Review #

- Devices, links, packet switches
- Protocols define format and order of messages sent and received among network entities
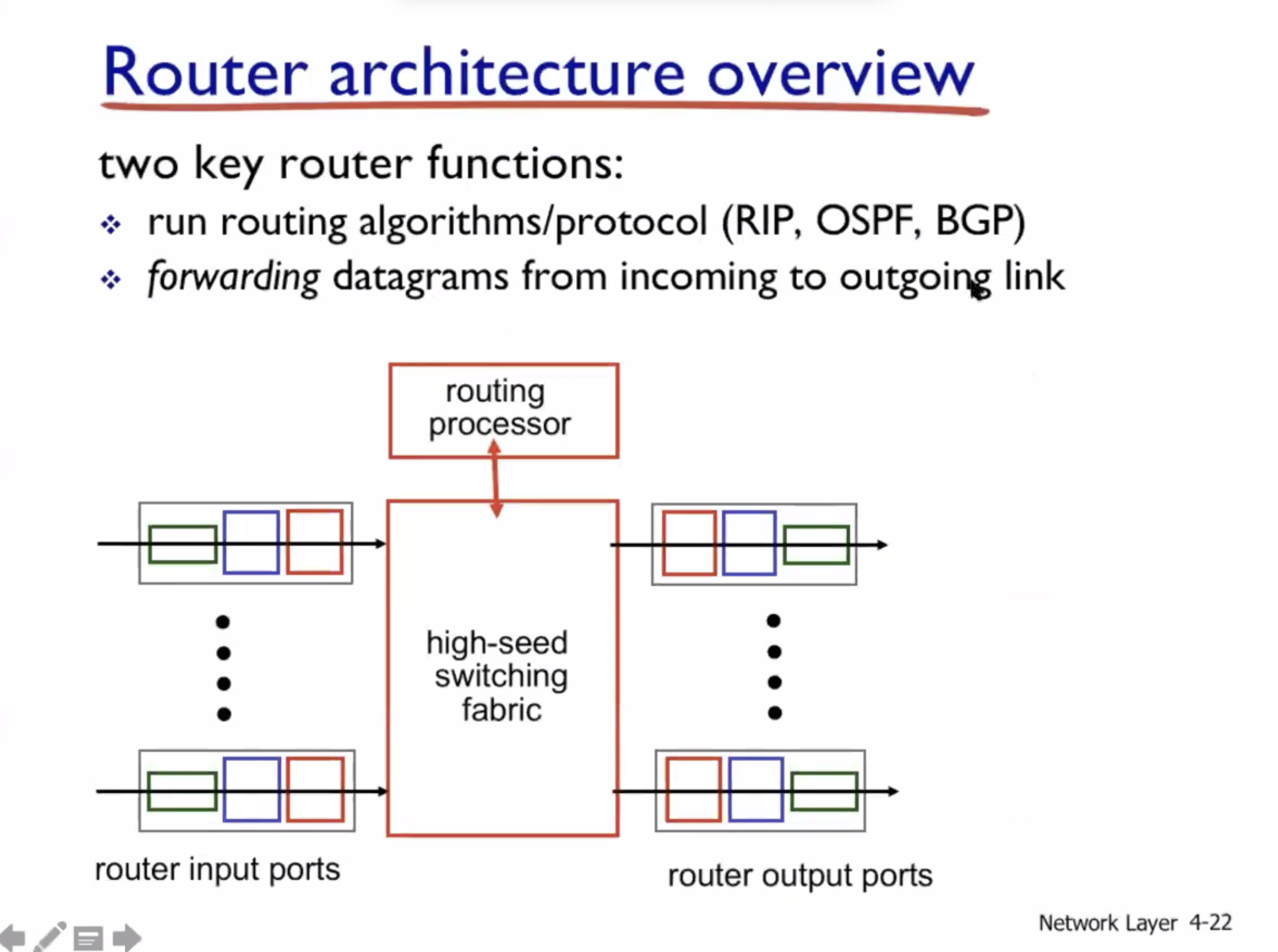
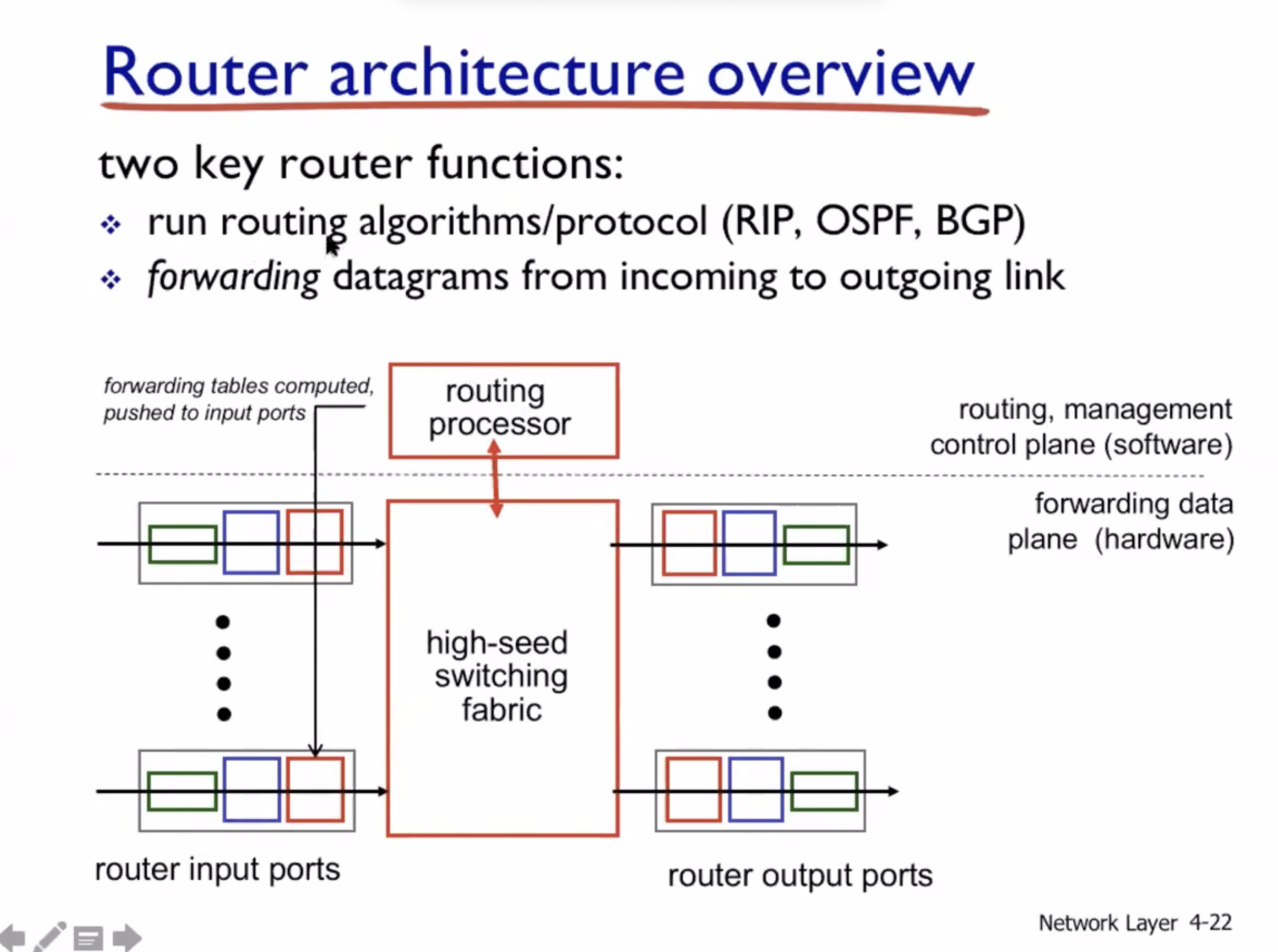
- Routers
- Routing and forwarding
- Packet switching
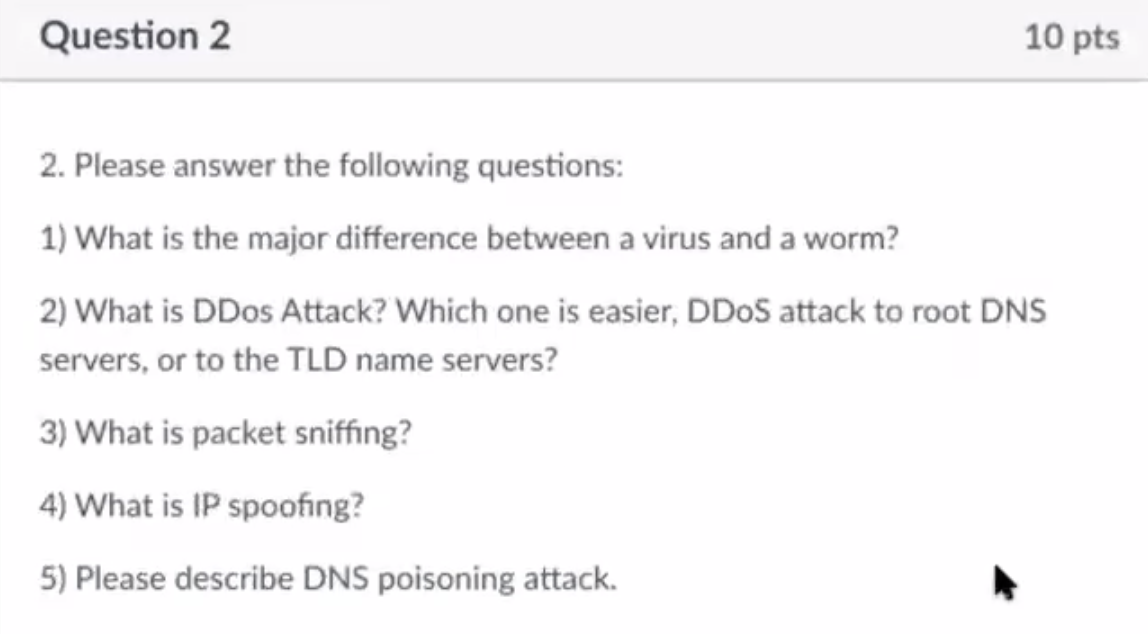
- Worms do not need user’s interaction, viruses do
- Distributed denial of service. TLD name servers are easier to attack
- Recording packets passing through network
- Sends a packet with a forced source address
- Sends bogus replies to the DNS servers

- P2P is more scalable
- IP address and port number
- TCP, because it is reliable
- TCP
- SSL is implemented at the app layer

