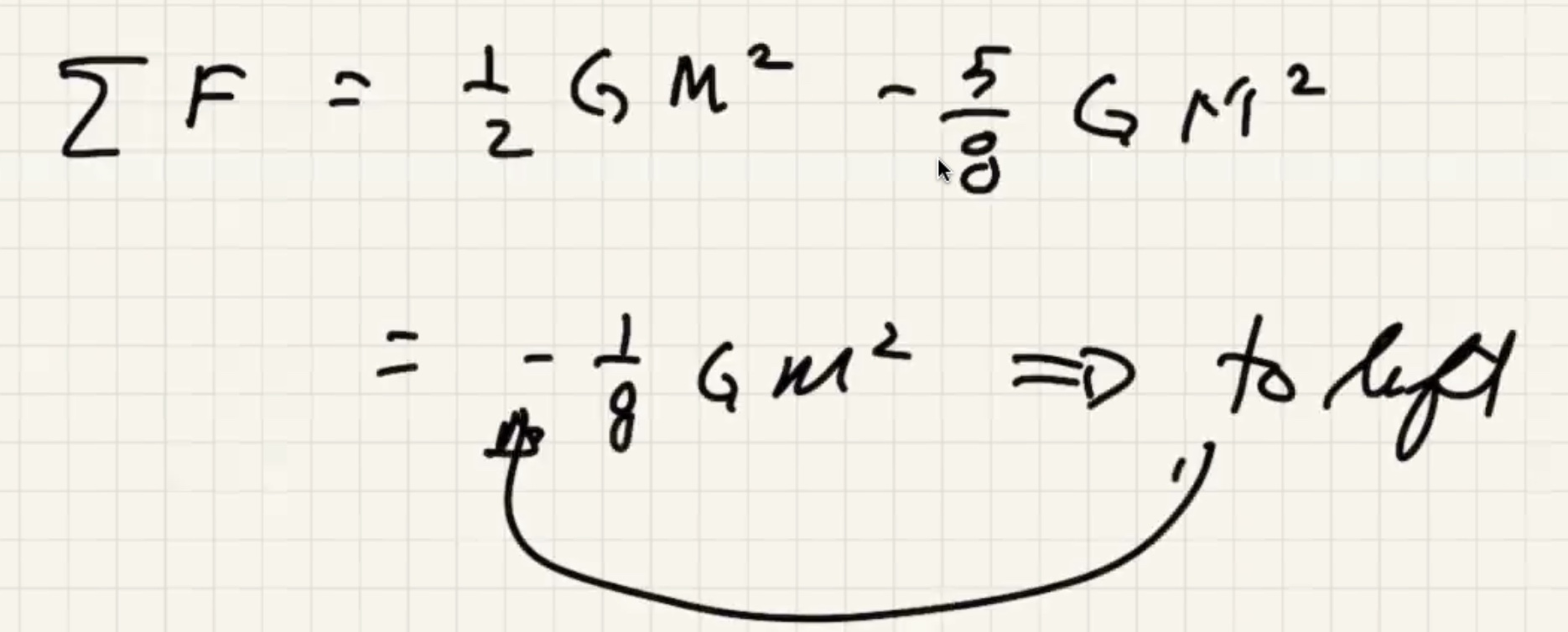
To find the net force equaling 0, solve this for x:
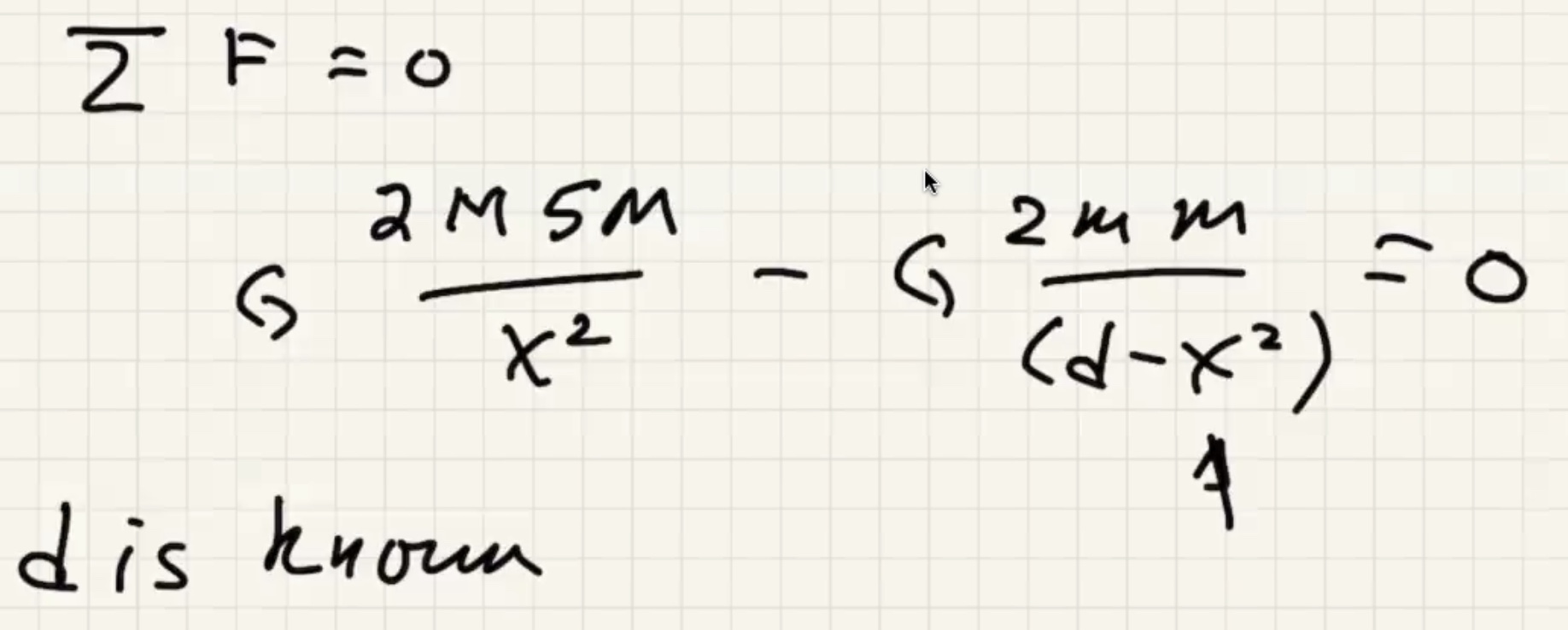
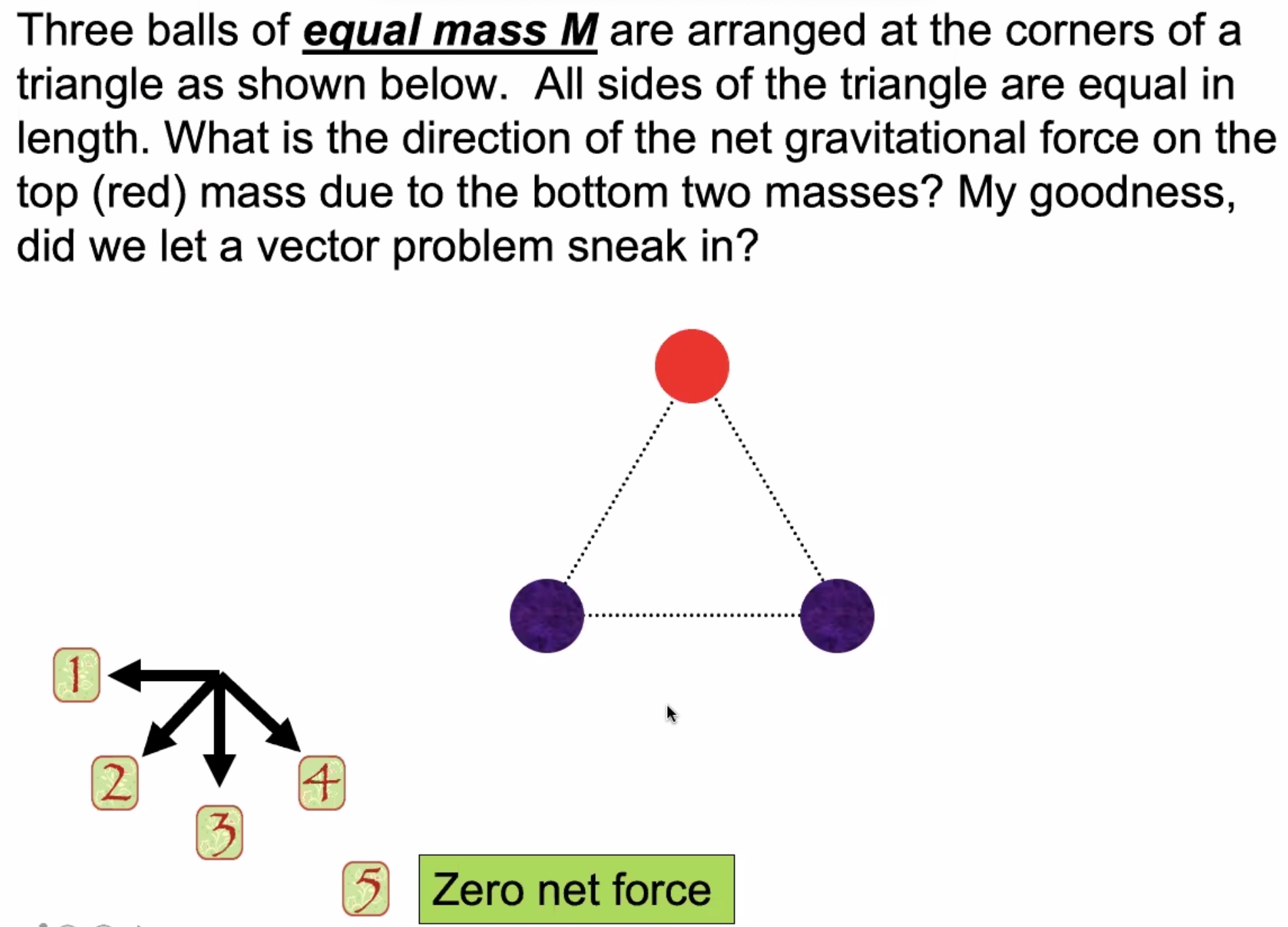
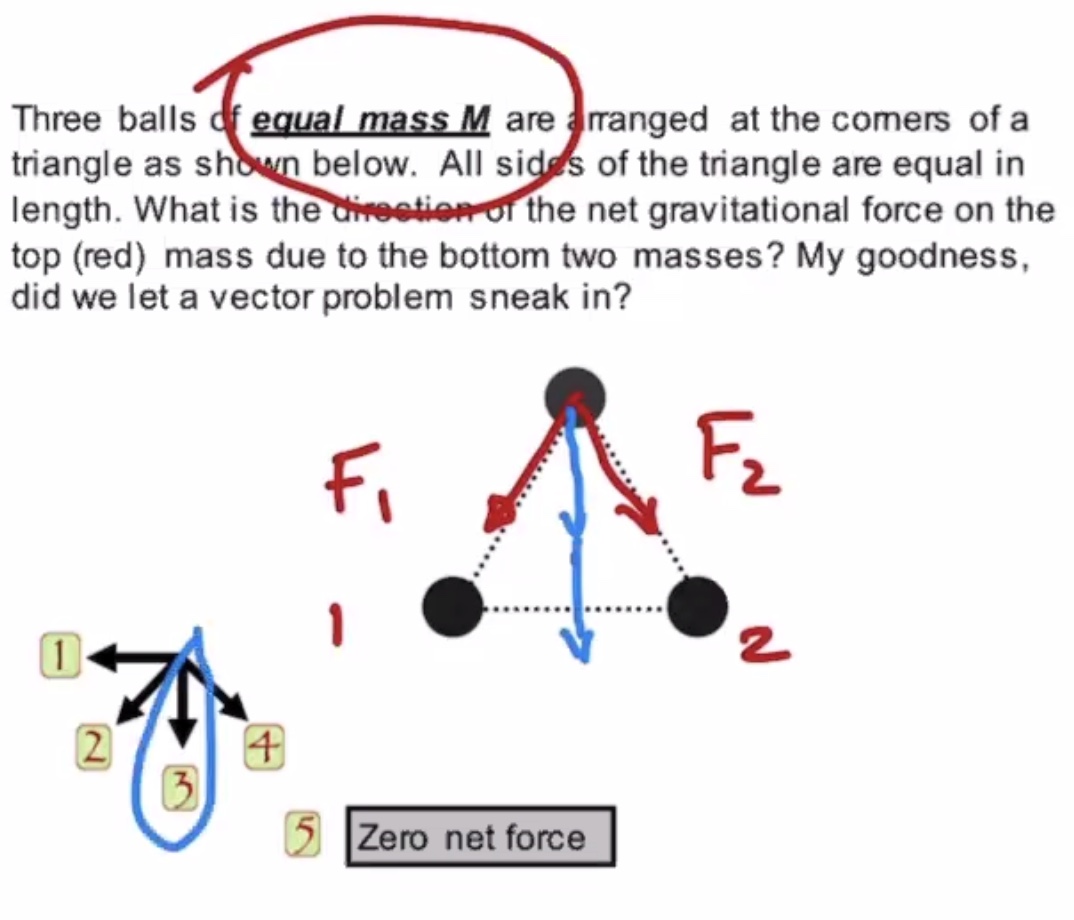
