Introduction cont #

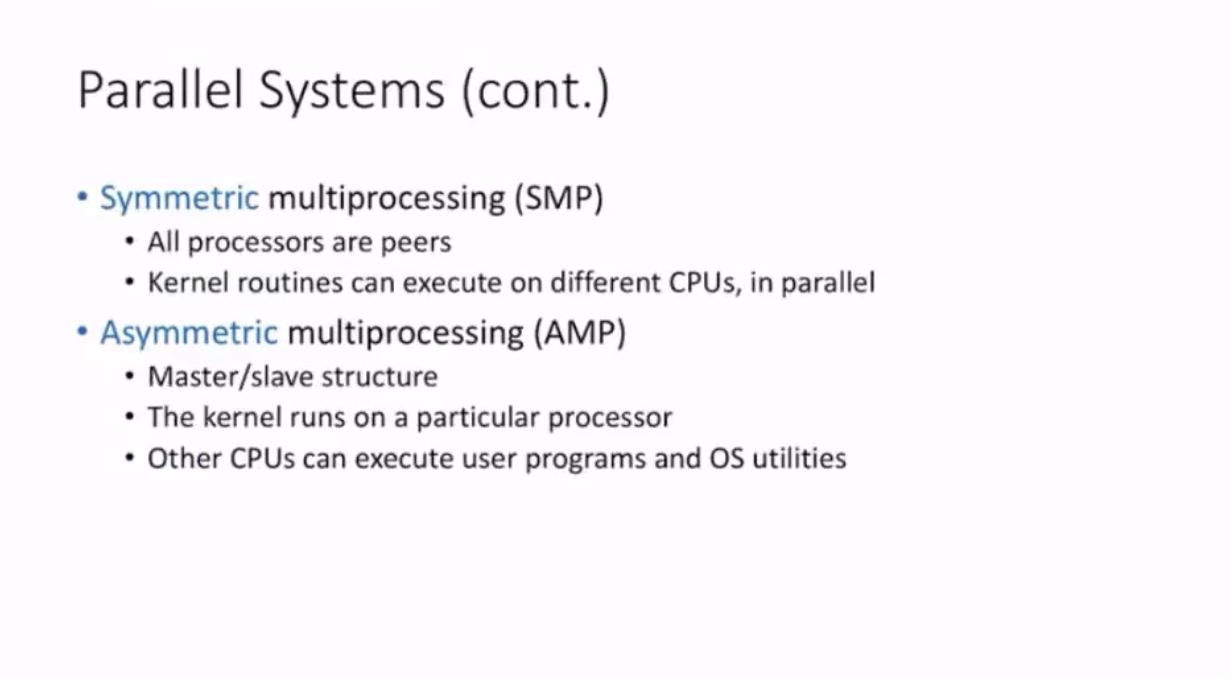
Parallel systems #
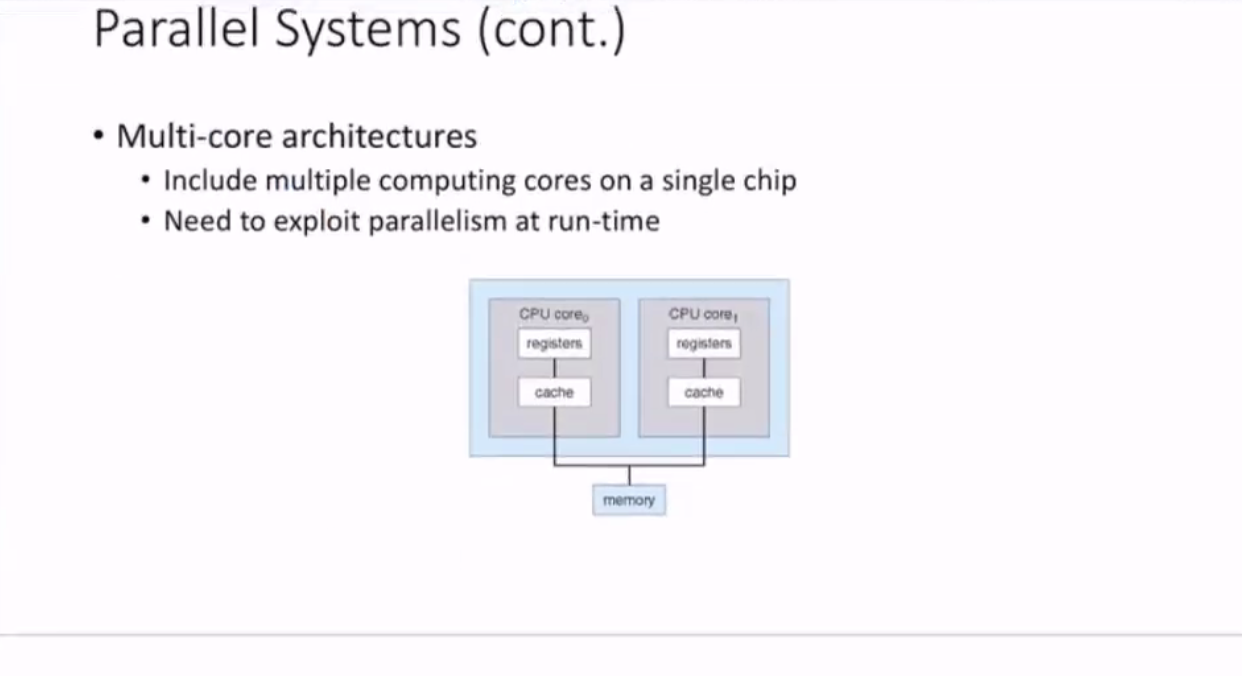
Intrachip transfer is much faster than interchip transfer.