- Persistent allows multiple objects to be sent over a single connection
set-cookiecookie- Database or back end
- Cookie file managed by browser
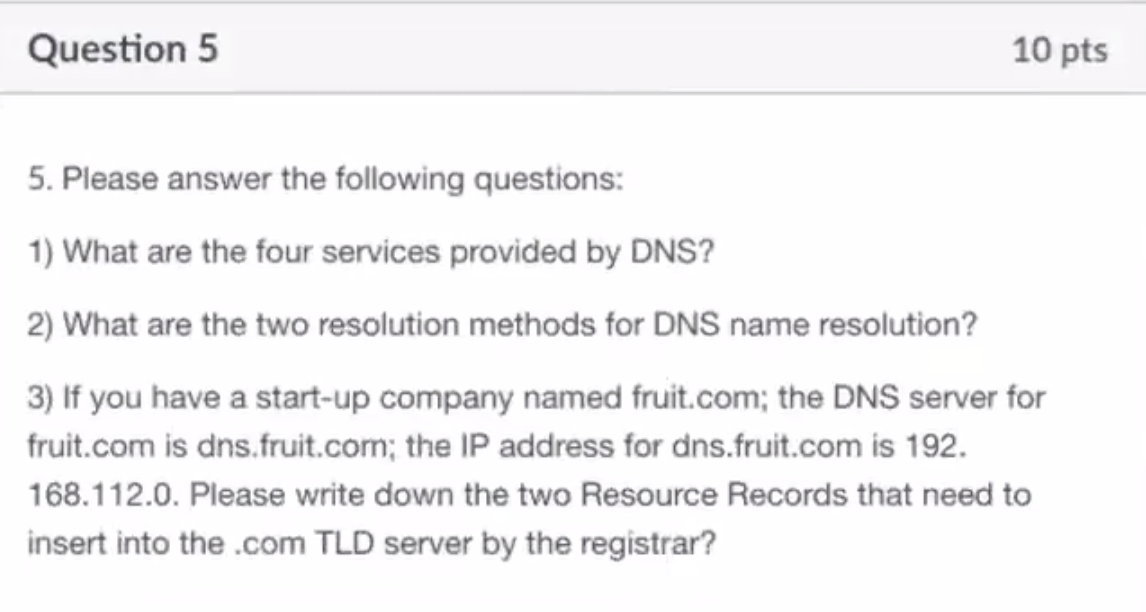
- host to IP mapping, host nick name, mail server nick name, load distribution
- iterative and recursive
(fruit.com, dns.fruit.com, NS),(dns.fruit.com, 192.168.112.0, A)
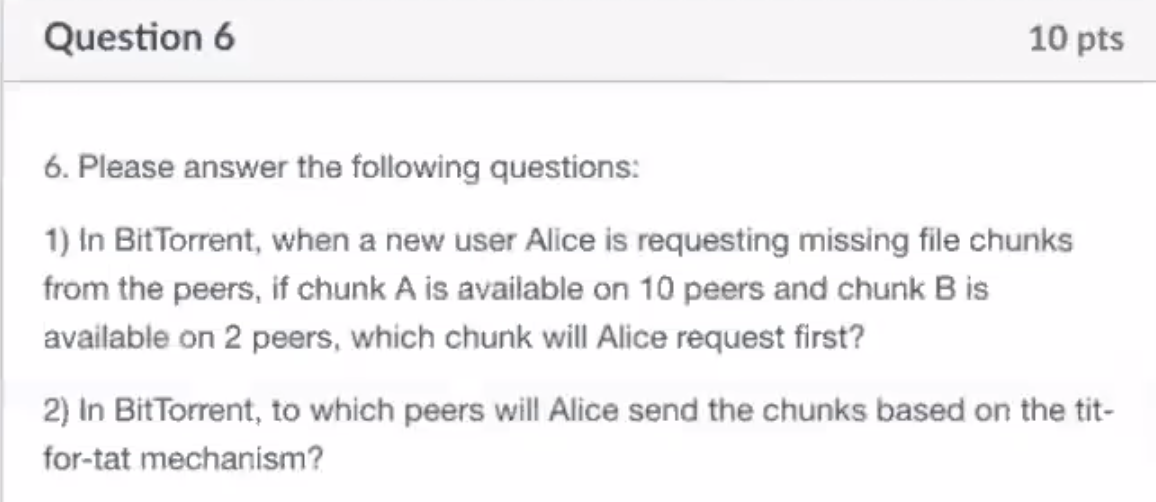
- The rarest chunk first, B
- The top 4 peers that seed her the most

SOCK_DGRAMsendto- The client needs to close, but the server’s socket is reused
- 1 global socket to hand shake, 1 per connected client
- The socket connected to the client can be closed. The hand shake socket stays open.