Lecture #
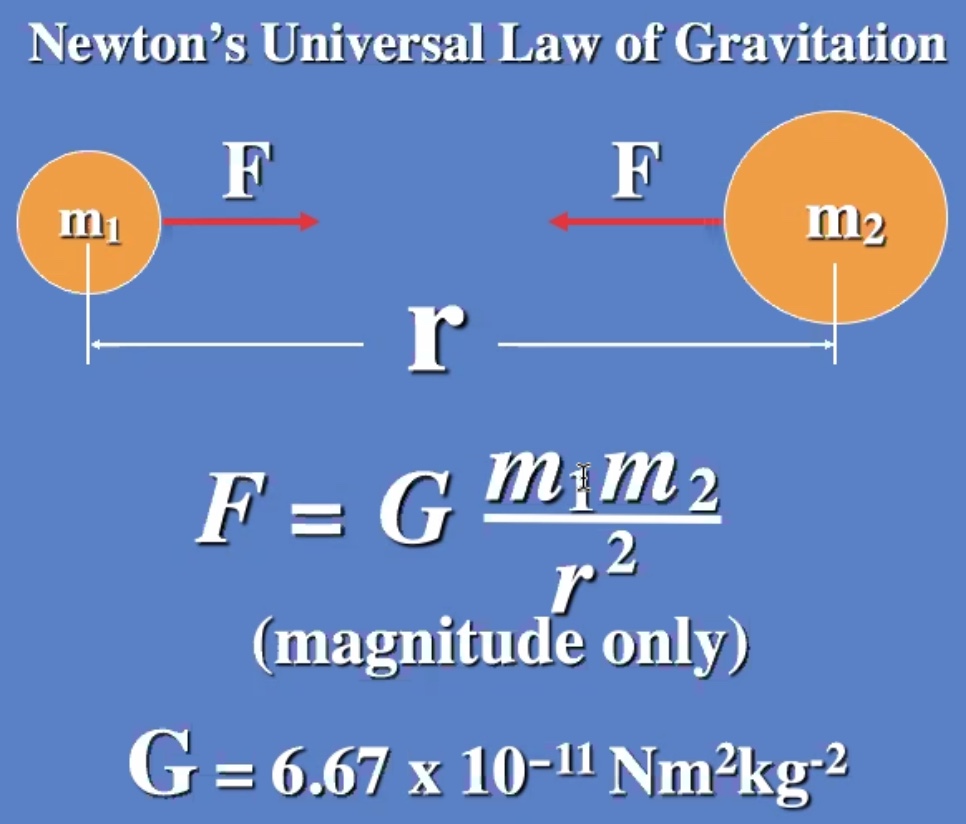
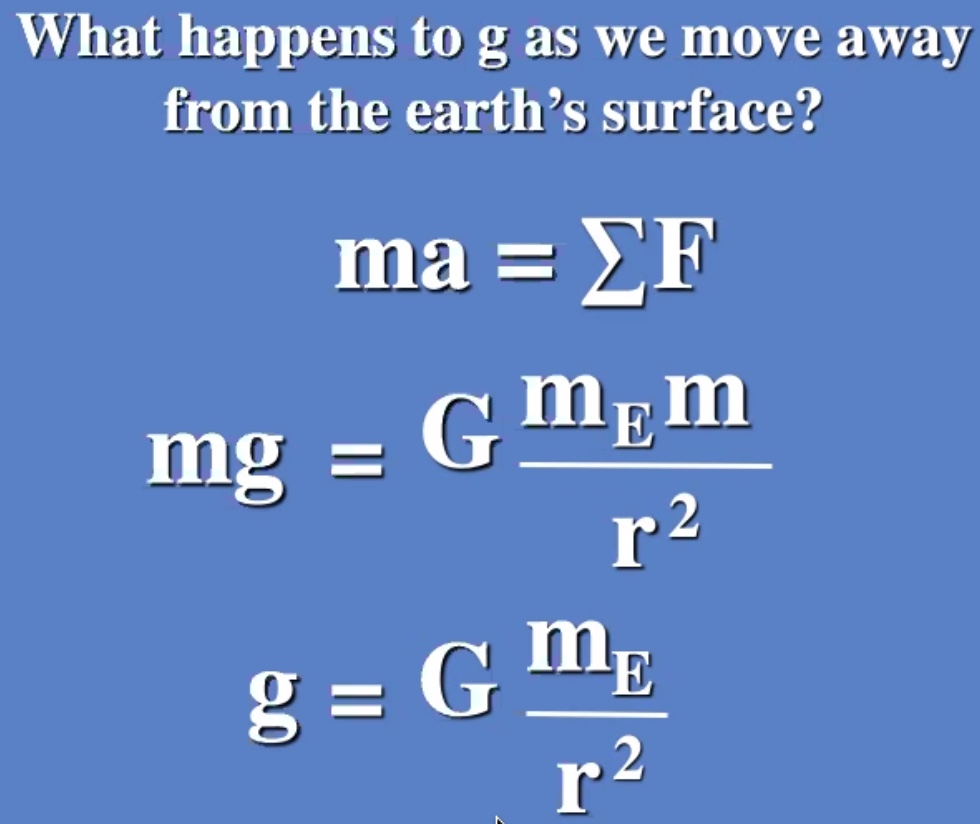
$G$ is really small, so for it to be appreciable at least one of the masses needs to be big (for instance Earth).