Distributed systems #
Real-time and embedded systems #
Other systems #


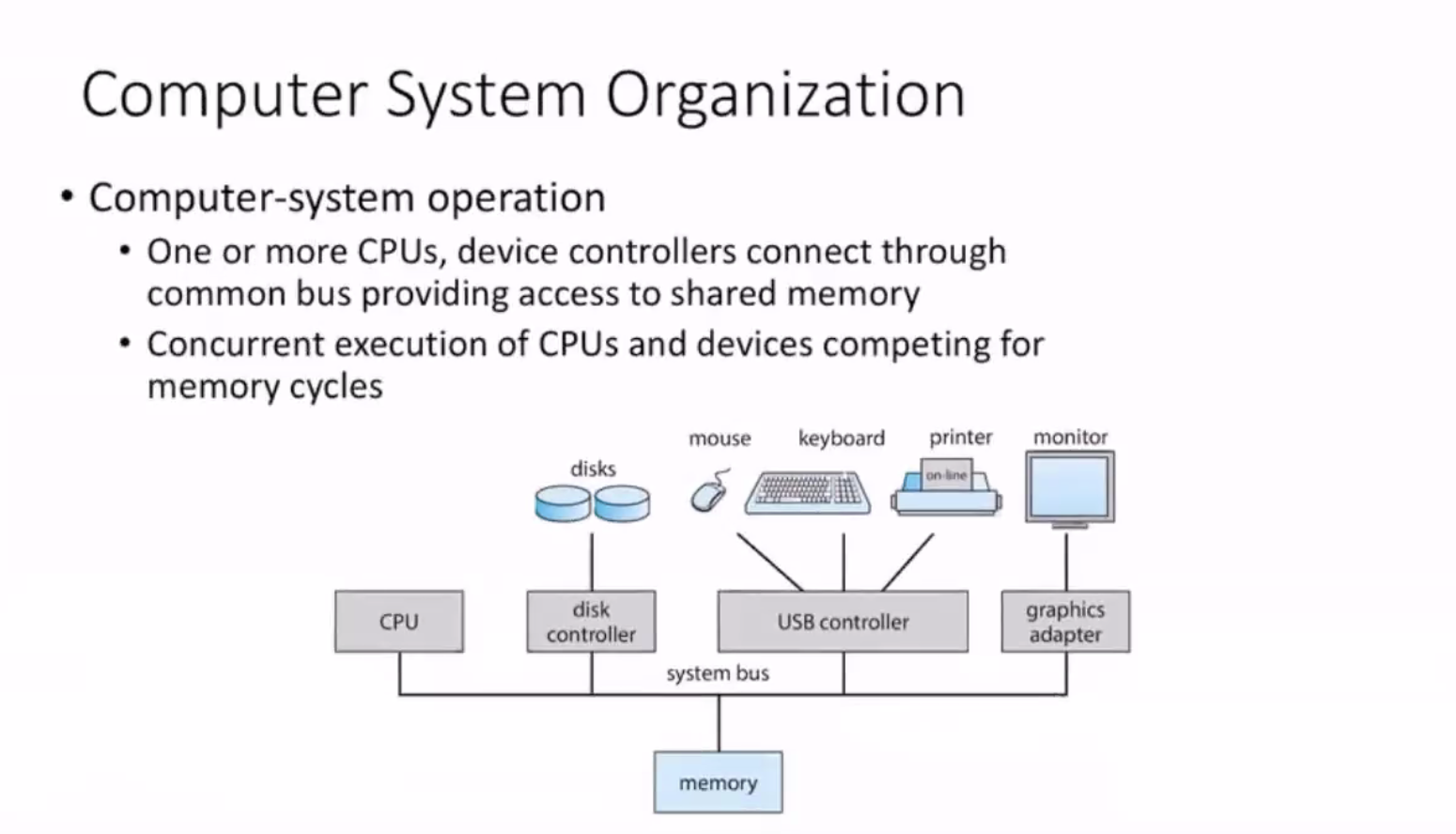
Organization #
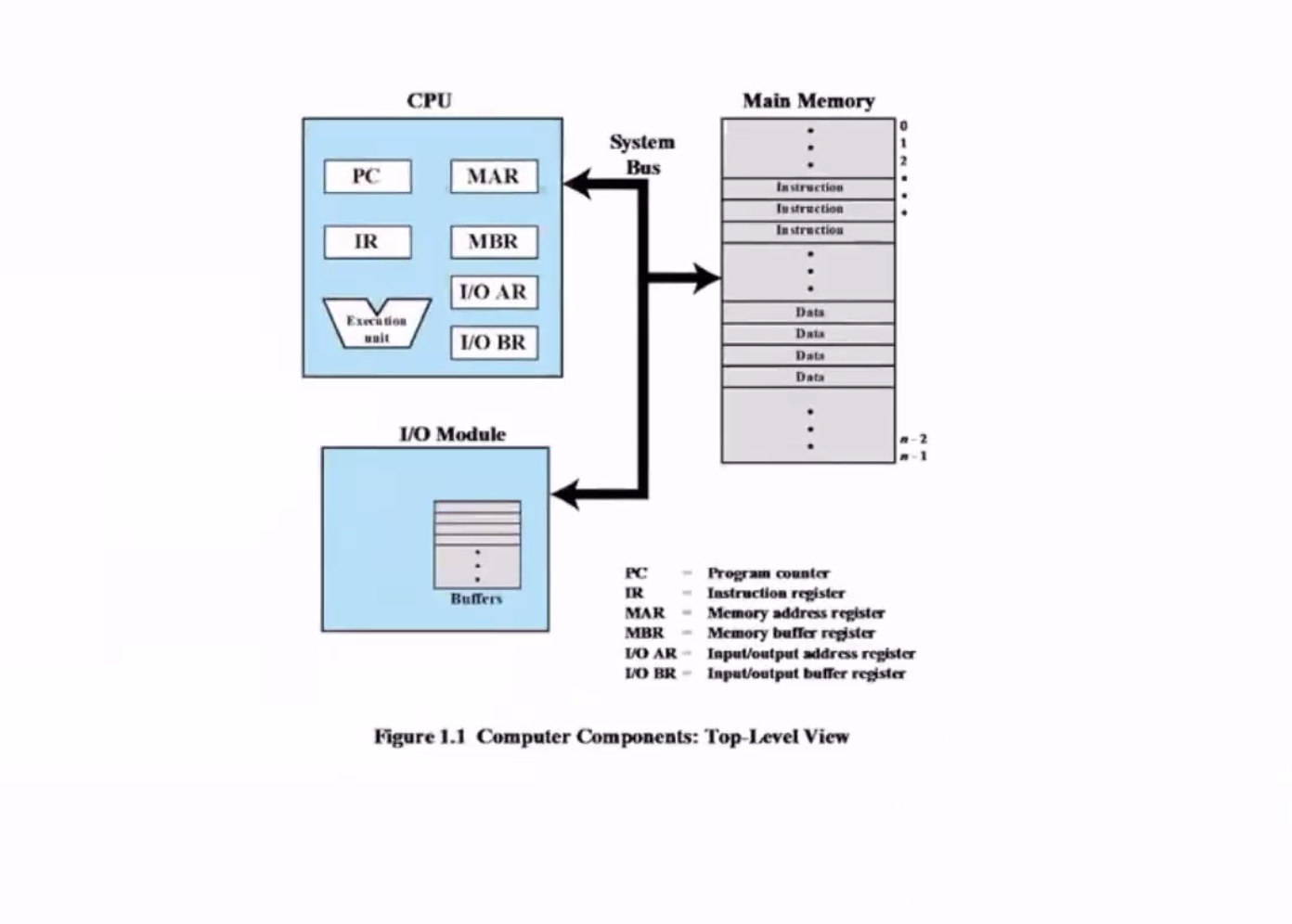
- PC = program counter, the address of the next instruction
- IR = instruction register, the address of the current instruction
- MAR = memory address register, address of the next memory IO
- MBR = memory buffer register, actual data to be read/written to/from memory
- I/O AR = input output address
- I/O BR = input output buffer register, the data
Memory is an array of bytes, each with its own address.