- application, presentation, session, transport, network, link, physical
- presentation and session
- save time, save bandwidth, save traffic
if-modified-since304not modified


- \( \frac{L}{R} = \frac{30}{3} + \frac{30}{5} + \frac{30}{10} = 19 \)
- \( \frac{D}{S} = \frac{100}{20} = 5 \)
- \( 19 +5 + 2(2) + 1(2) = 30 \)
- queuing
- 3 Gbps is the bottleneck

- SMTP or HTTP
- SMTP
- POP3 or IMAP or HTTP
- port 25
- TCP
Network layer cont #
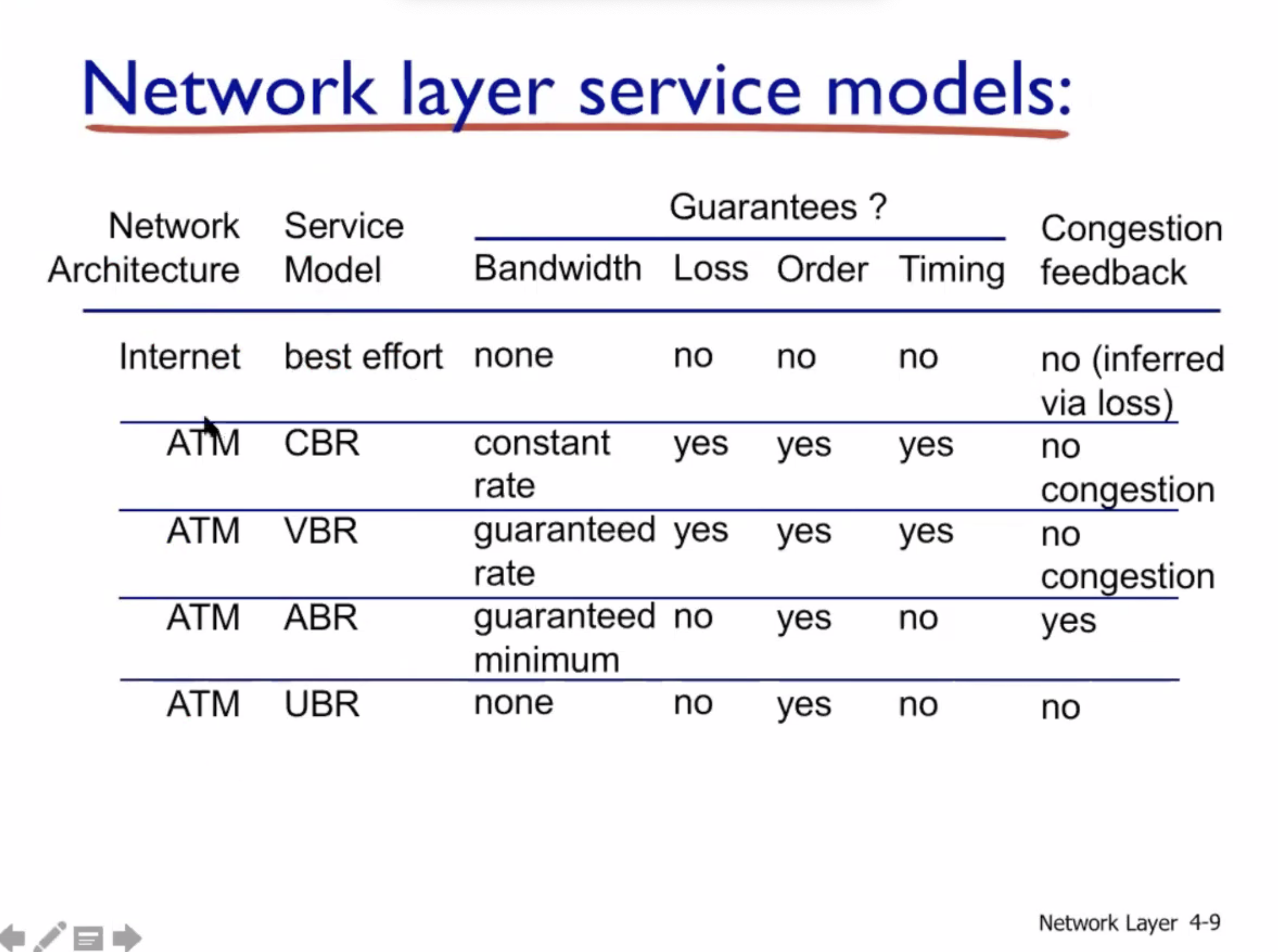

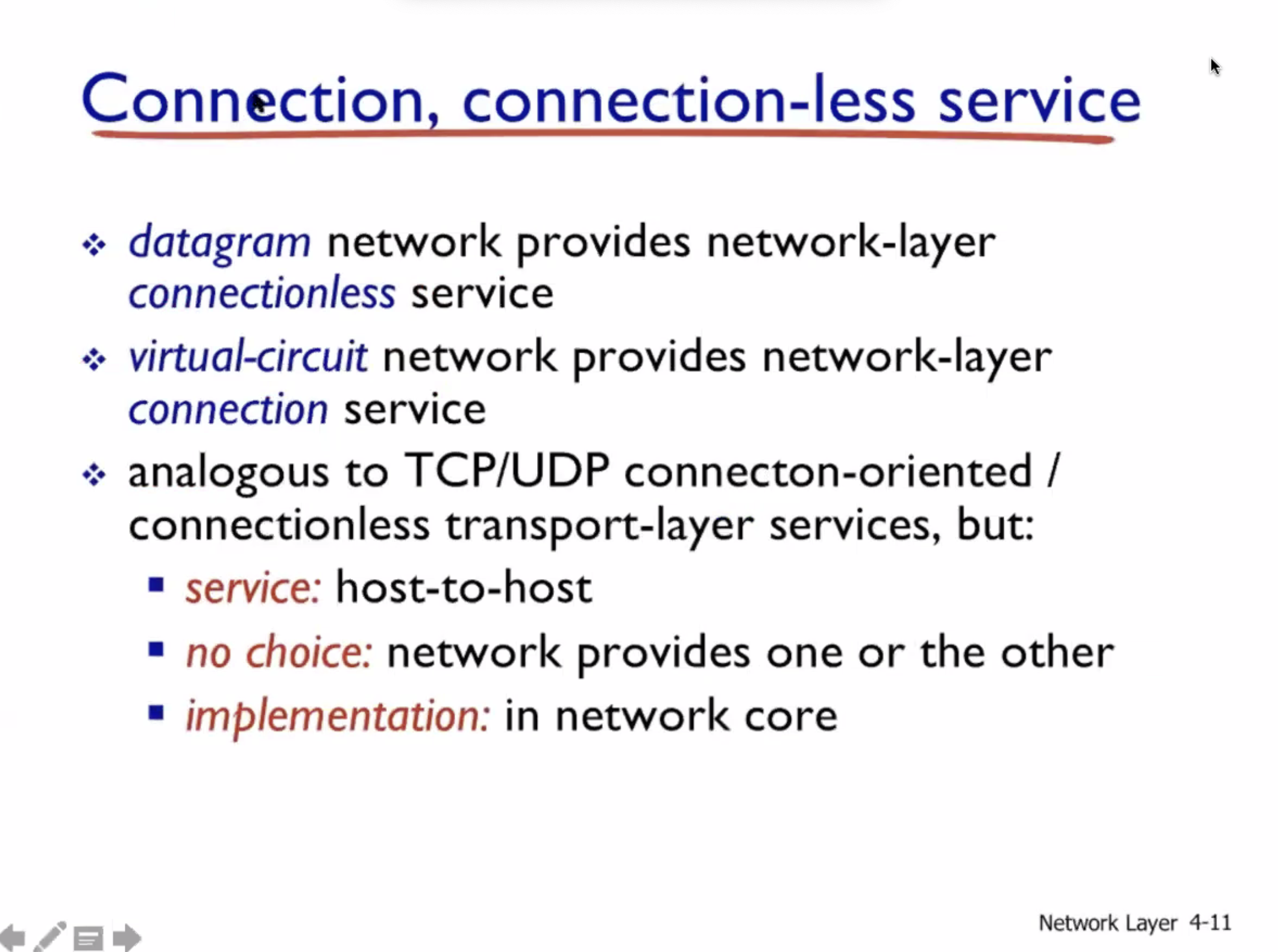
TCP vs UDP
- Transport layer connection vs connectionless