Direction of the force is always toward center of mass.


Mass is a property independent of location. Mass is a measure of inertia, but also a source of the gravitational force.

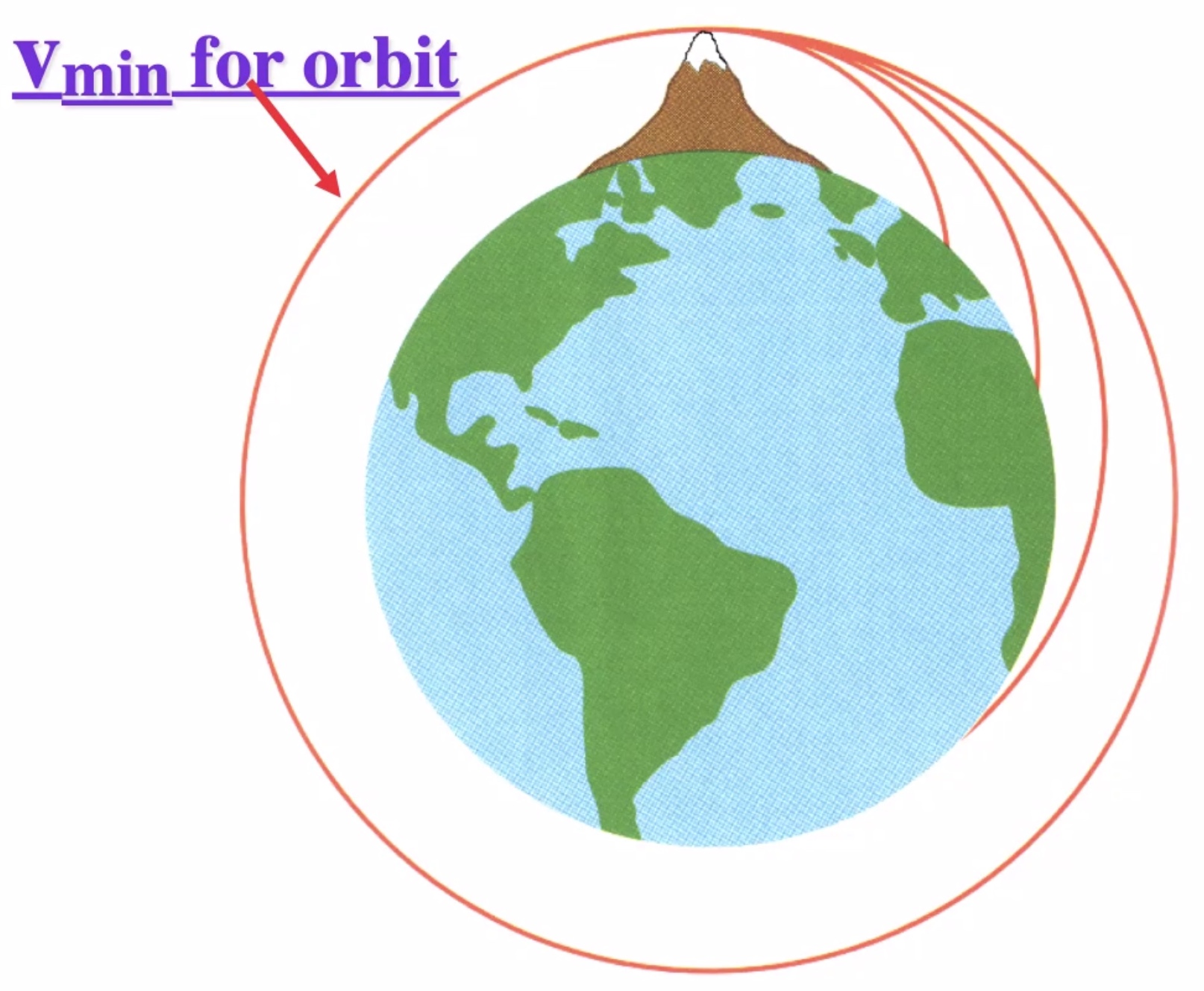
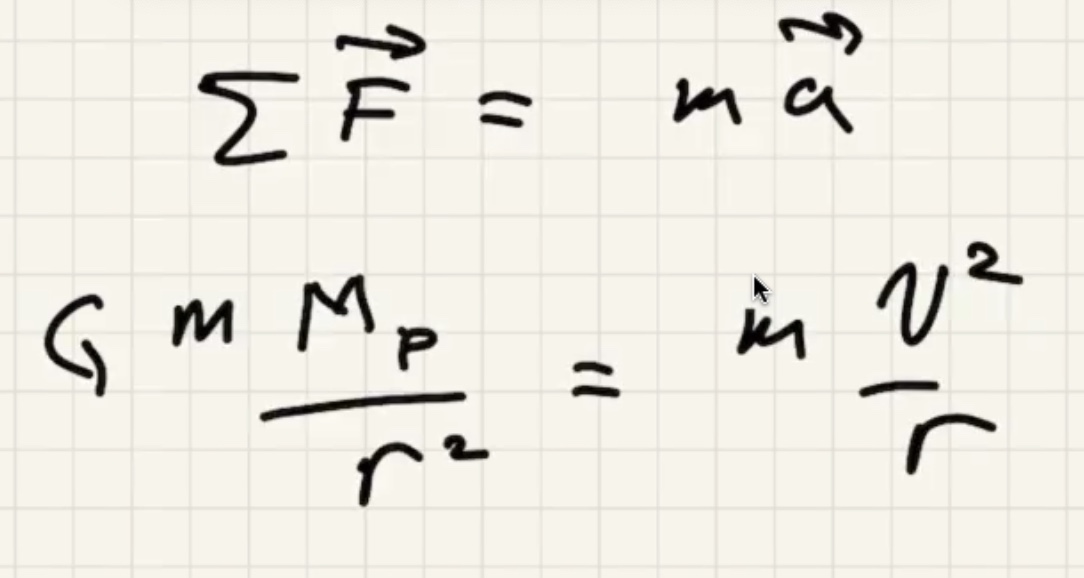