I/O devices constantly content for memory cycles, so every controller has a local buffer.
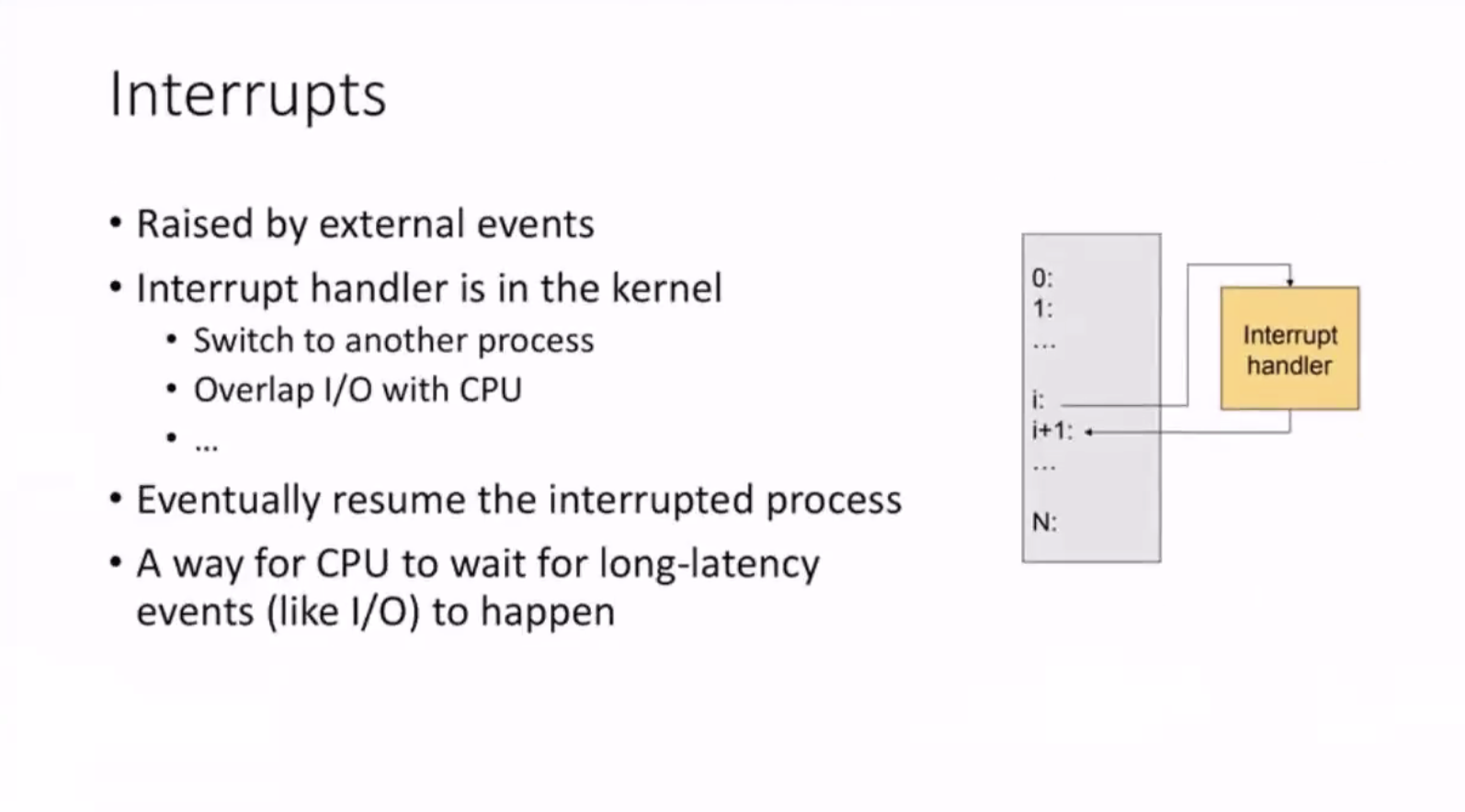
Interrupts #
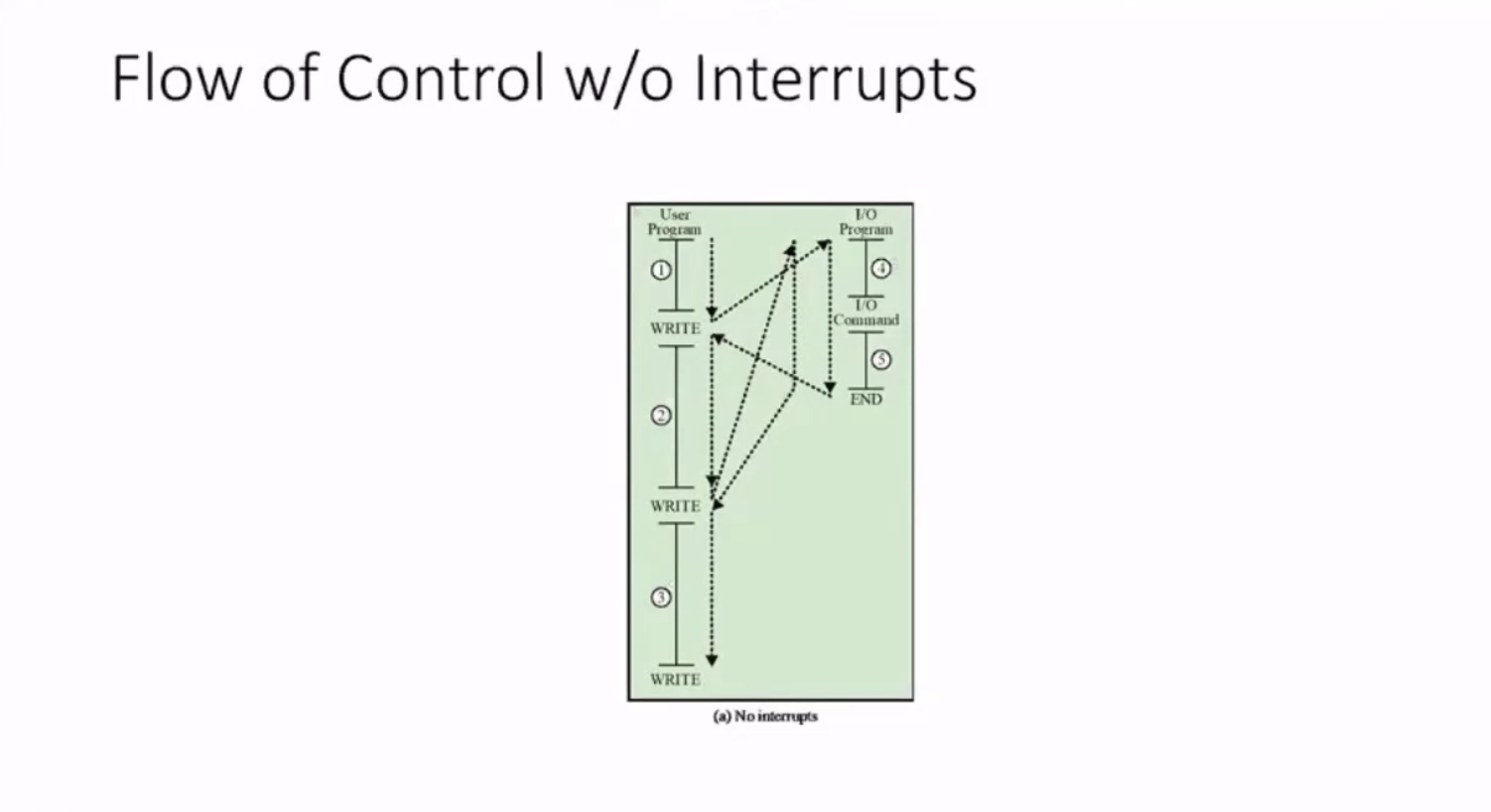
