Threads cont. #
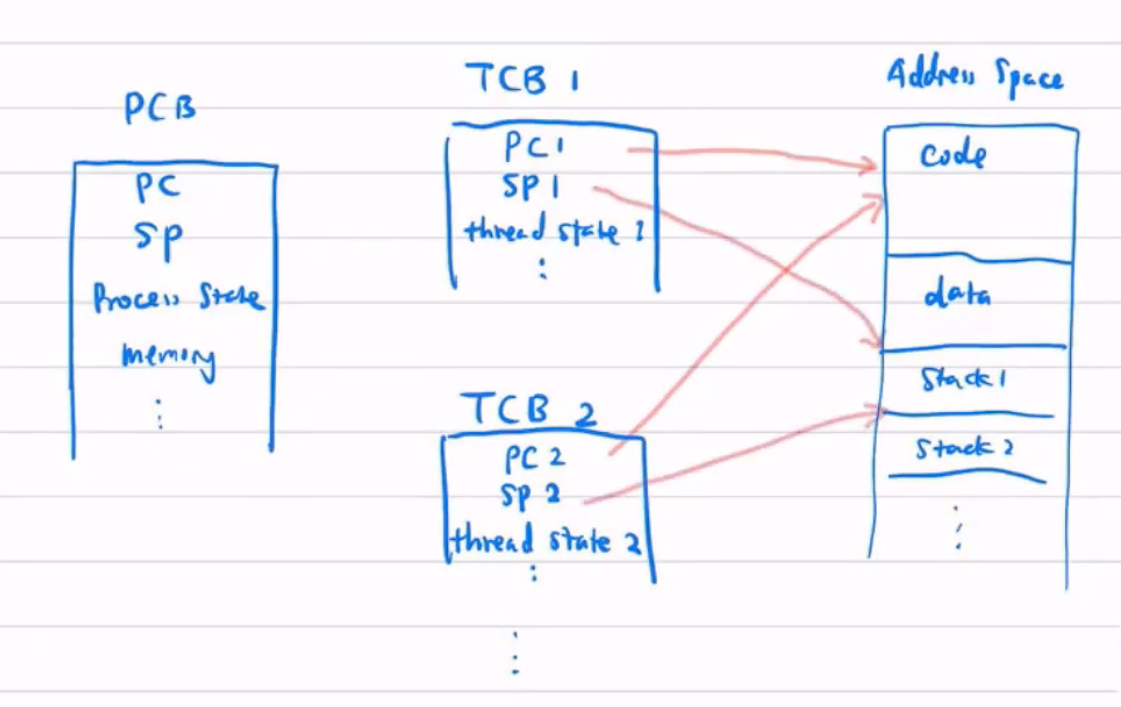
How TCBs are mapped to the processes address space.
User-level threads #

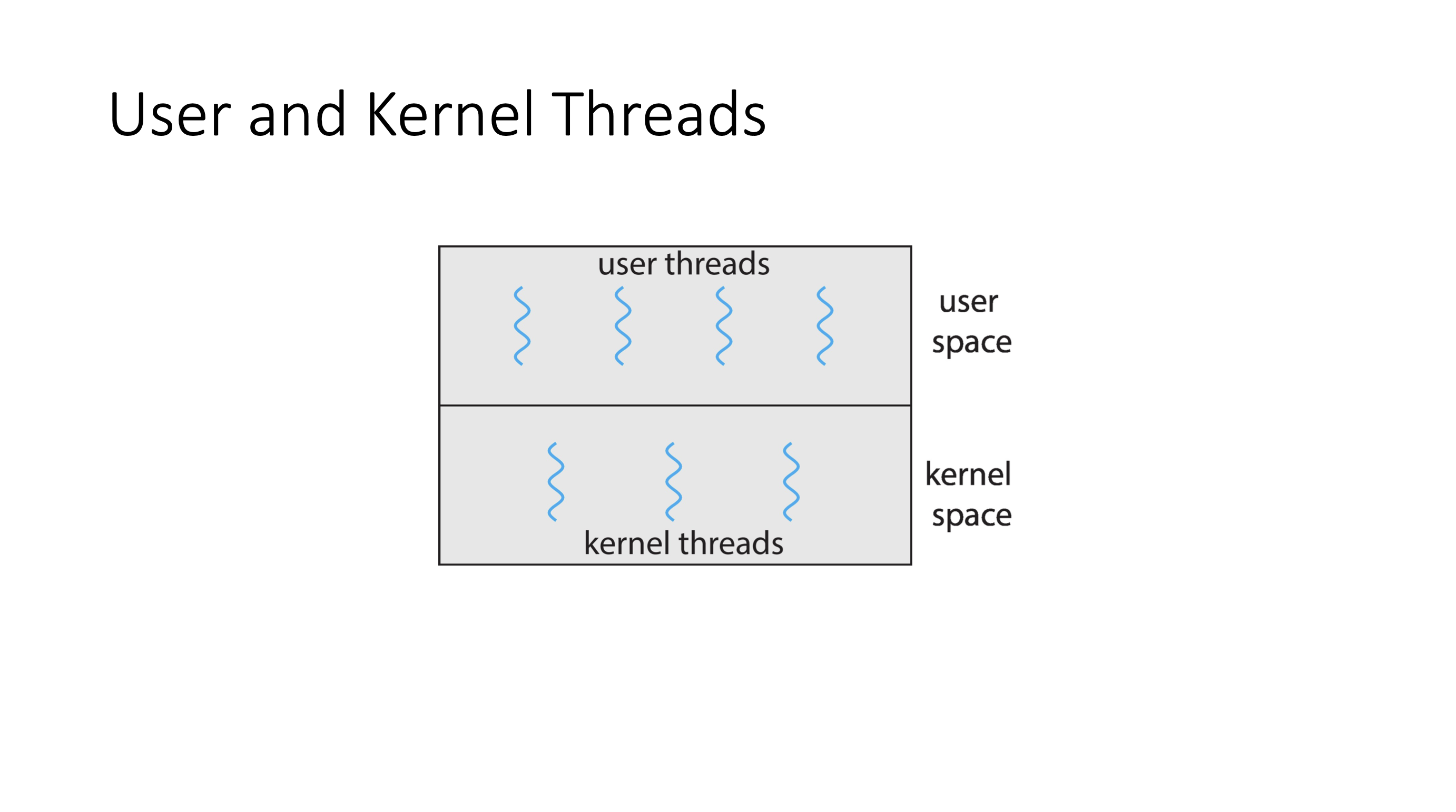