Minimum speed for a circular orbit:

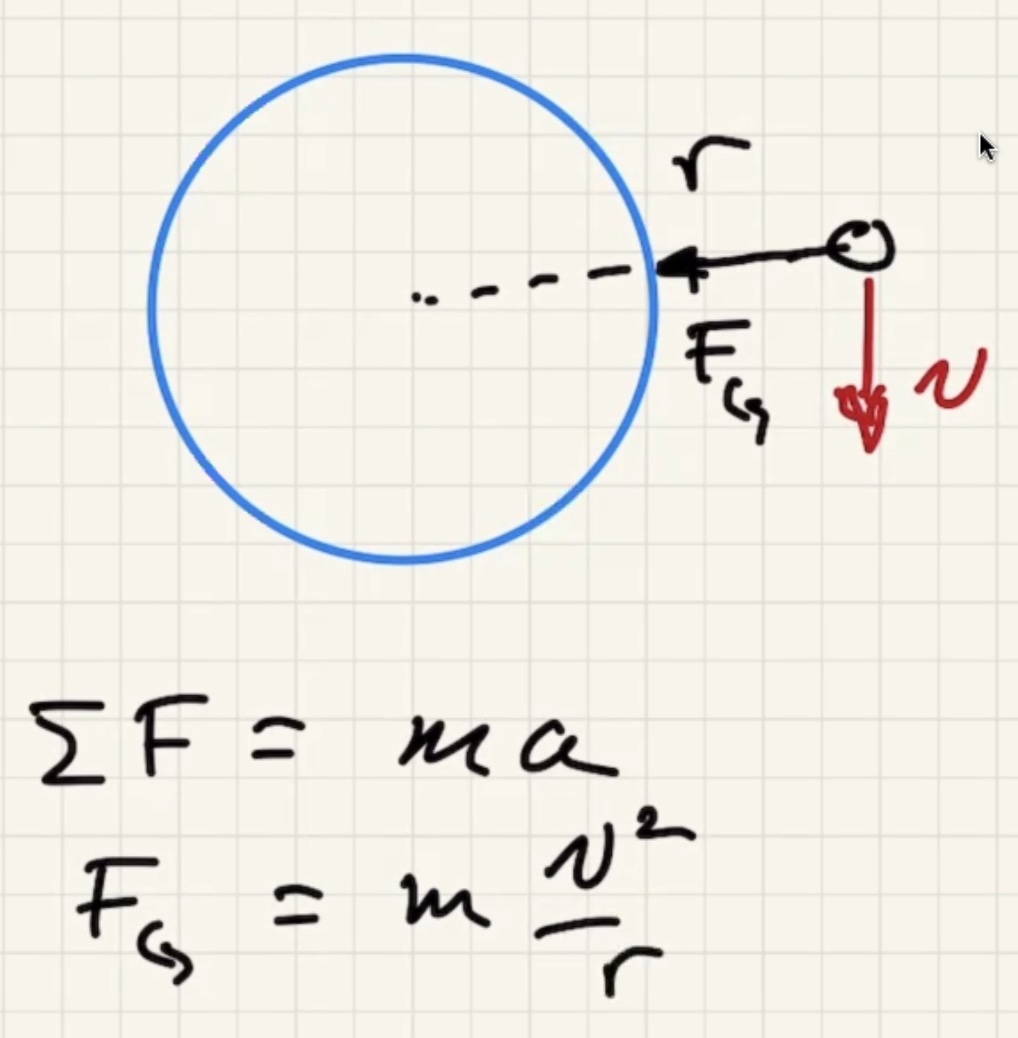
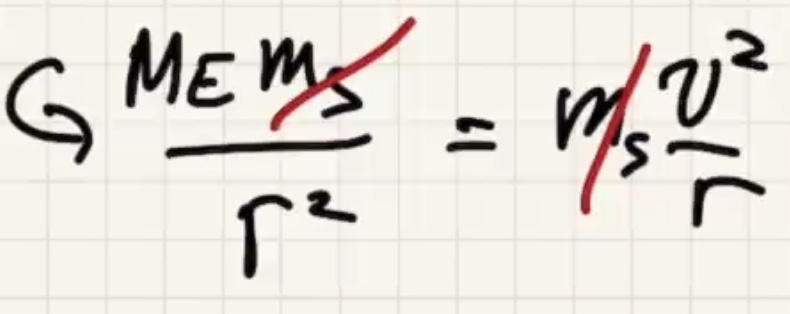
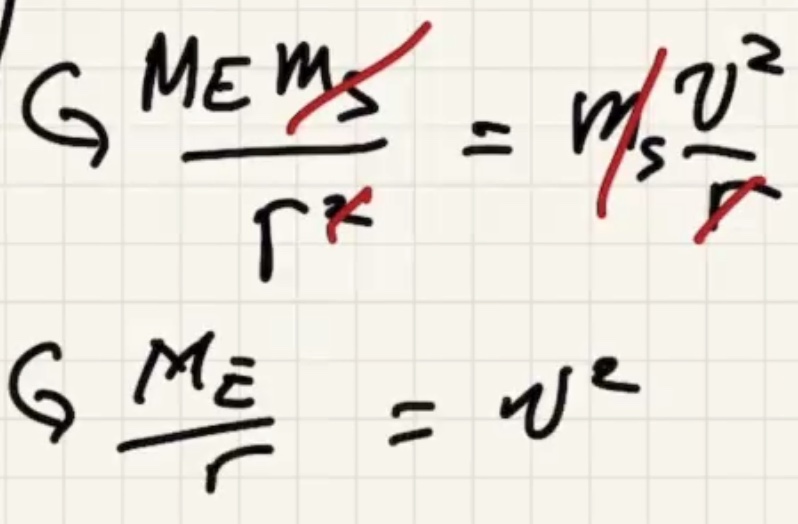
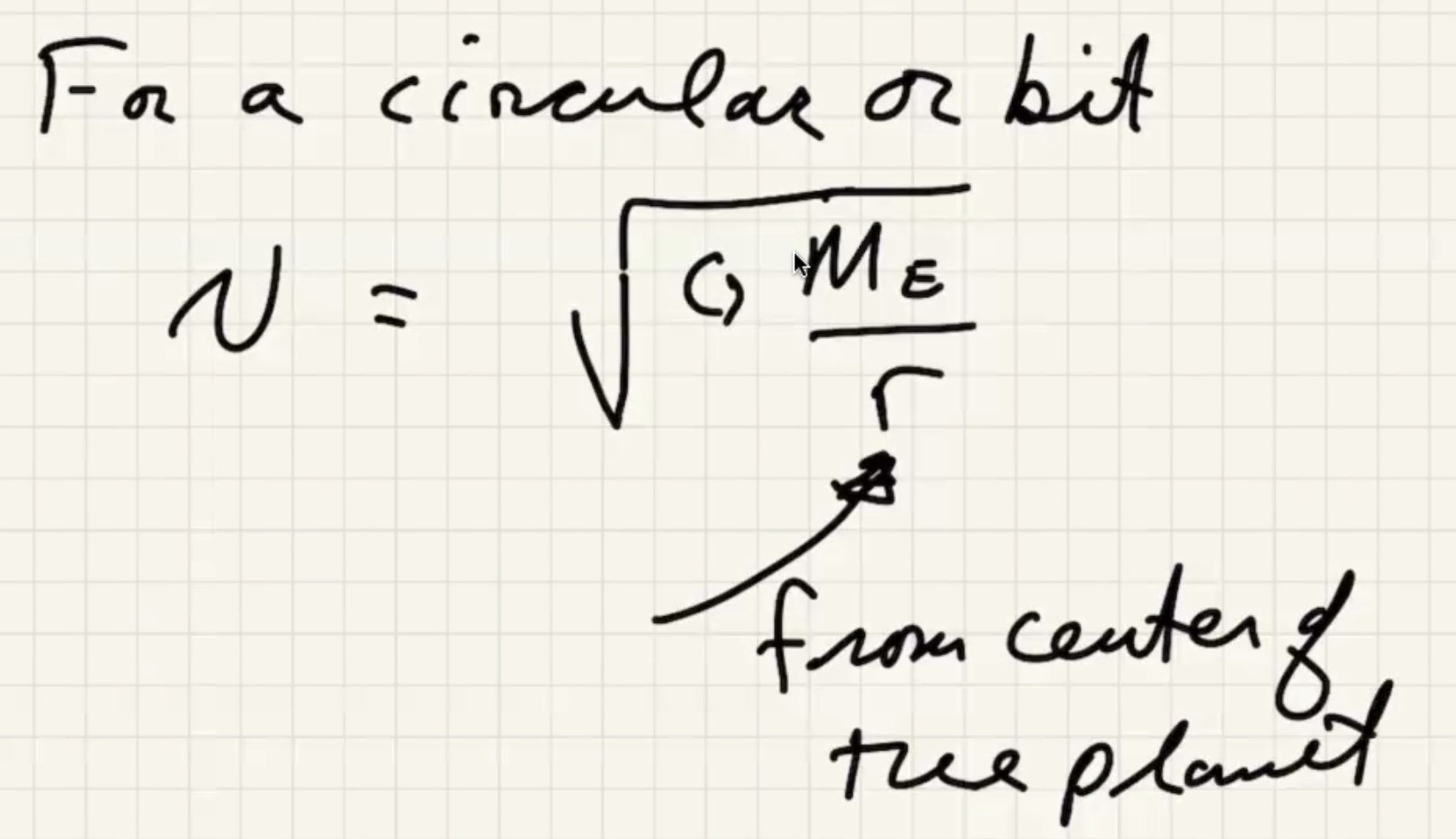

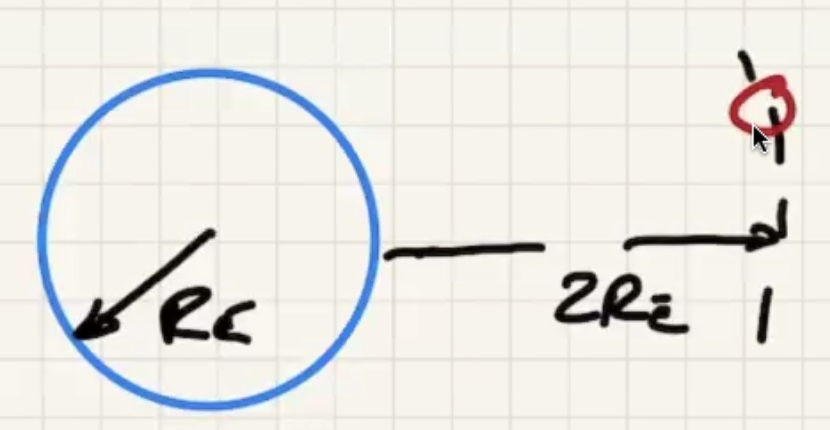