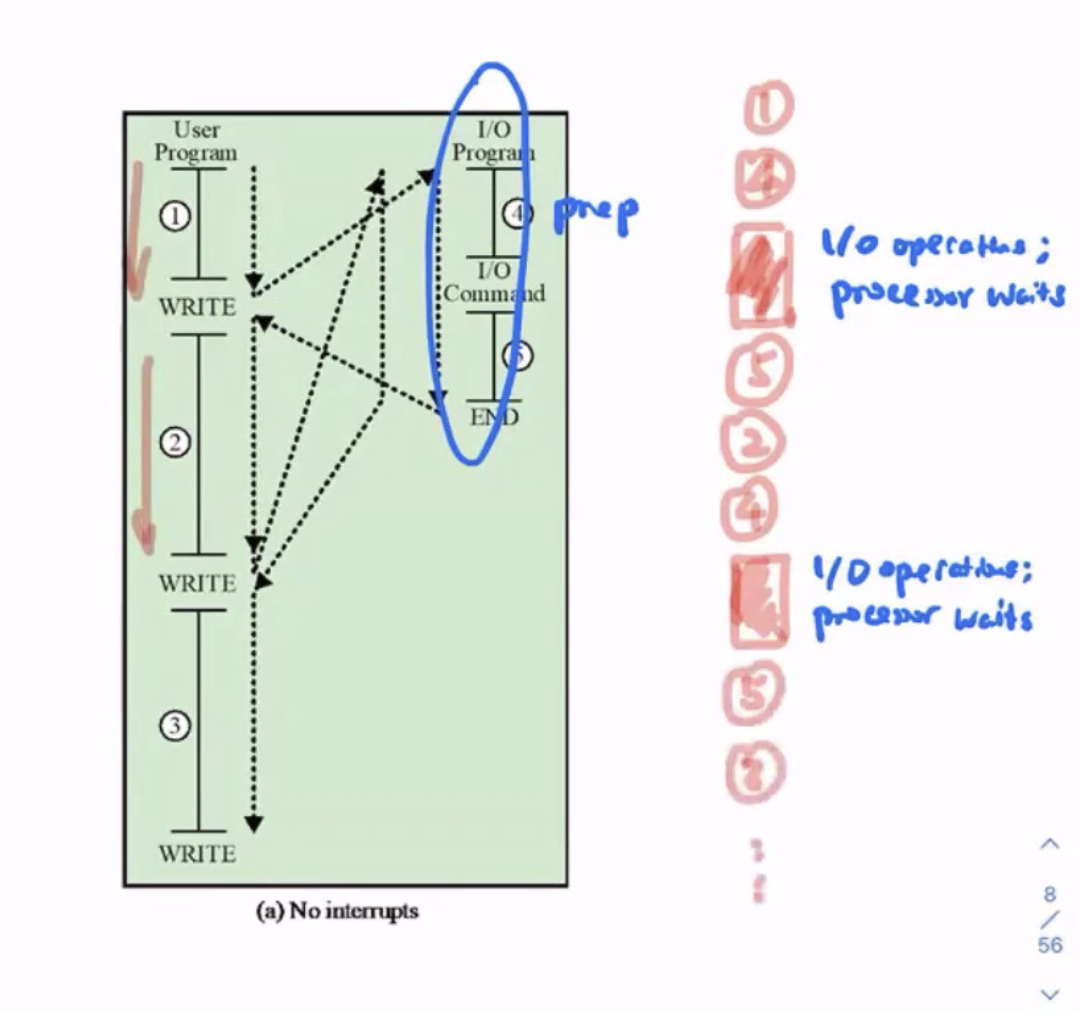
Flow control with interrupts #
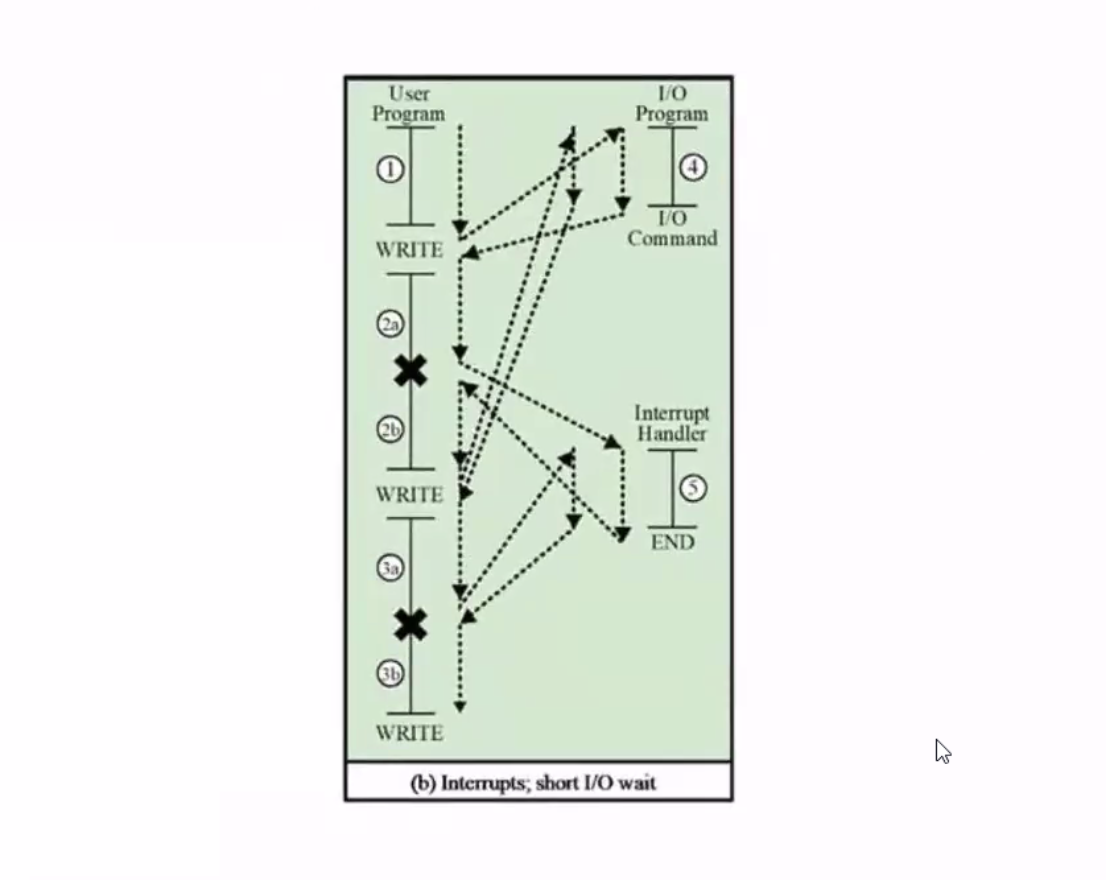