- Programmers have the choice to use TCP or UDP, by giving different parameters to the
socketfunction - Process to process
- Done within network devices
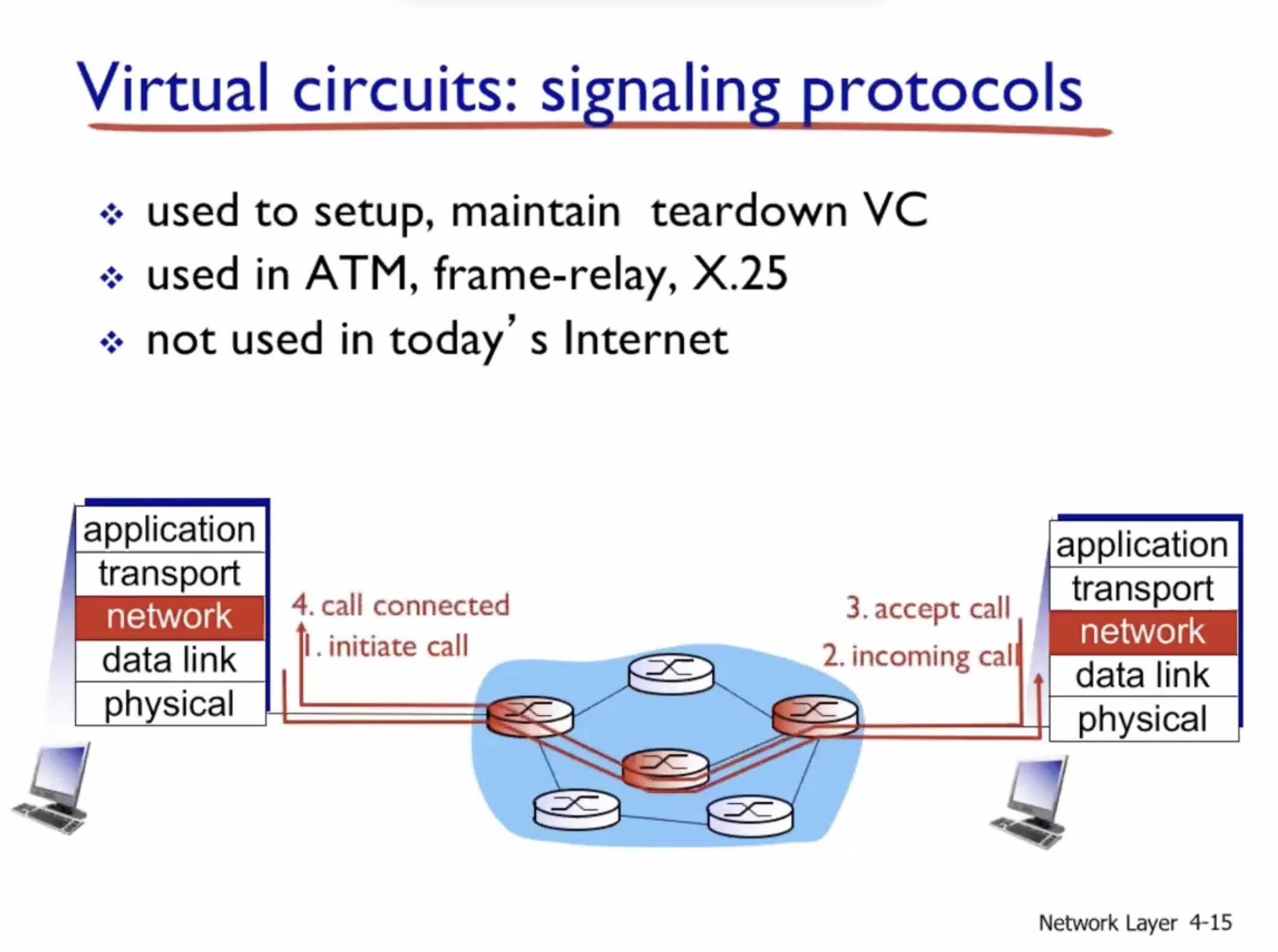
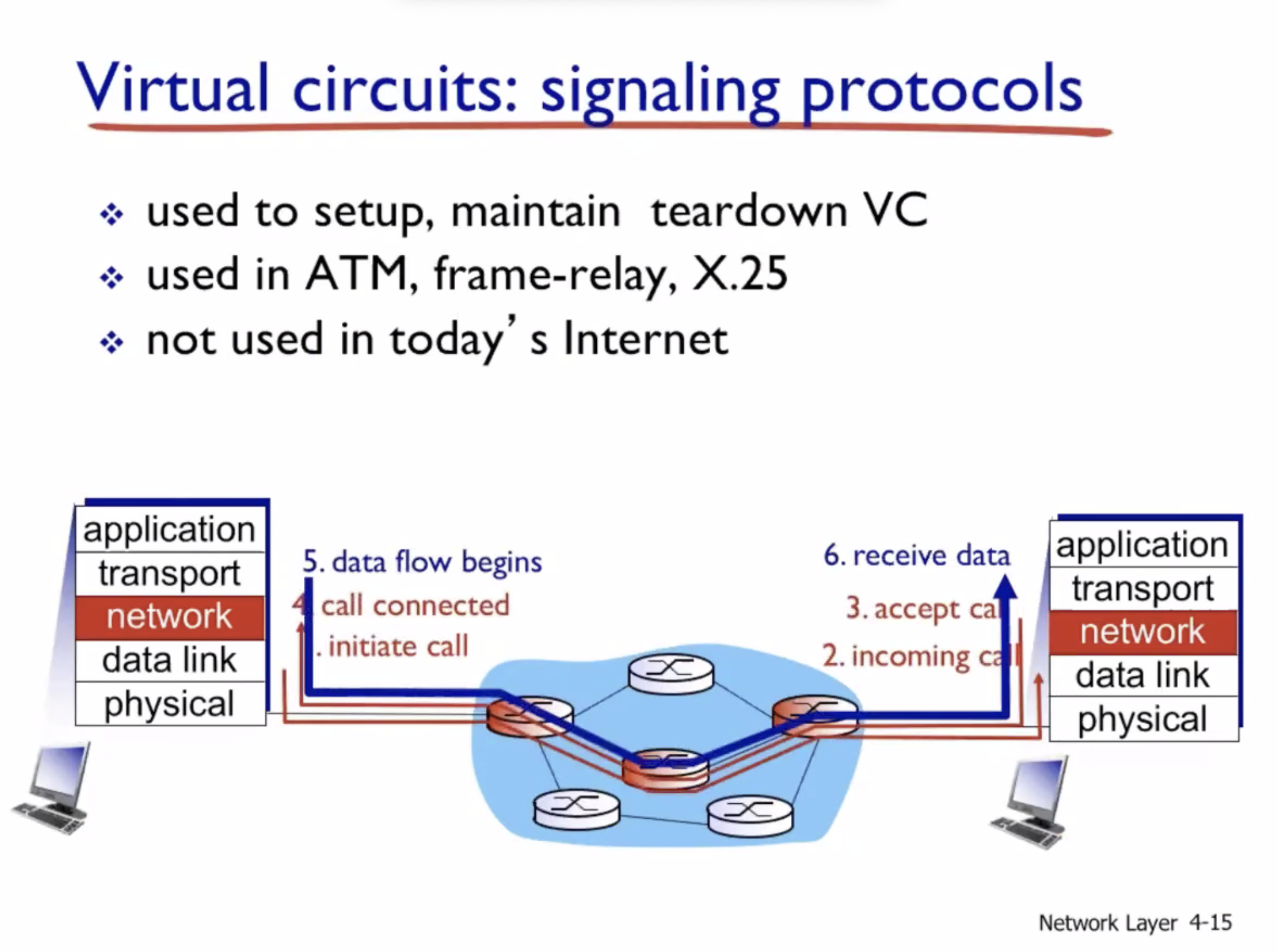
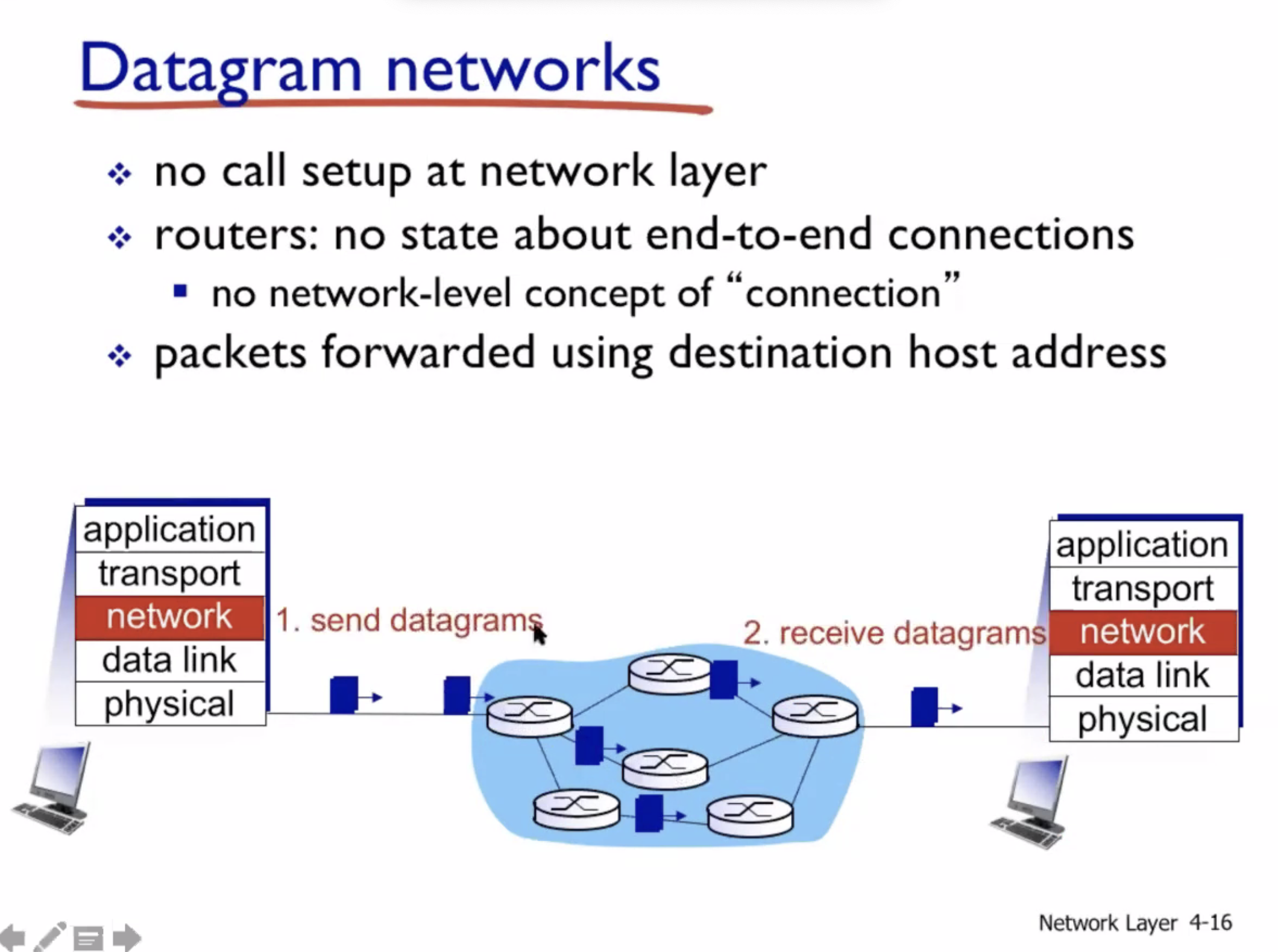
Datagram vs Virtual circuit
- Network layer connection vs connectionless
- No choice for programmers, the network provides one or the other
- Host to host
- Done on network core (routers)
Our internet uses Datagrams, hence it is connectionless on the network layer. We use TCP to get a connection service at the transport layer.