Multithreading models #

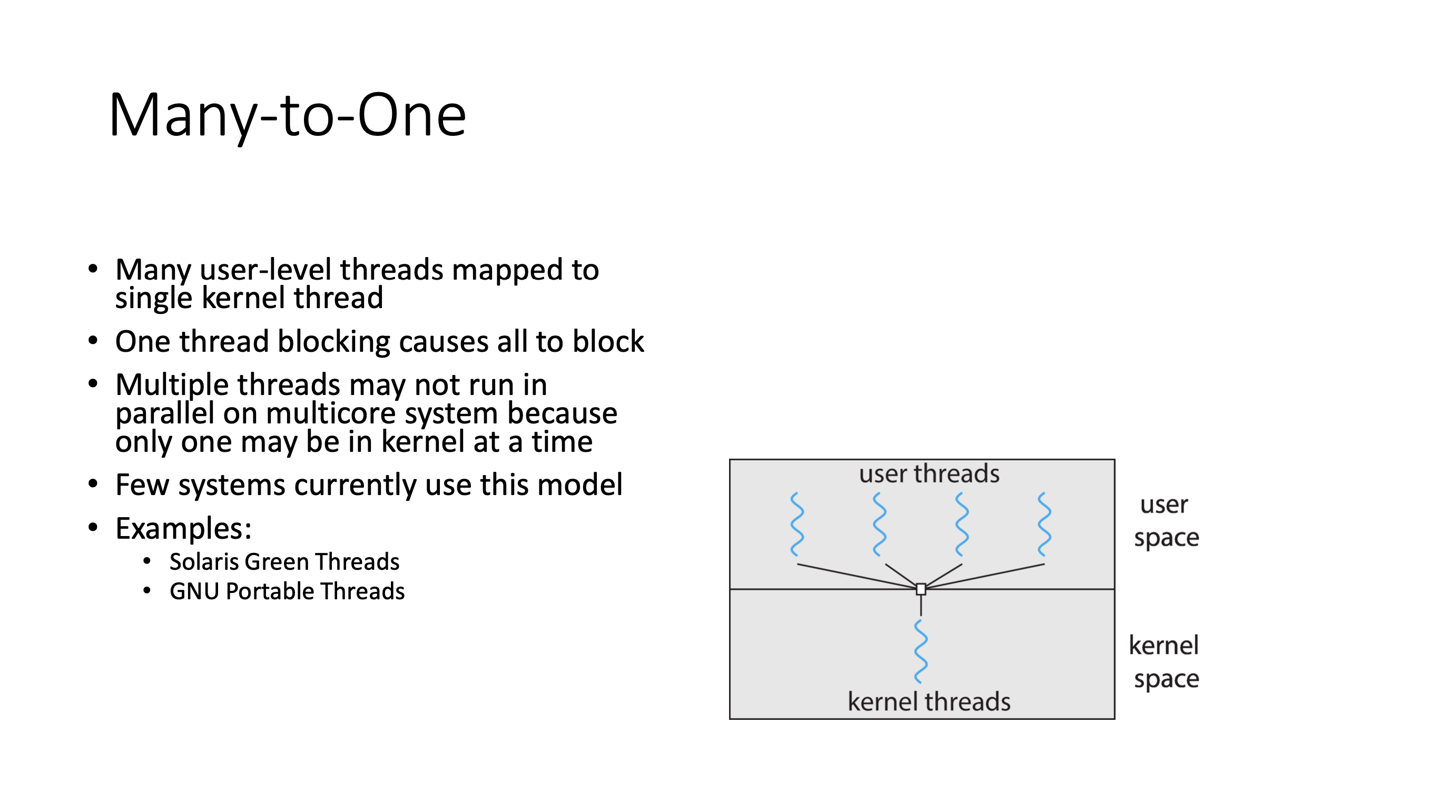
The bottleneck created by the many-to-one model can be alleviated in the one-to-one model.