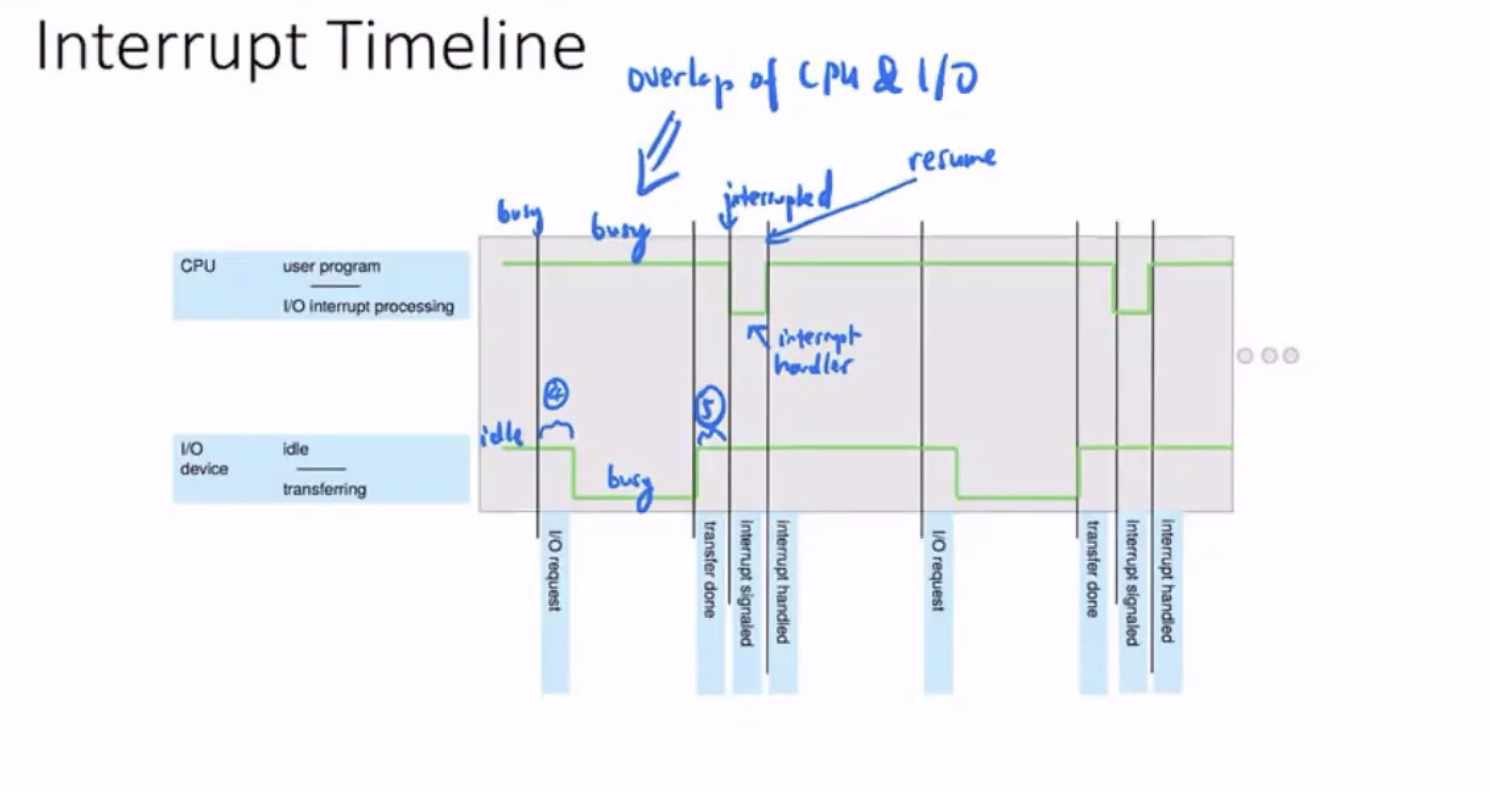
Here, the IO operation is concurrent with CPU processing.
