Memory technology #

IM = instruction memory, DM = data memory

RAM = random access memory, ROM = read only memory
EEPROM = electrically erasable programmable read only memory

SRAM = static RAM, DRAM = dynamic RAM
Peak memory bandwidth example #
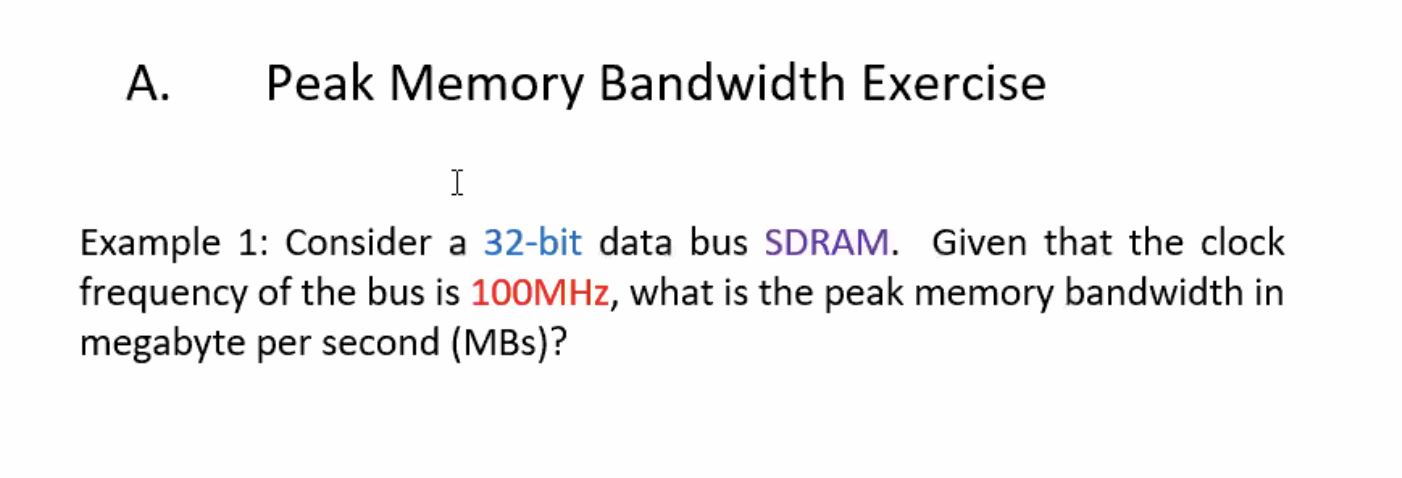
\( 32\text{ bits} \cdot \frac{1\text{ byte} }{8\text{ bits} } = 4 \text{ bytes} \\ \)
\( 1\text{ MB} = 1,000,000 \text{ bytes} \\ \)
\( 1 \text{ Hz} = 1 \text{ cycle/second}\\ \)