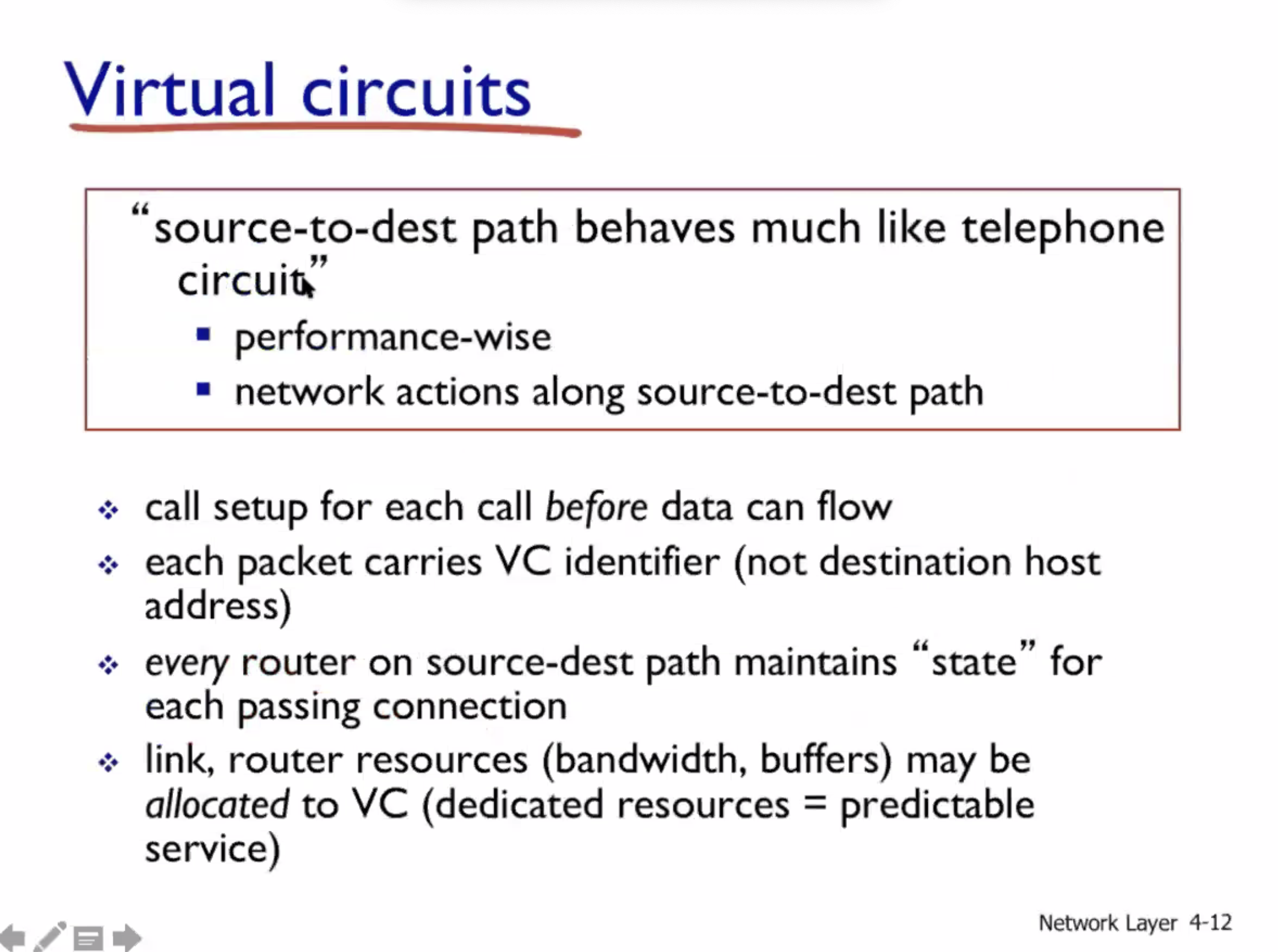
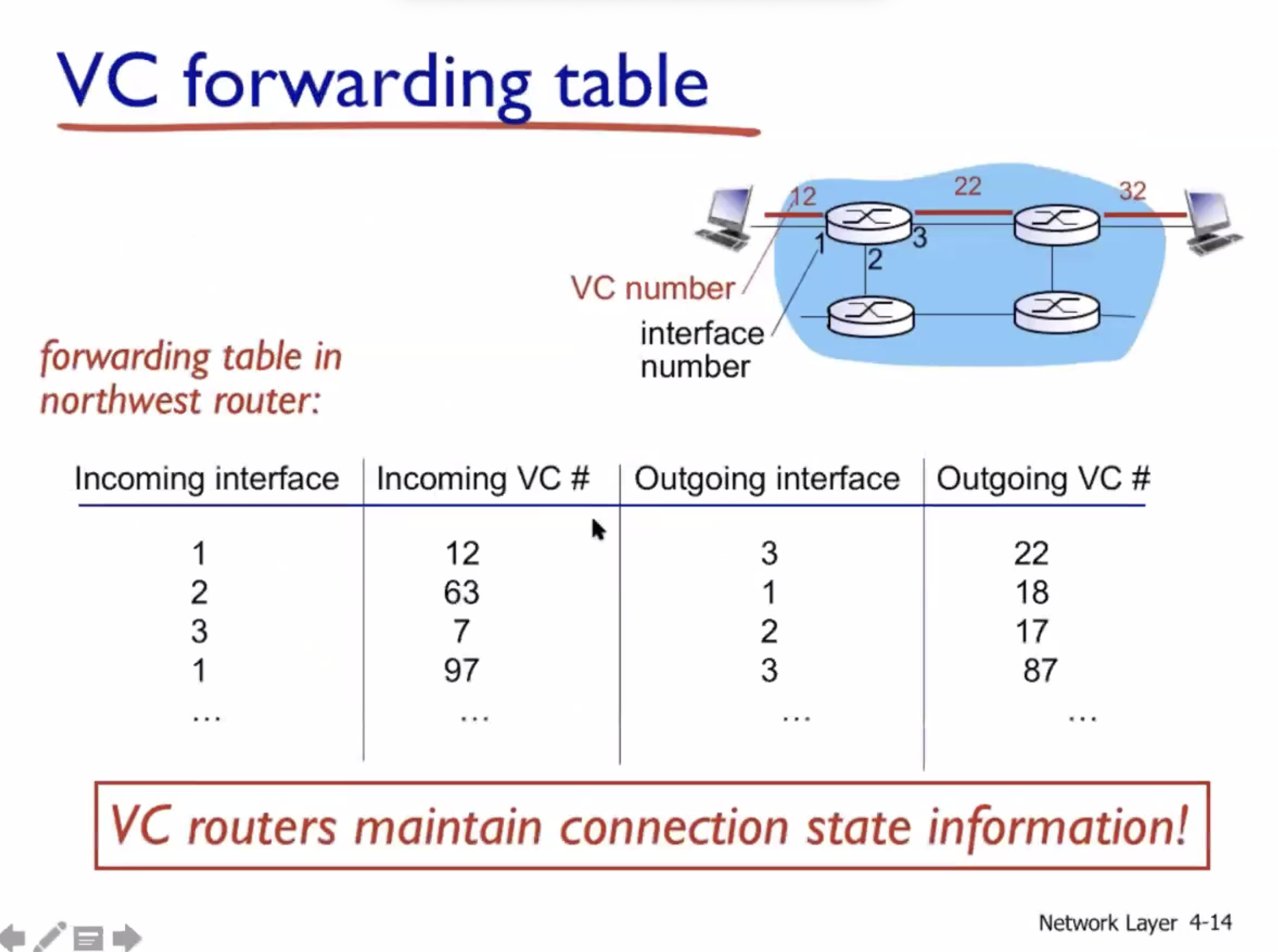
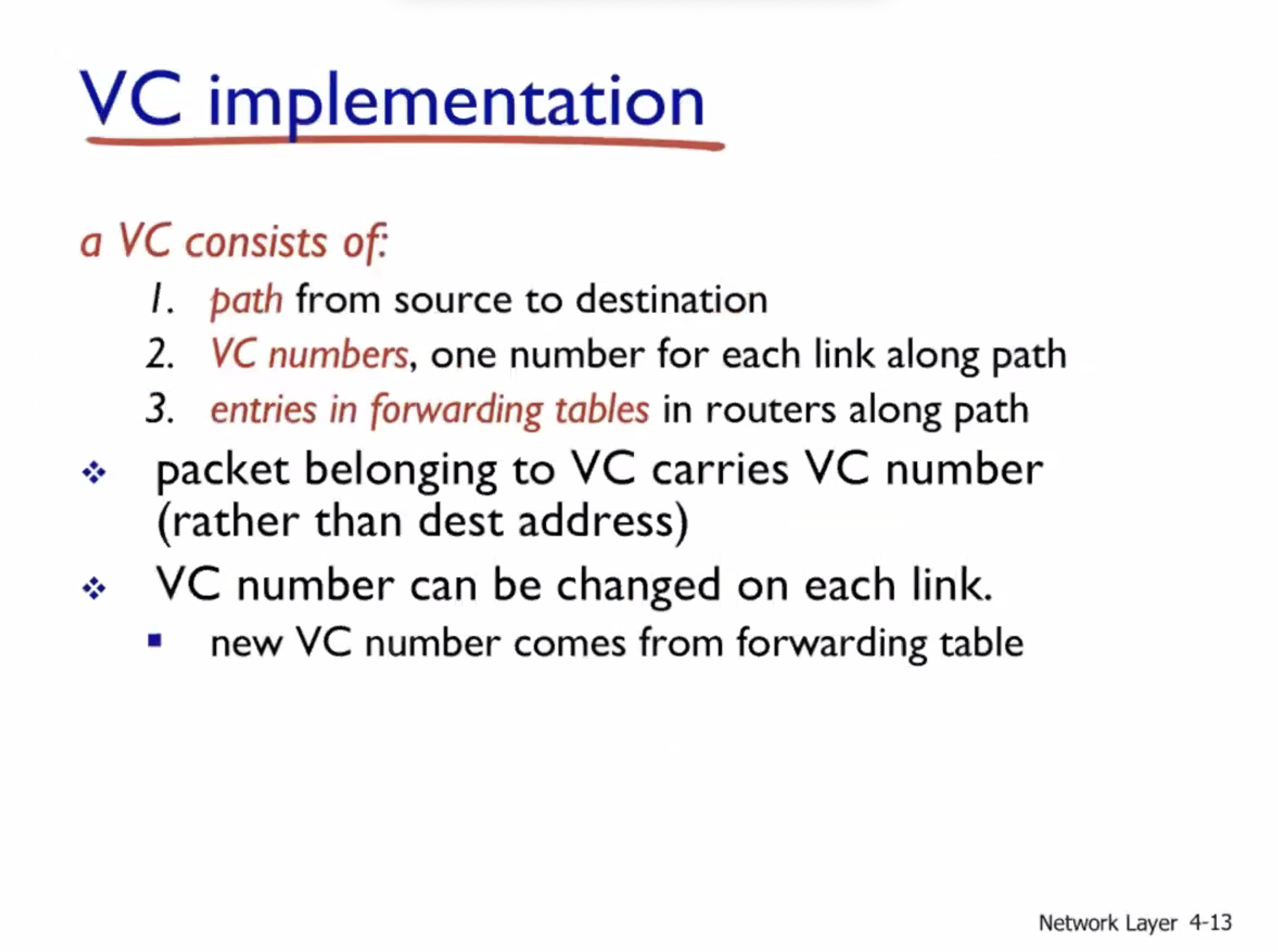