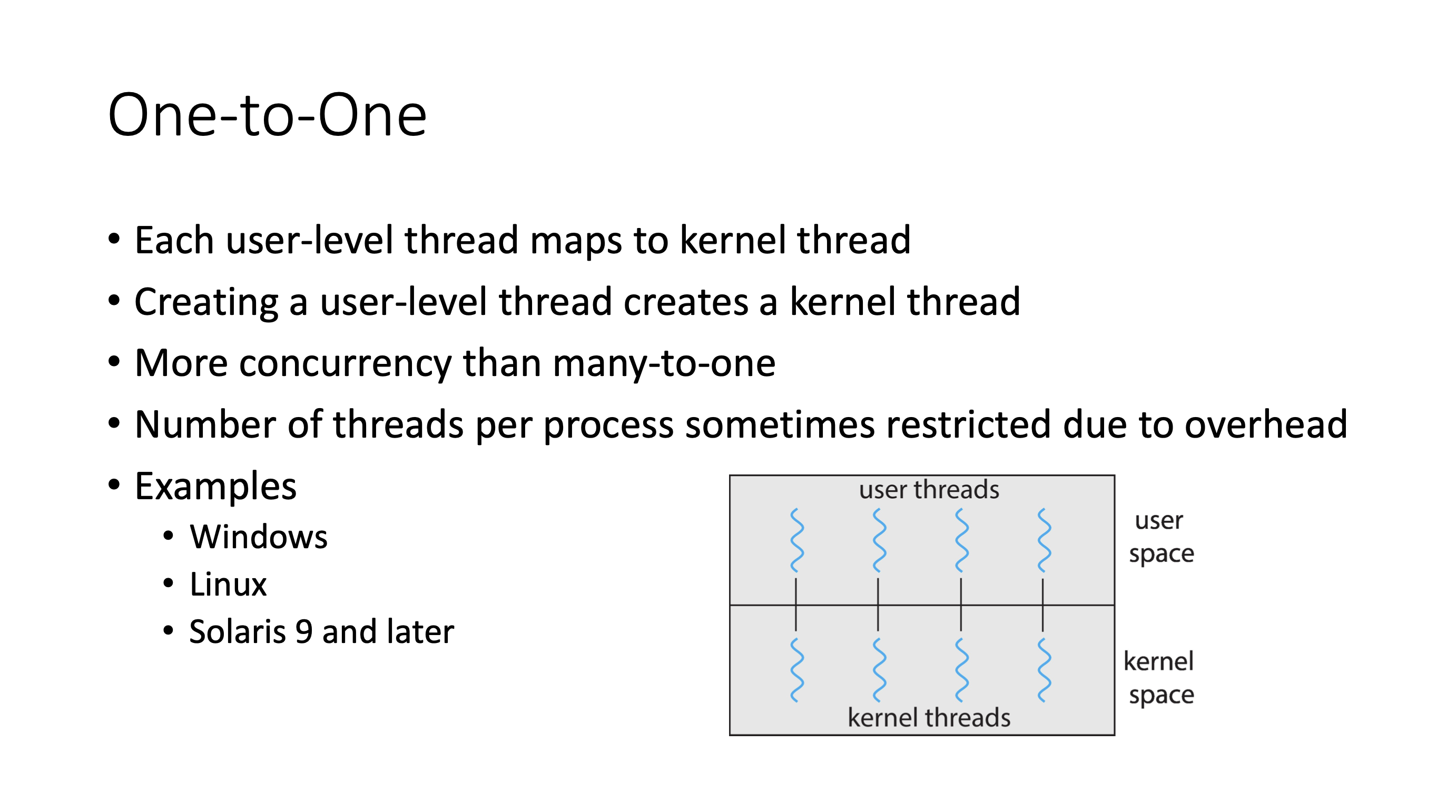
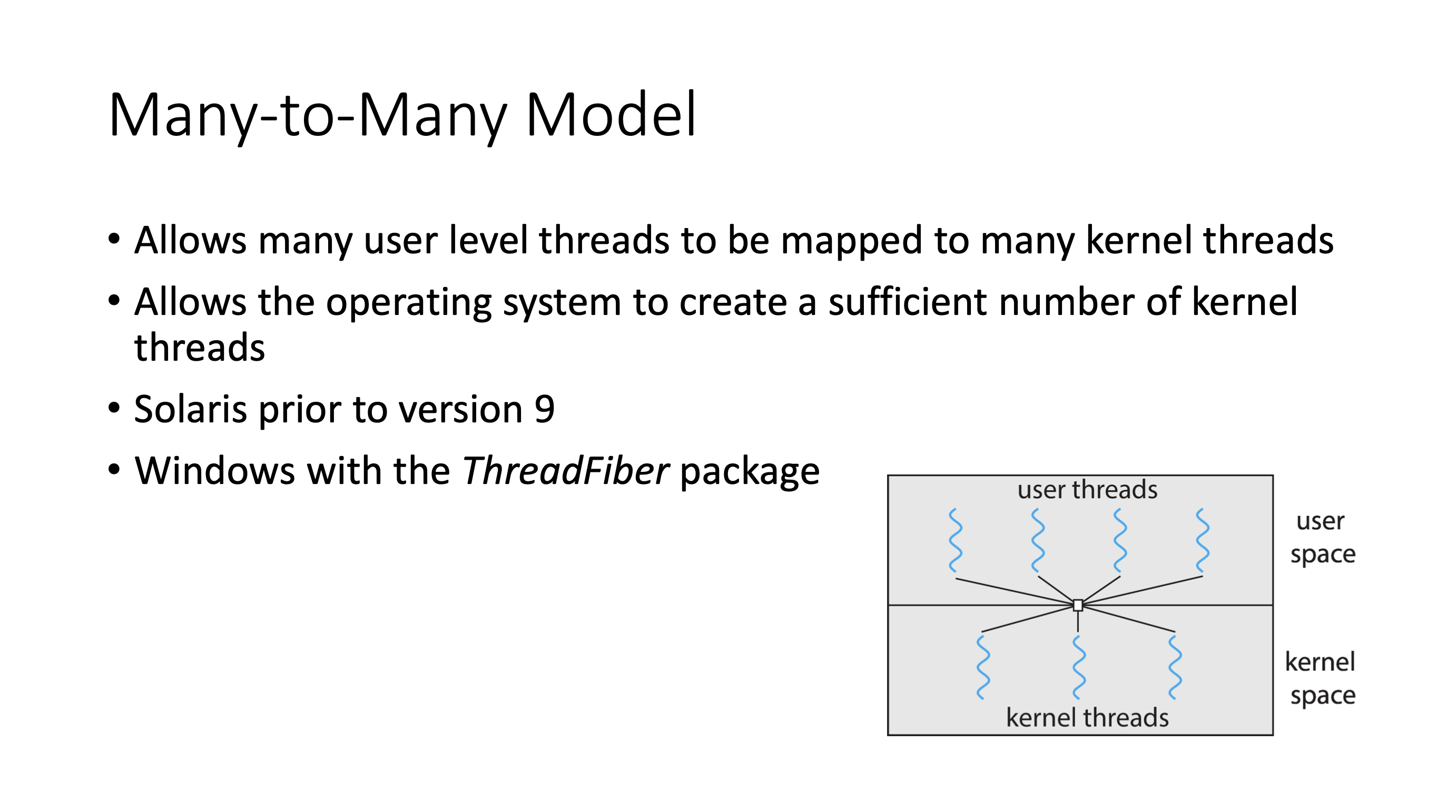
The M:M model maintains slightly more user threads than kernel threads.