\( 1 \text{ MHz} = 1,000,000 \text{ cycles/second} \\\)
\( 100 \text{ MHz} = 100,000,000 \text{ cycles/second} \\\)
So,
\[\begin{aligned} 100 \text{ MHz} \cdot 4 \text{ bytes/cycle} &= 400,000,000 \text{ bytes/sec} \\ &= 400 \text{ MB/sec} \end{aligned}\]SRAM cycle diagrams #
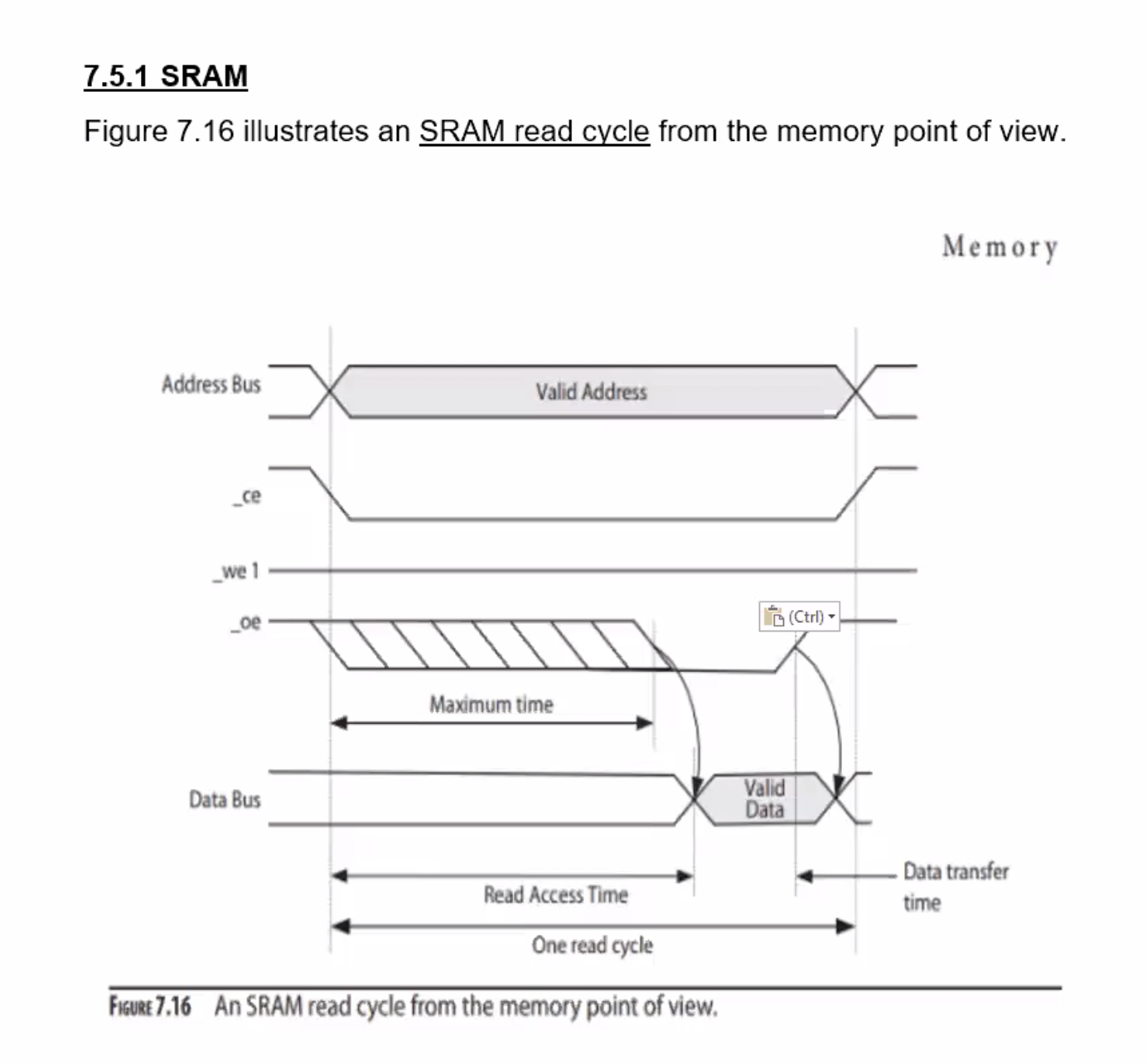
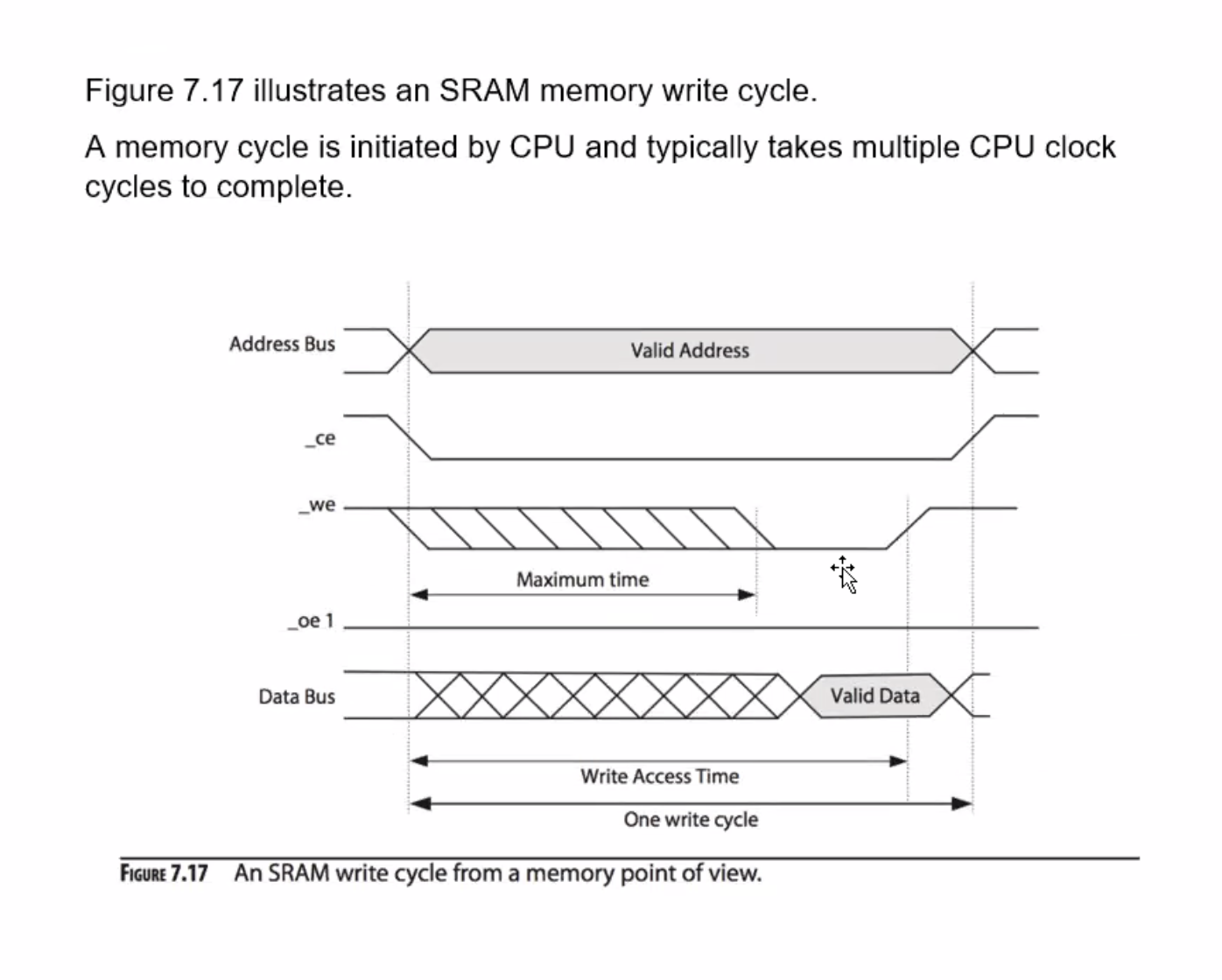
Anything beginning with an underscore _ means it is active low, activated when 0.