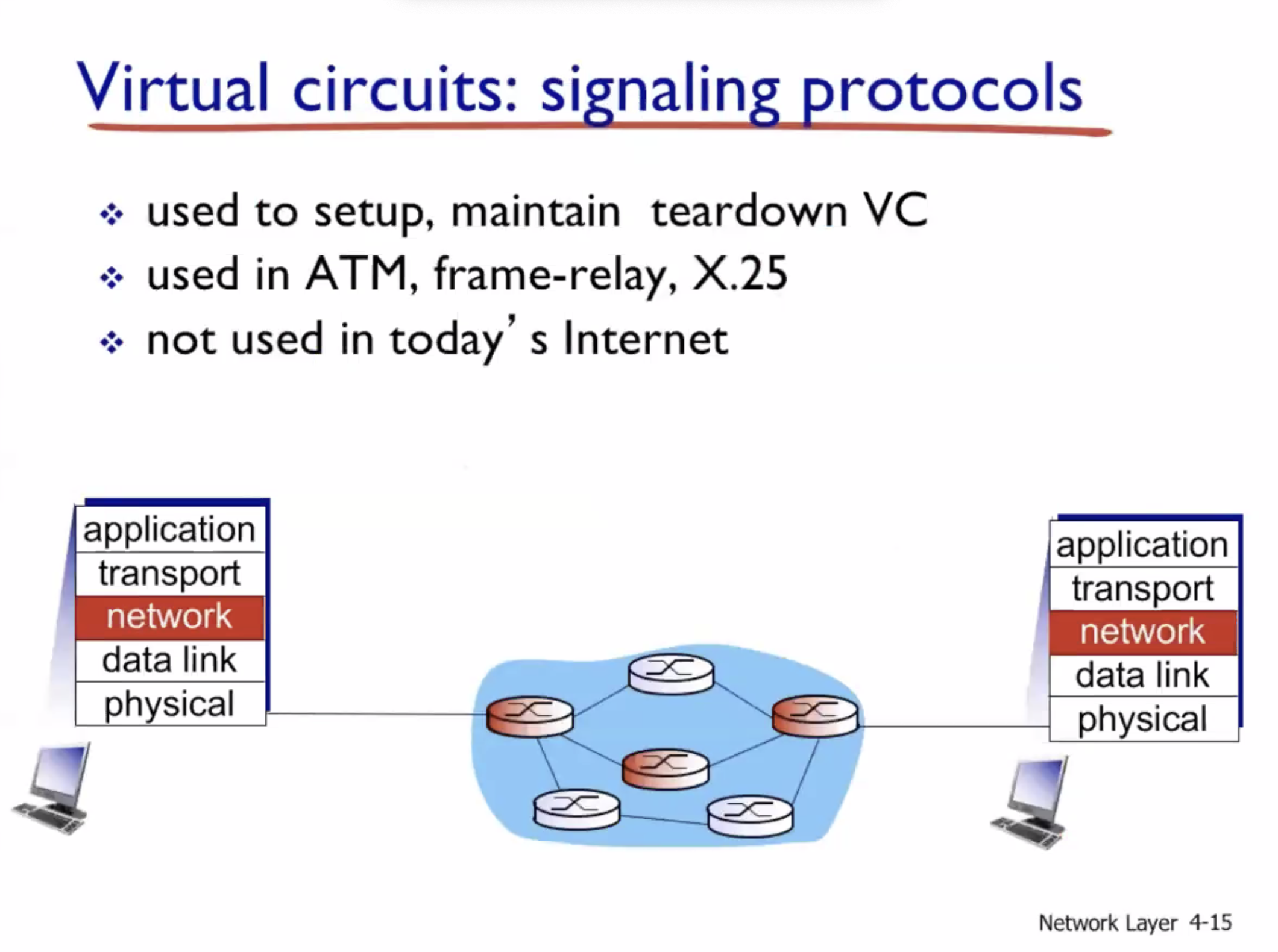
Virtual circuits (VC) #
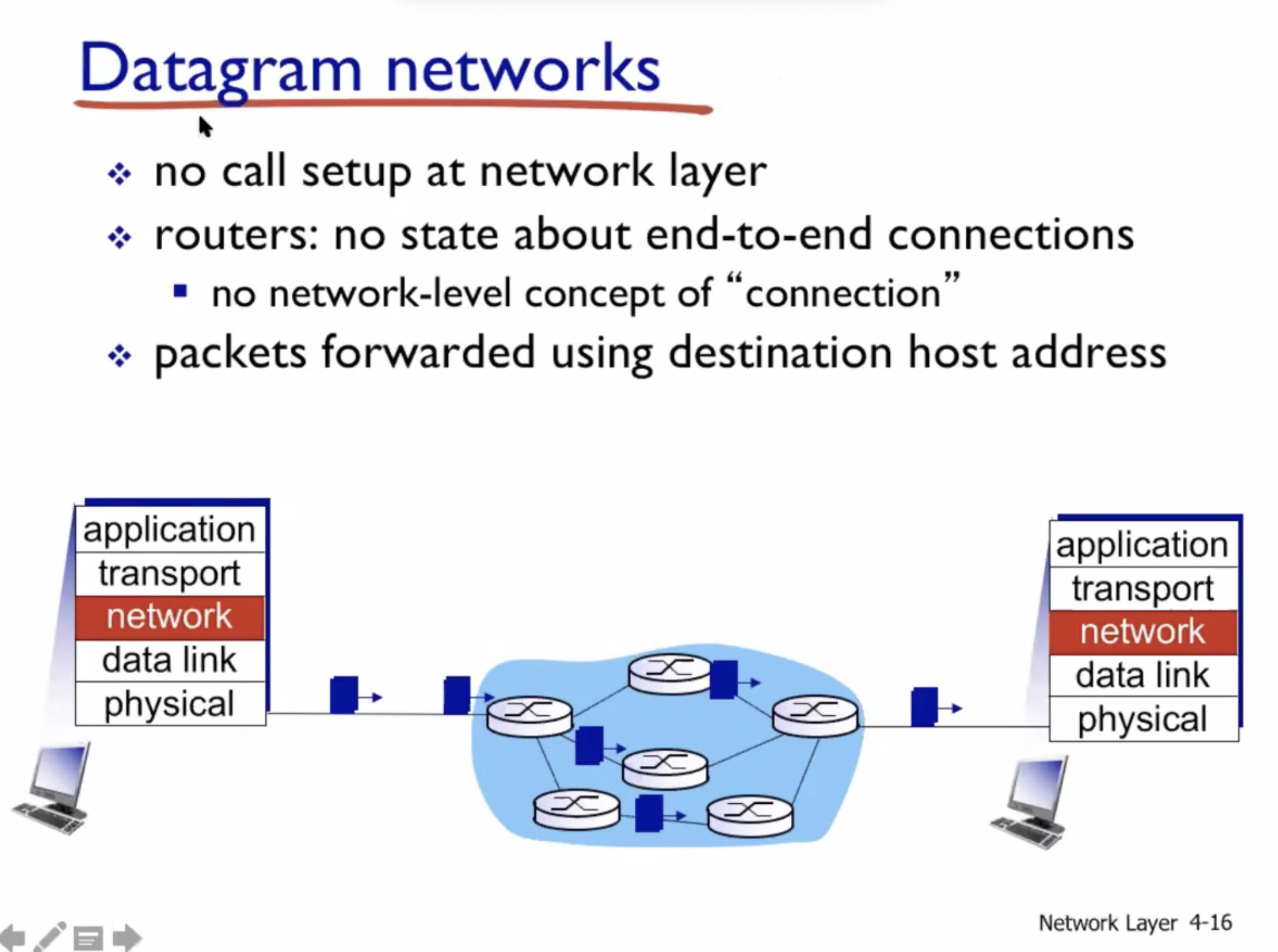