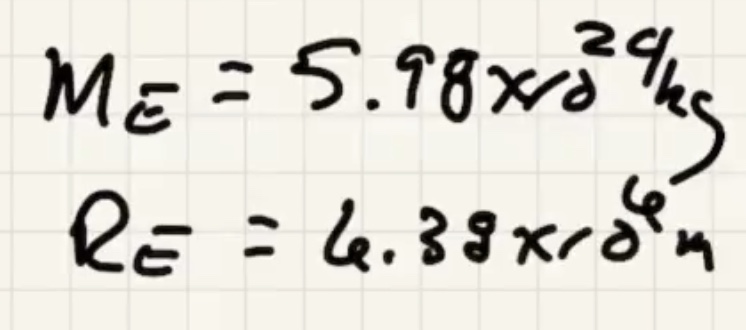
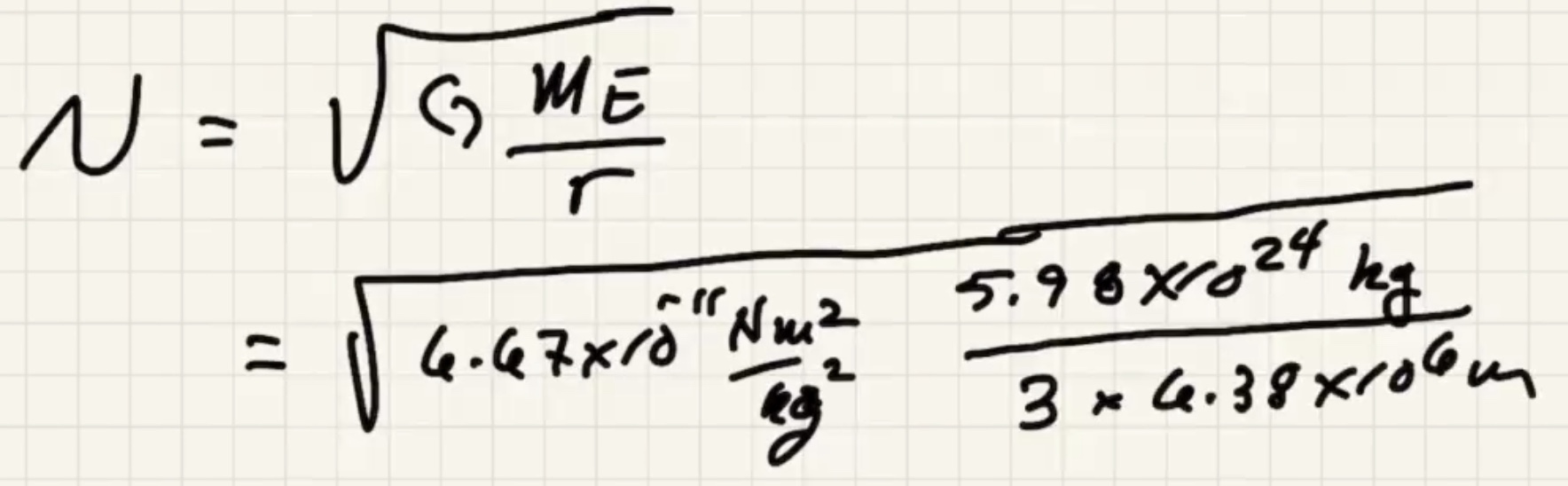
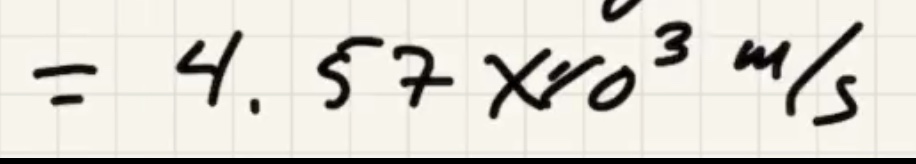

The time for one complete revolution of the Earth. Geosynchronous satellites orbit the Earth the same period as 1 day. They orbit the equator.