_ce = chip enable, _we 1 = write enable (determines whether in read cycle or write cycle), _oe = output enable.
Tri-state buffer #
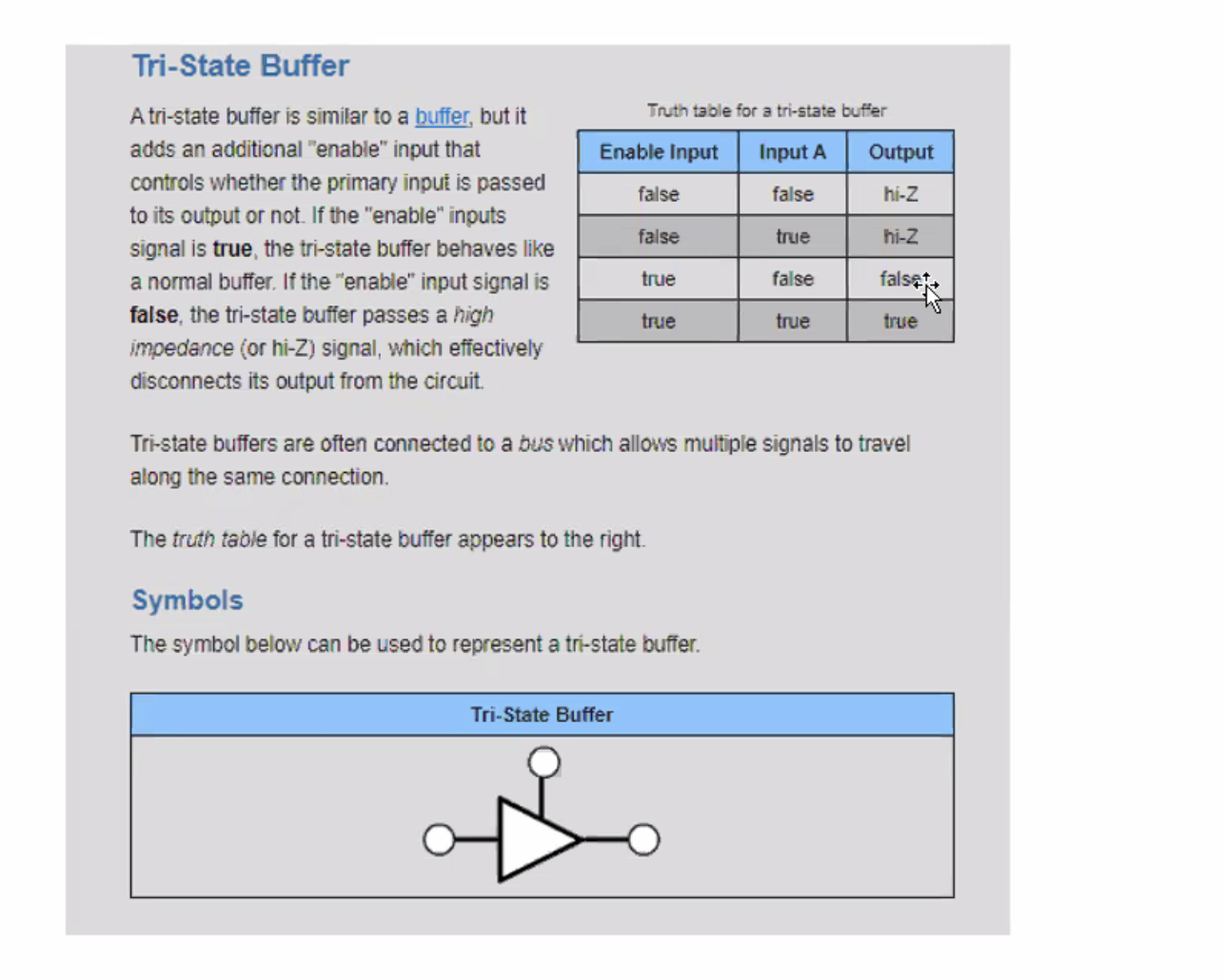
hi-Z = high impedance