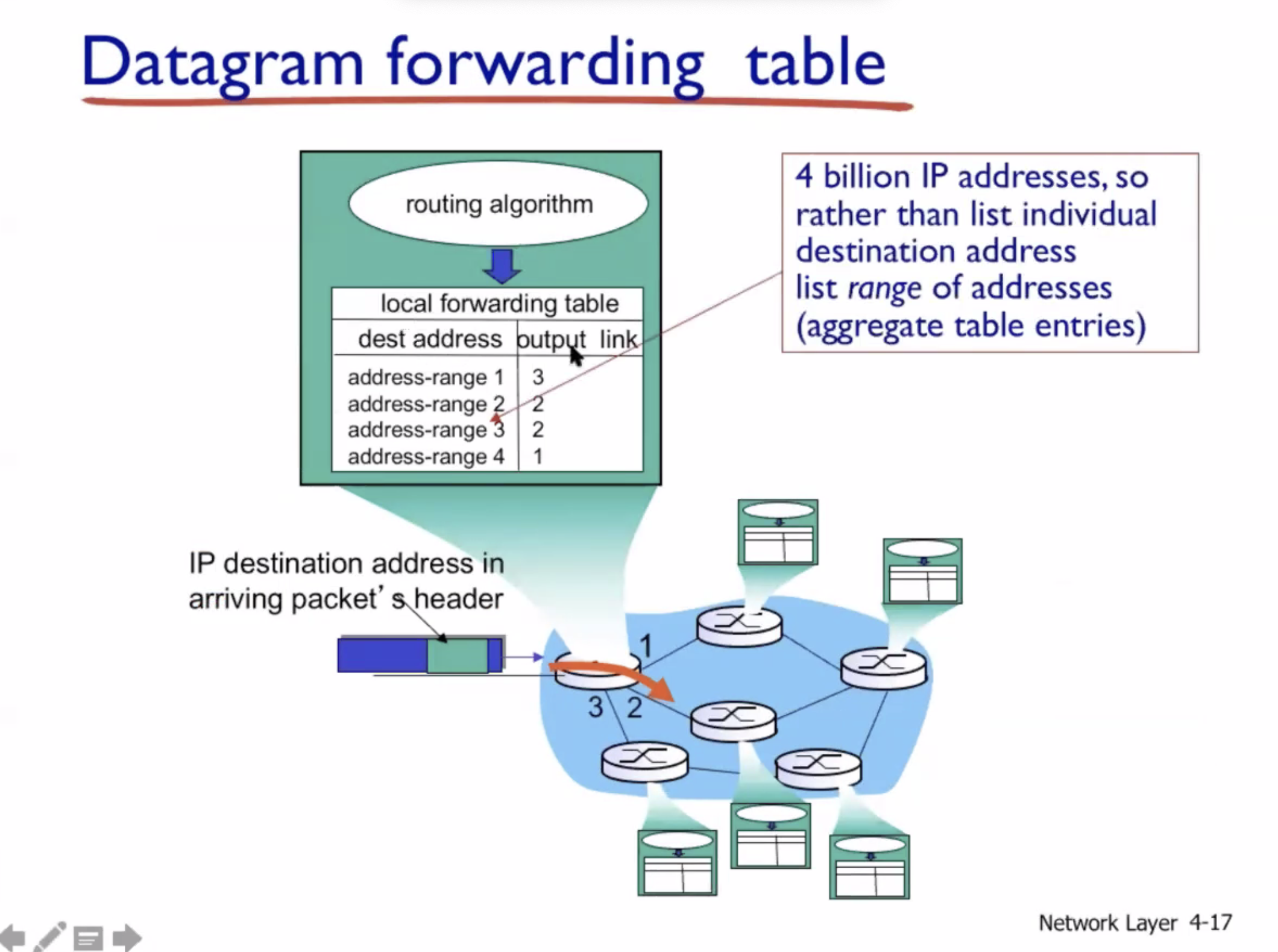
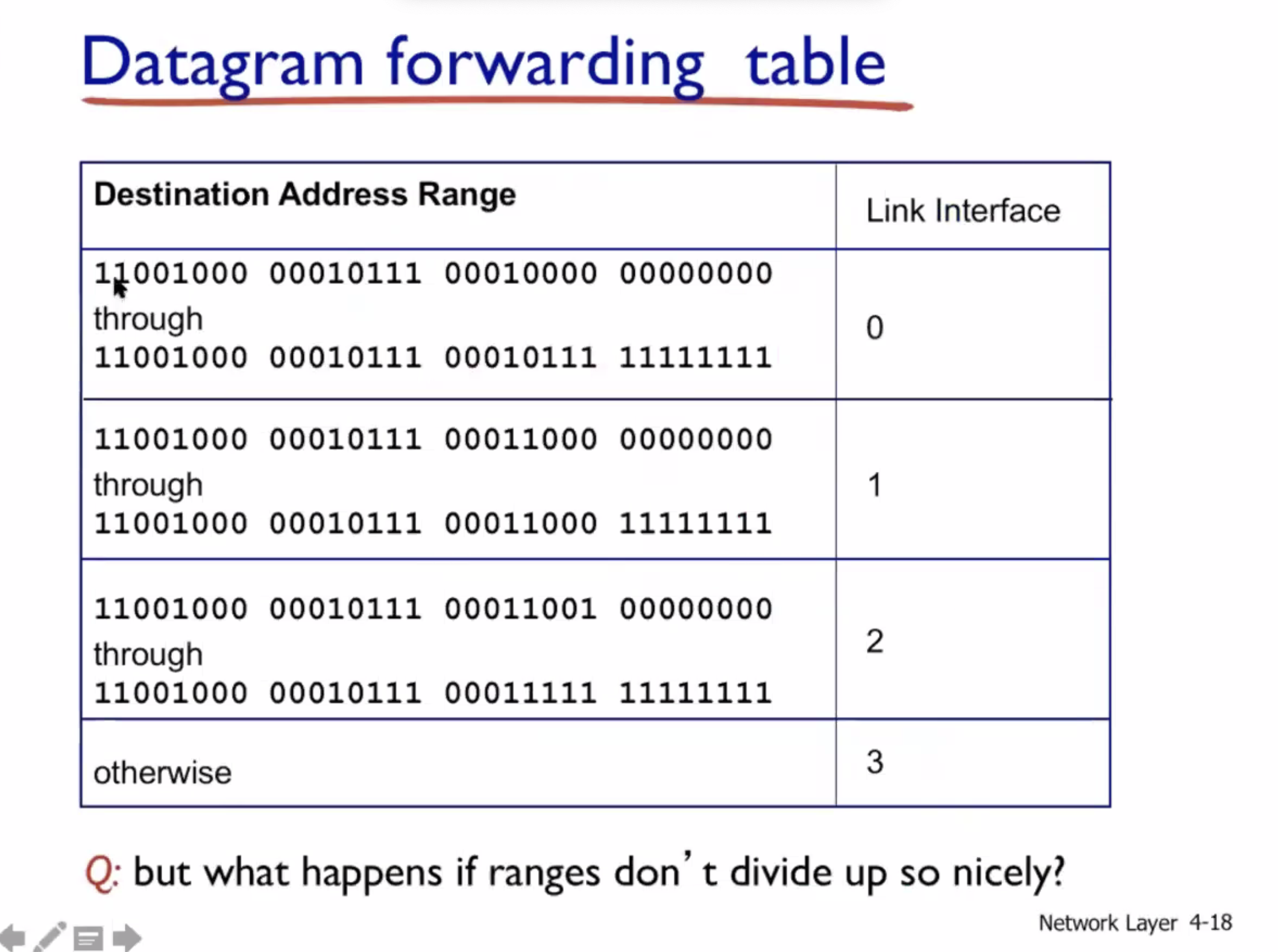
Datagram networks #