What is the $h$ to put the satellite into geosynchronous orbit:
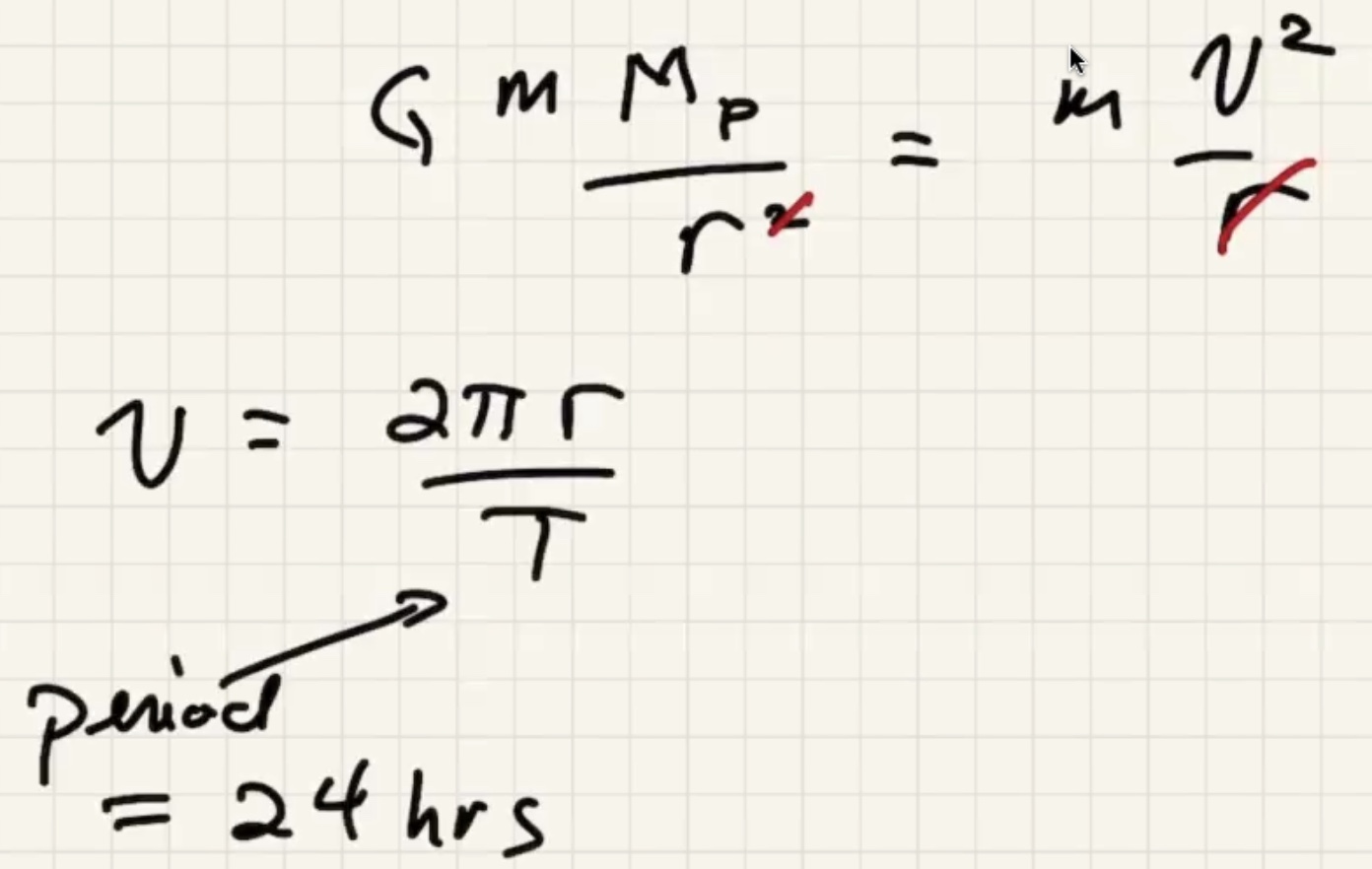
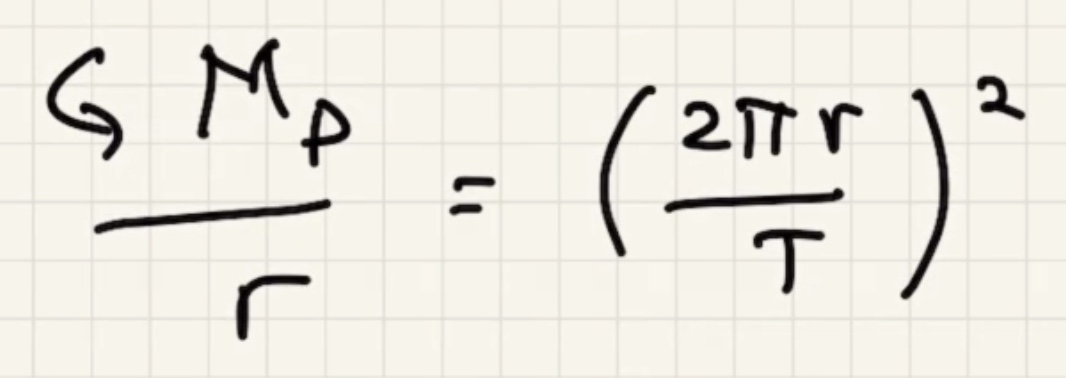
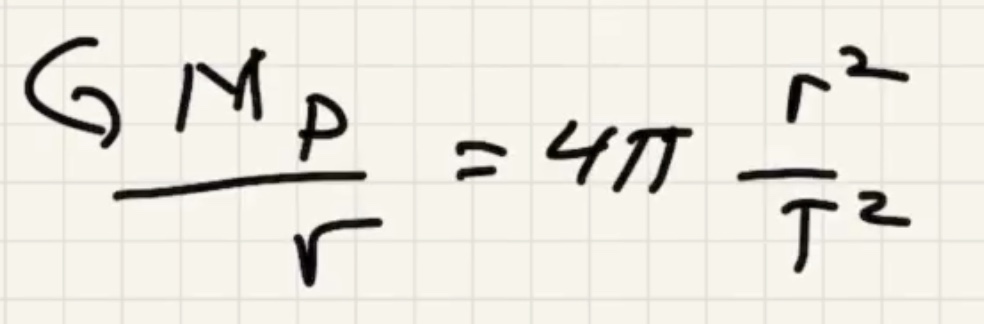
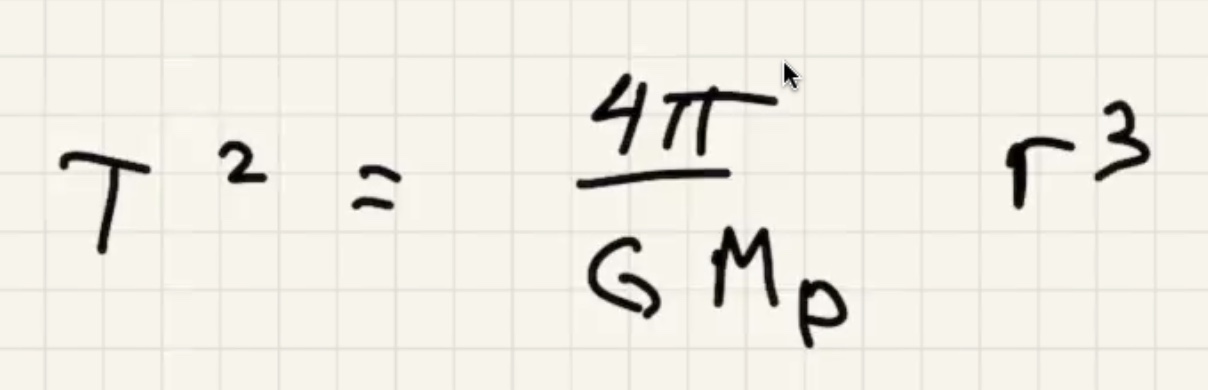
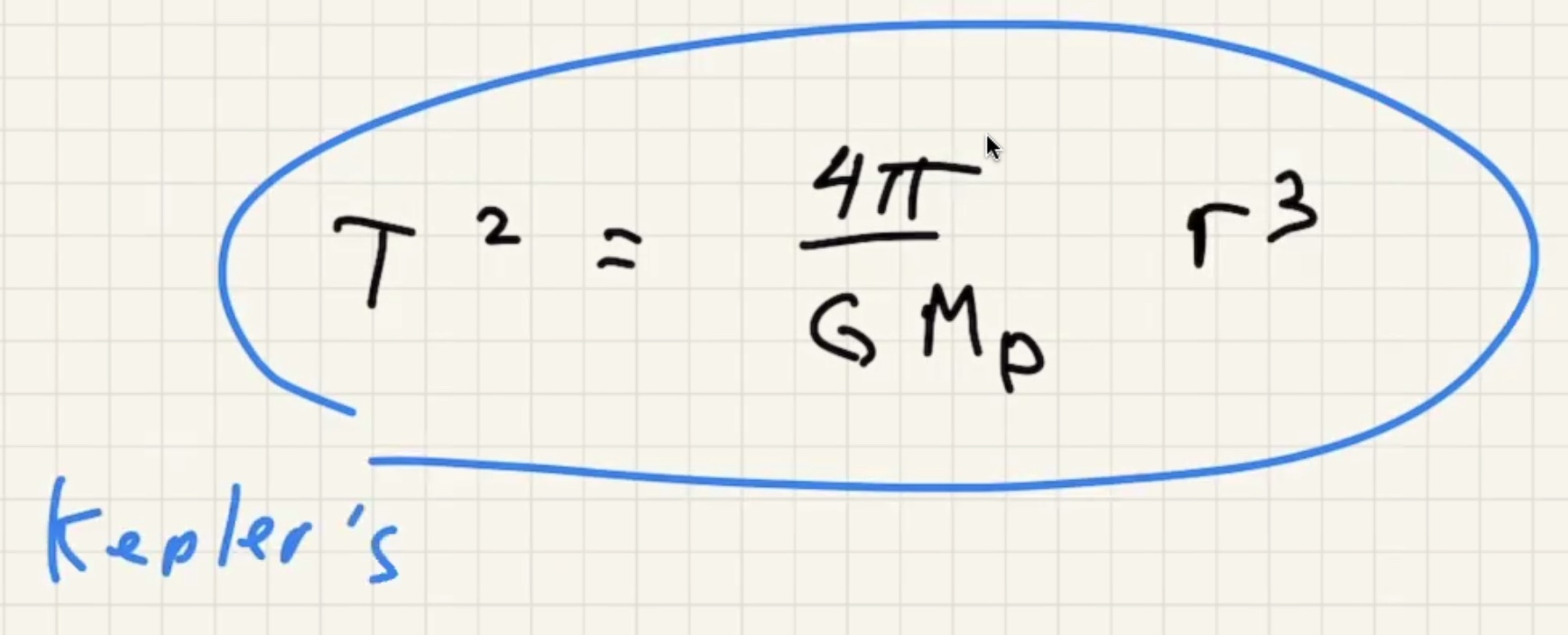
Kepler took data from a naked eye observatory to find this law.