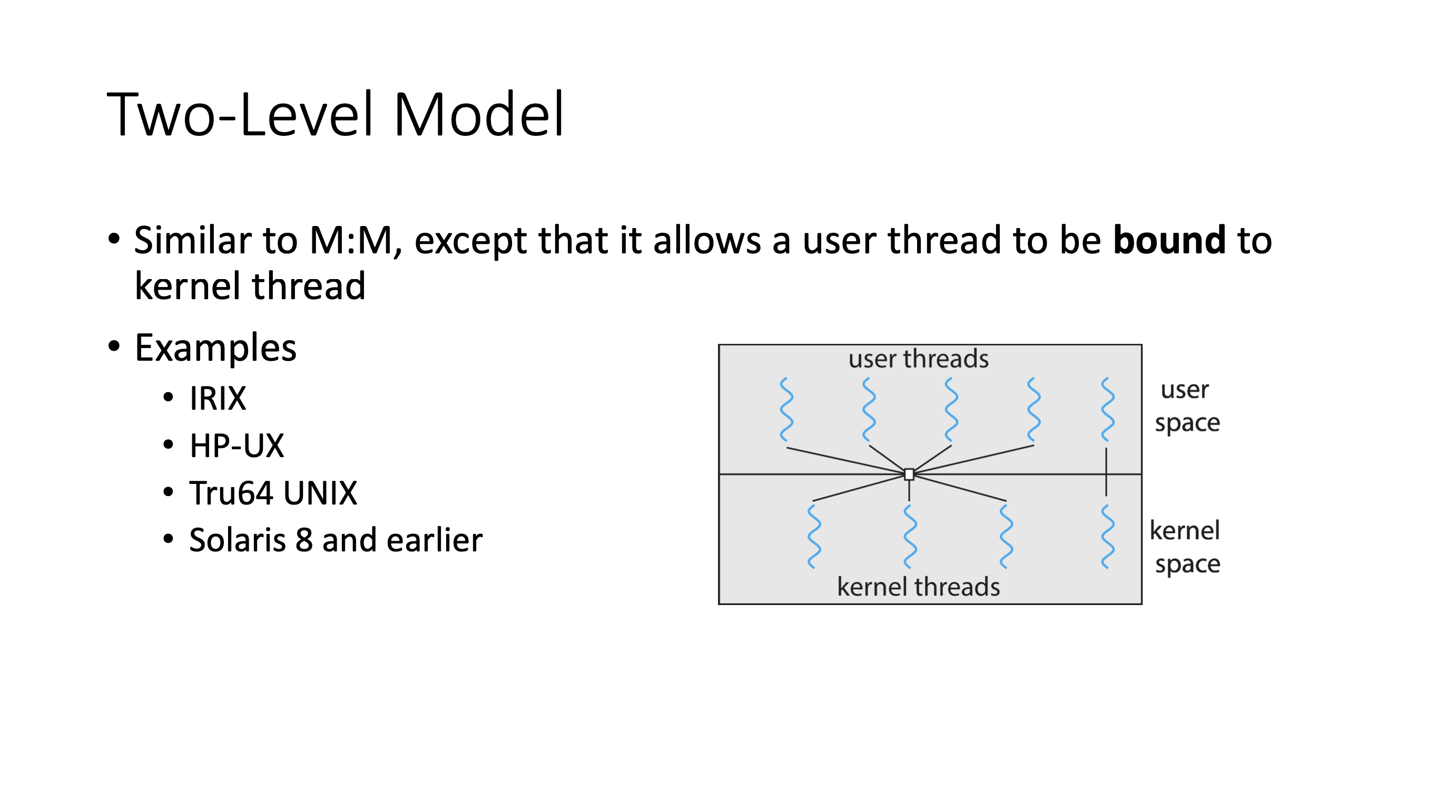
So why do the biggest OSes use the one-to-one model? More cores in CPUs, more CPUs in general.
Thread libraries #





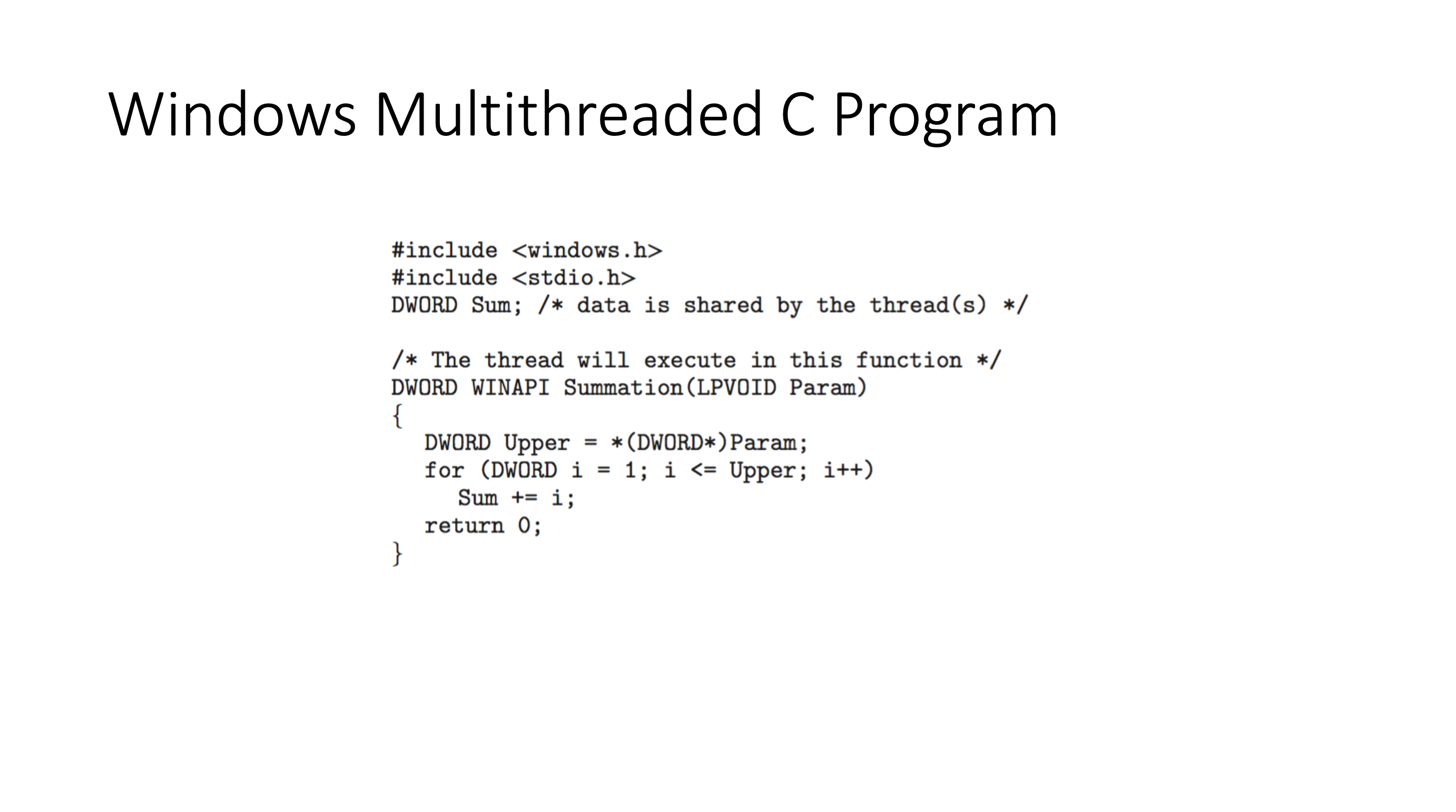