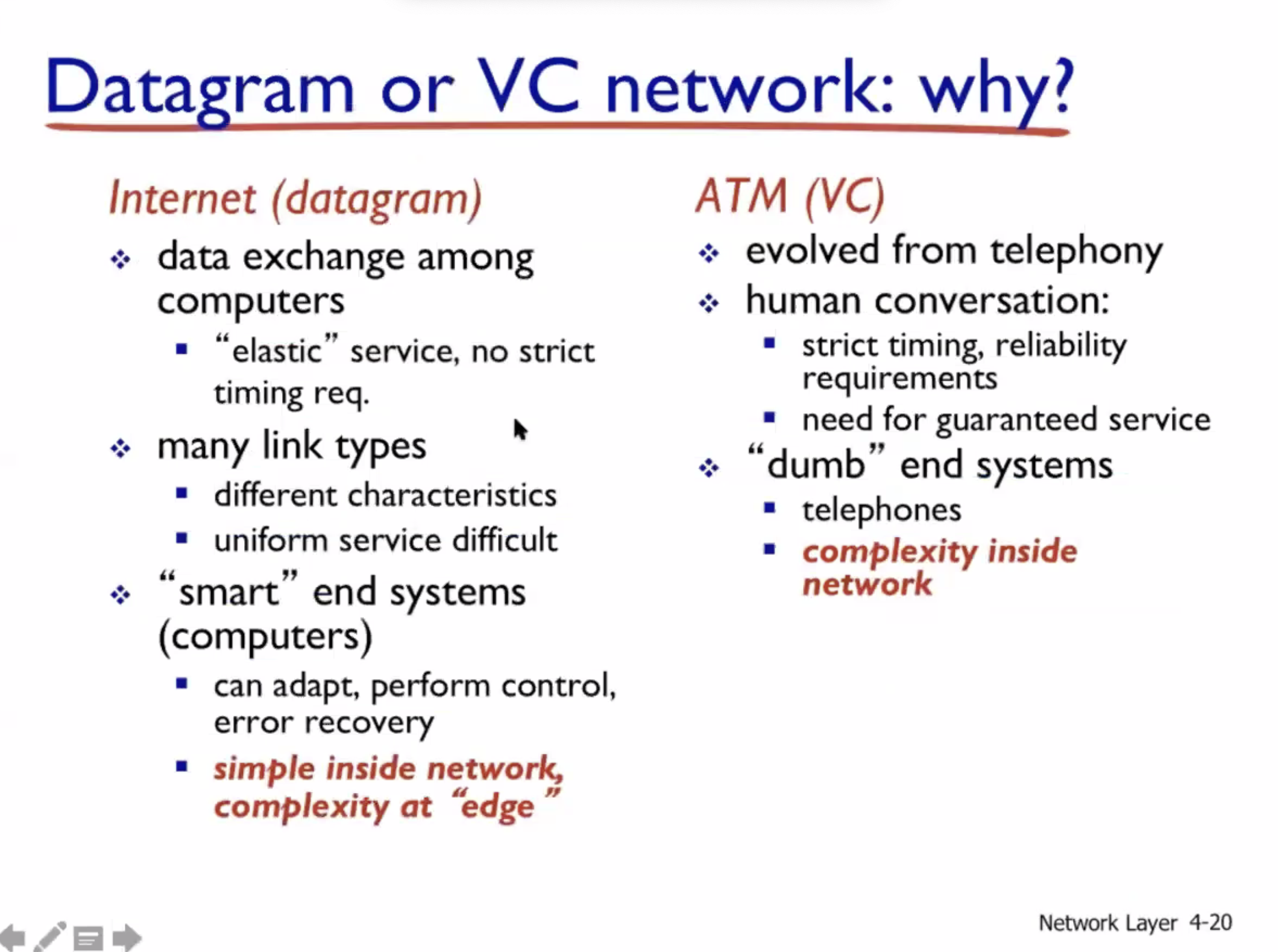
Datagram vs VC overview #
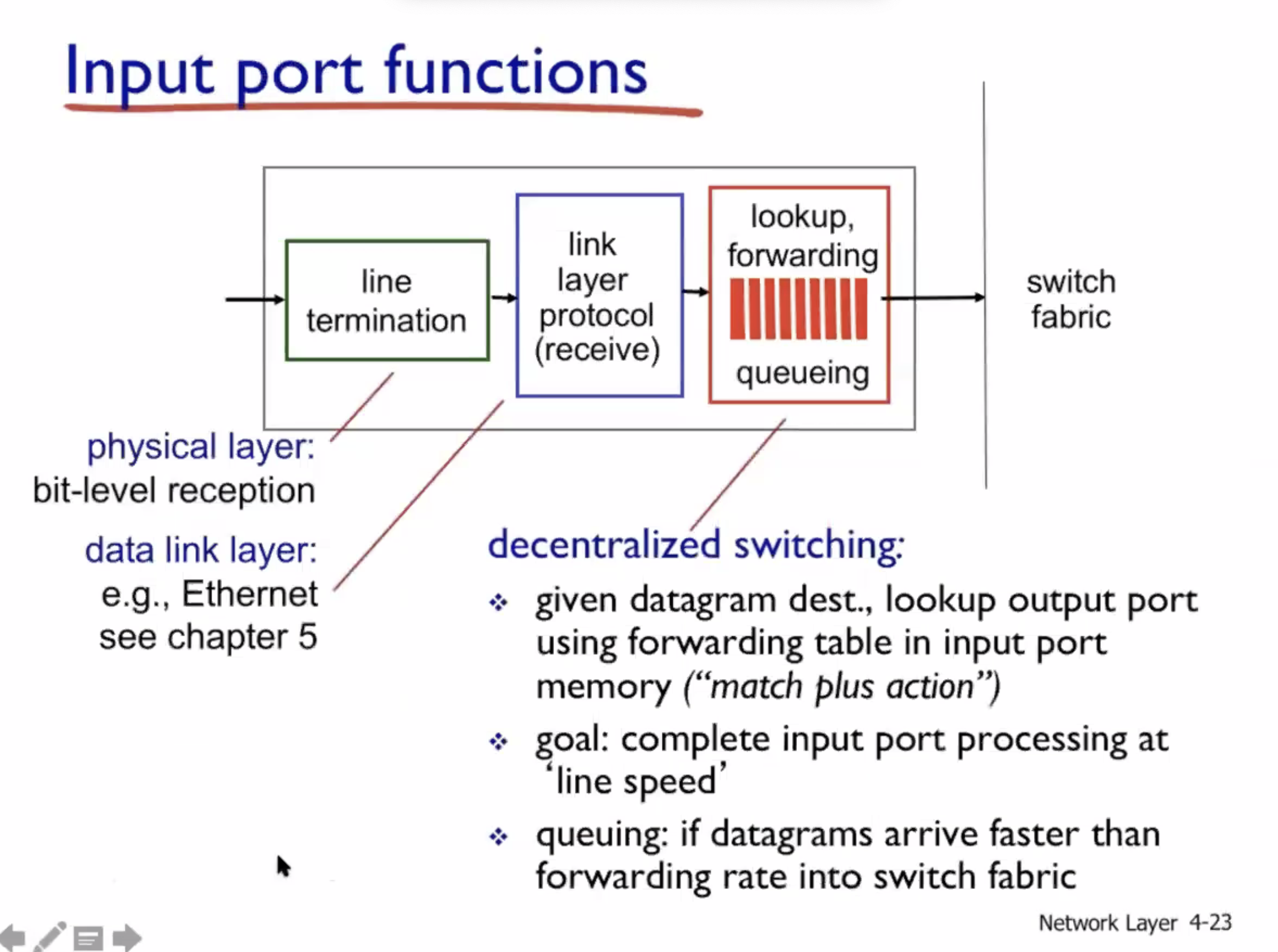
What’s inside a router #