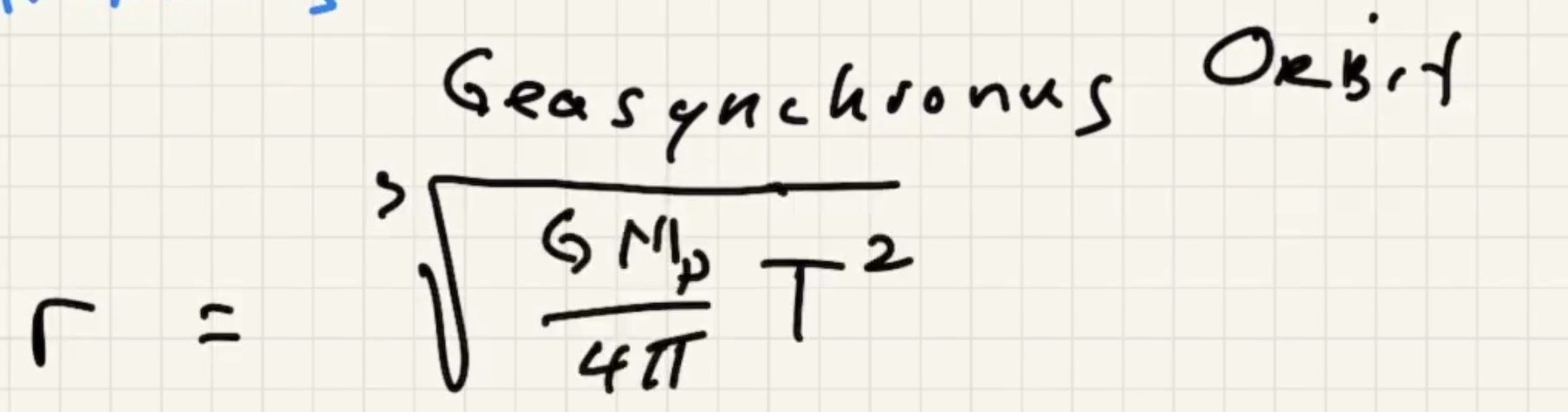

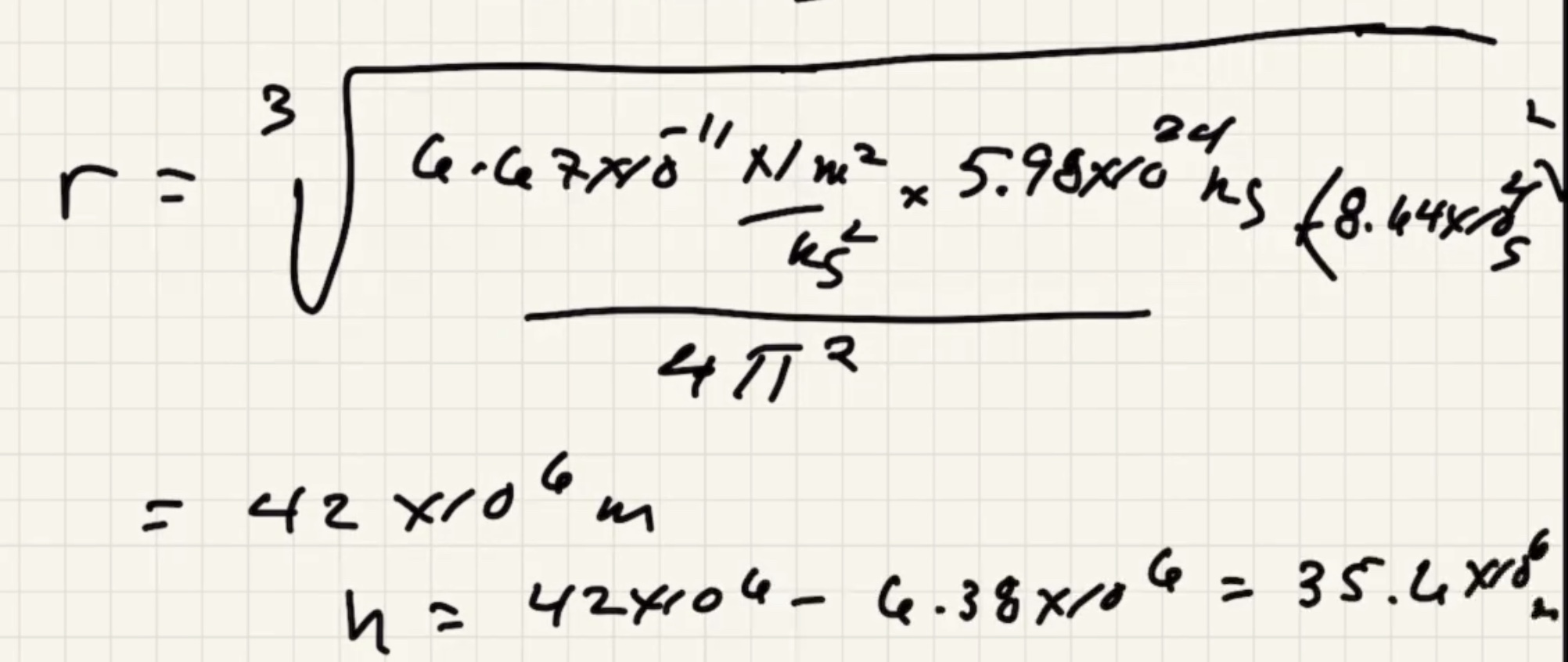

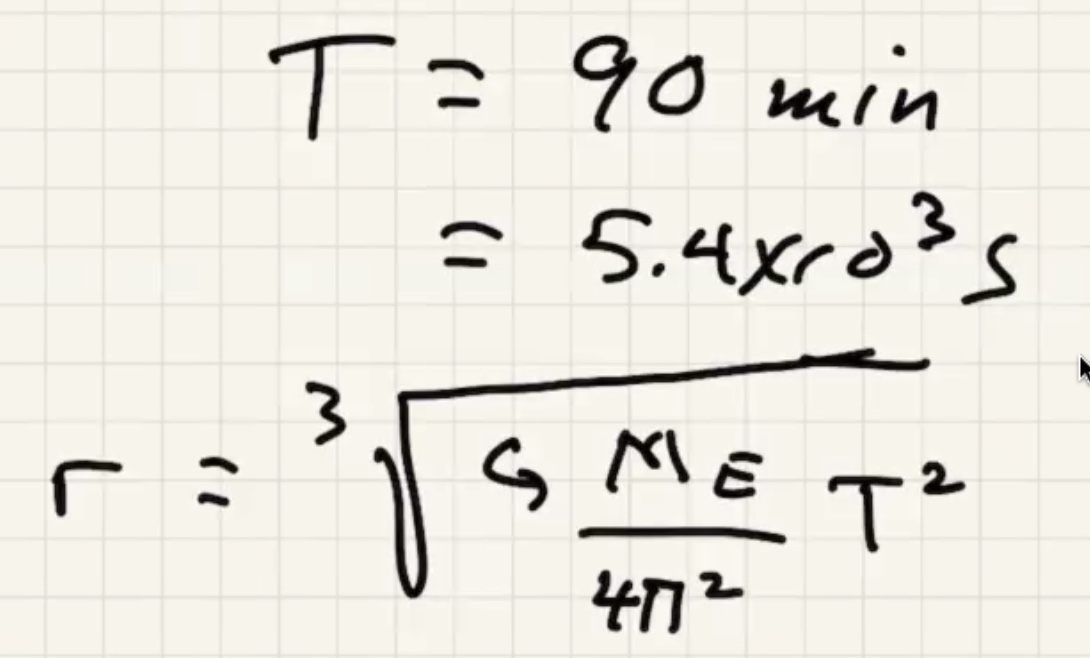
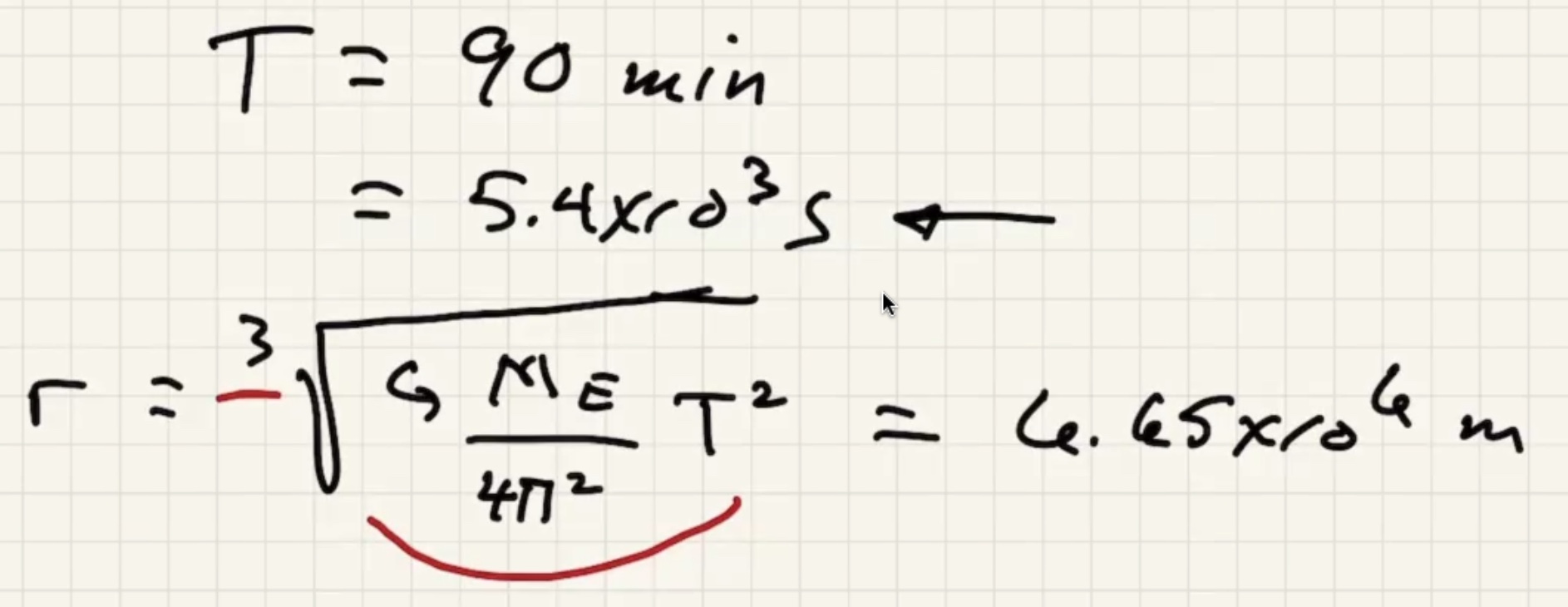

At the altitude of this orbit the gravitational force has only fallen by around 10%.




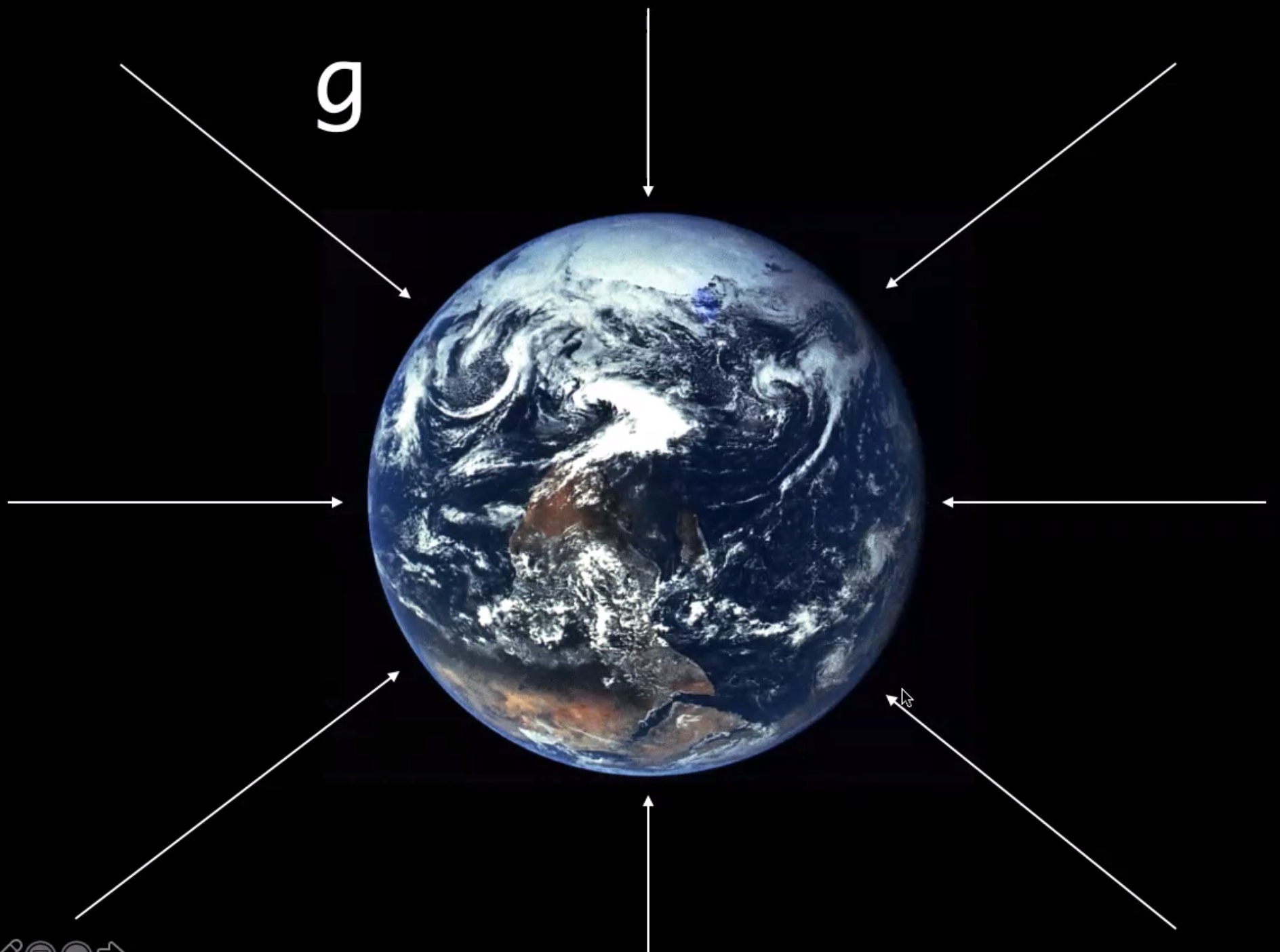
Stronger when closer to the planet. The idea of a field allows us to talk about how the force is transmitted. The universal law of gravity depends upon these fields. Einstein added another feature to this where the idea doesn’t involve a mass (we’re not going to worry about that).
Field lines can never cross.