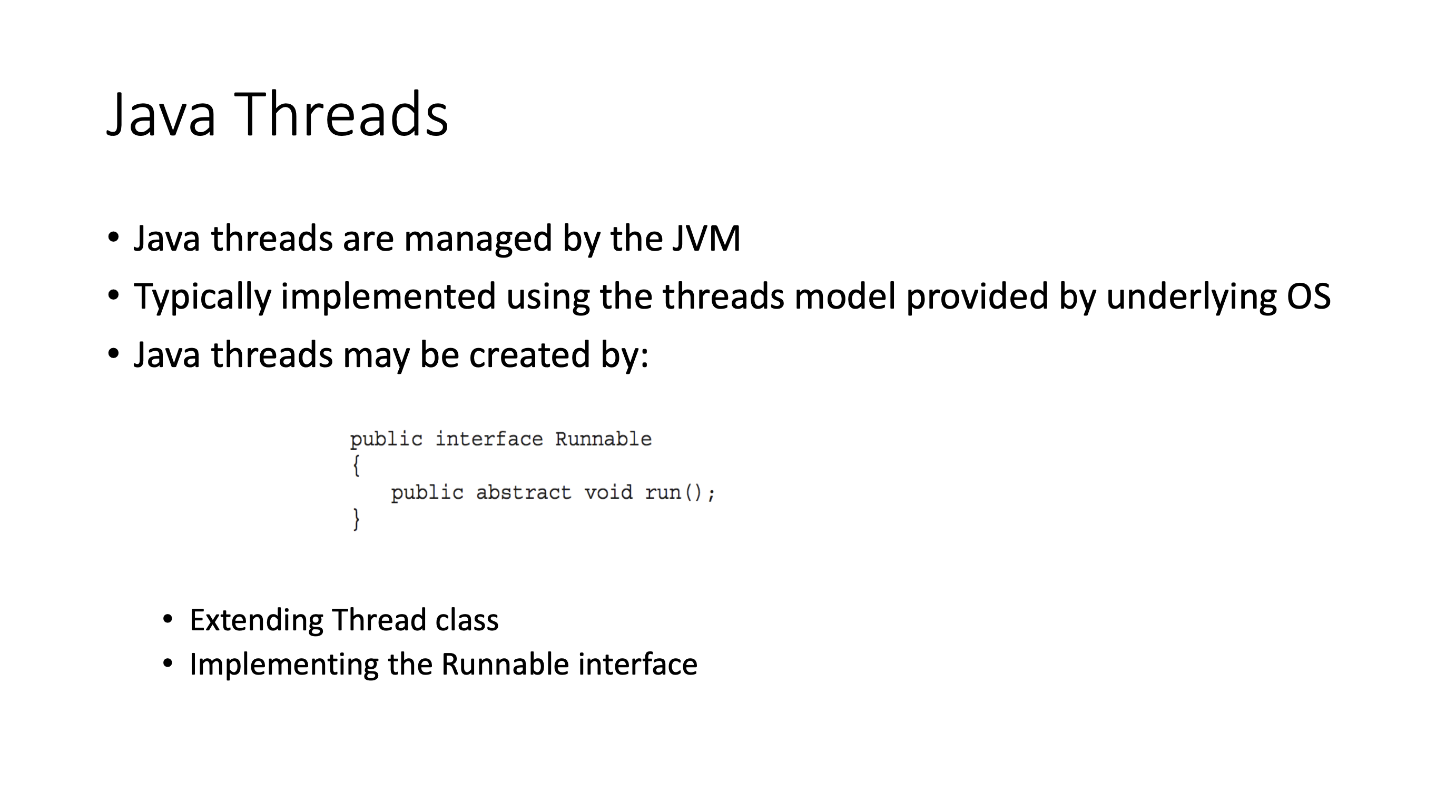


Implicit threading #


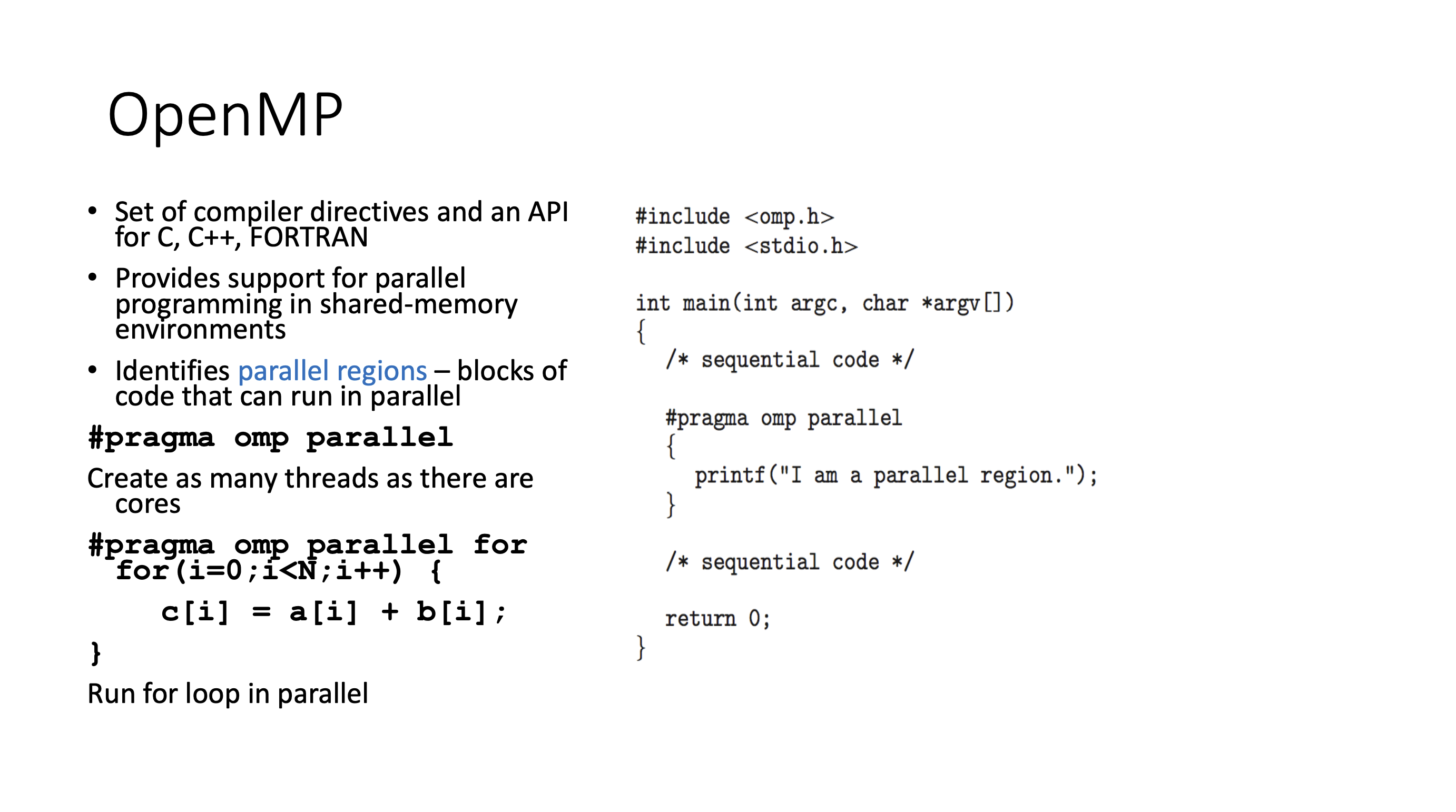
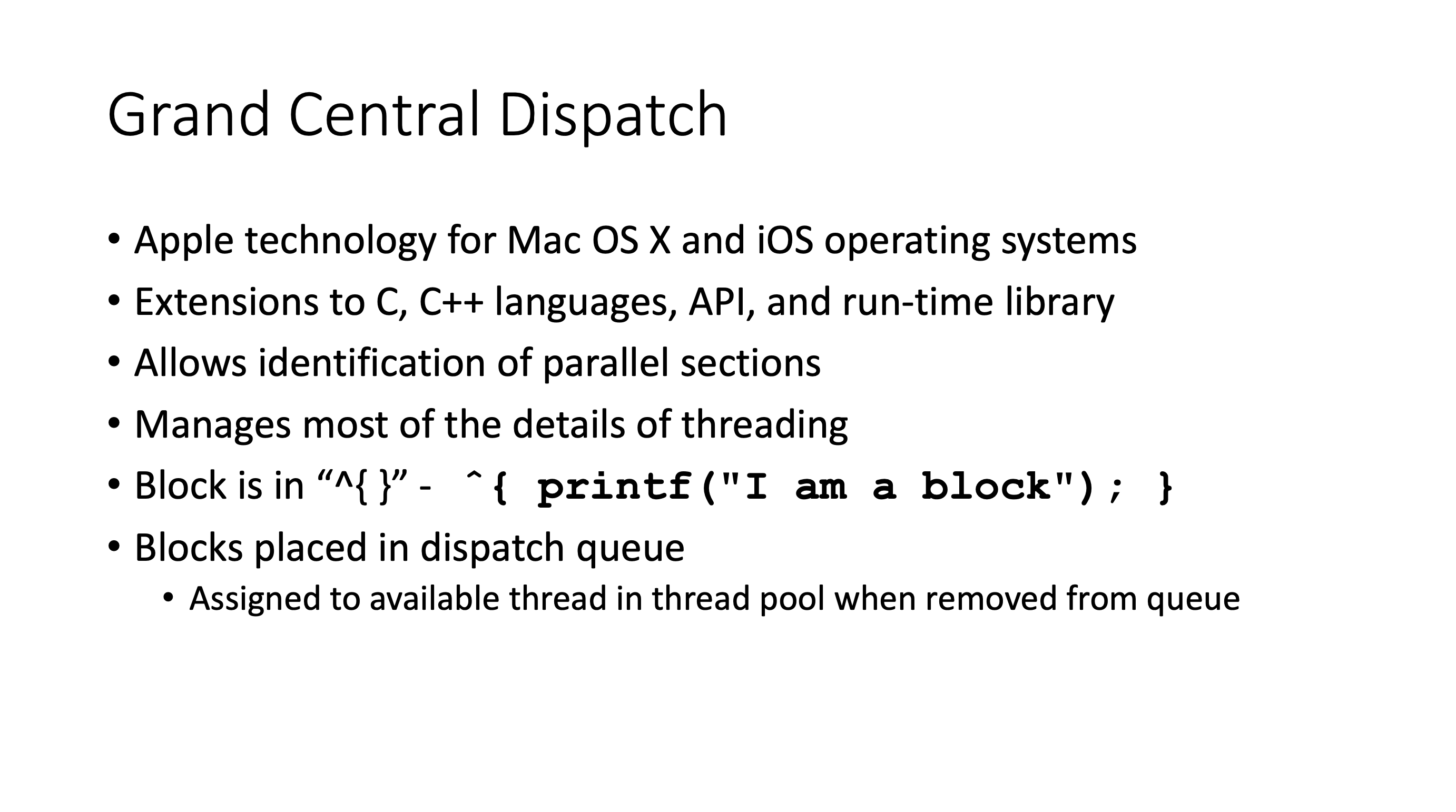

Issues #


Single threaded


Multi-threaded has 2 possibilities
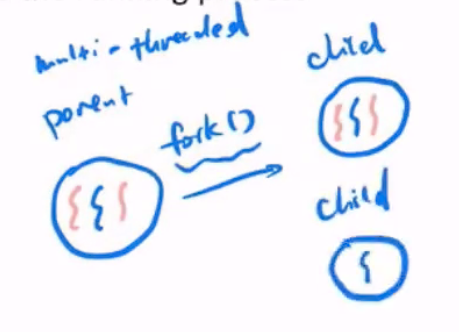 The child can either have 1 thread (the invoking thread), or all.
The child can either have 1 thread (the invoking thread), or all.
 The child can either have 1 thread (the invoking thread), or all.
The child can either have 1 thread (the invoking thread), or all.

Thread local storage is stuff like
- stack allocated variables
- parameters
- return values
- other things on stack