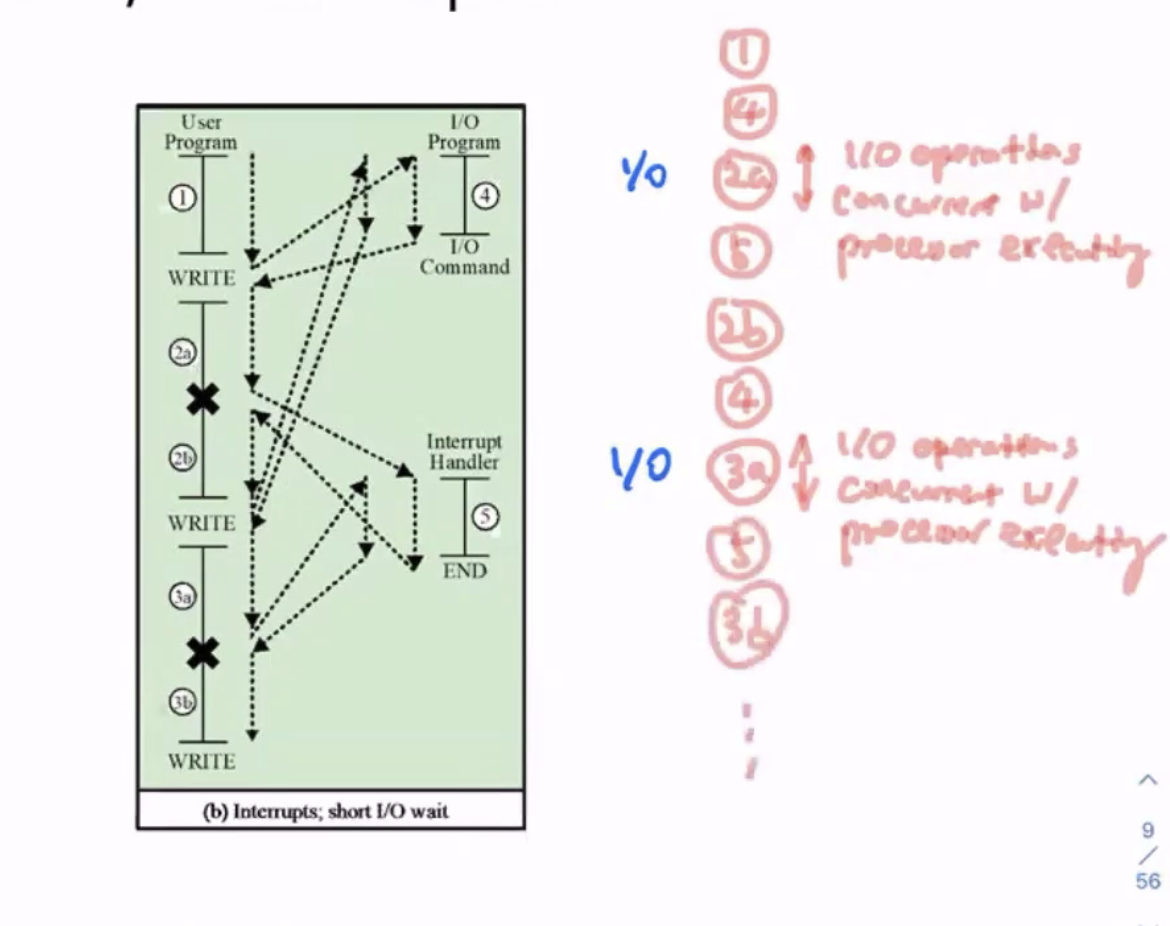
Interrupts allow overlap of CPU and IO operations.
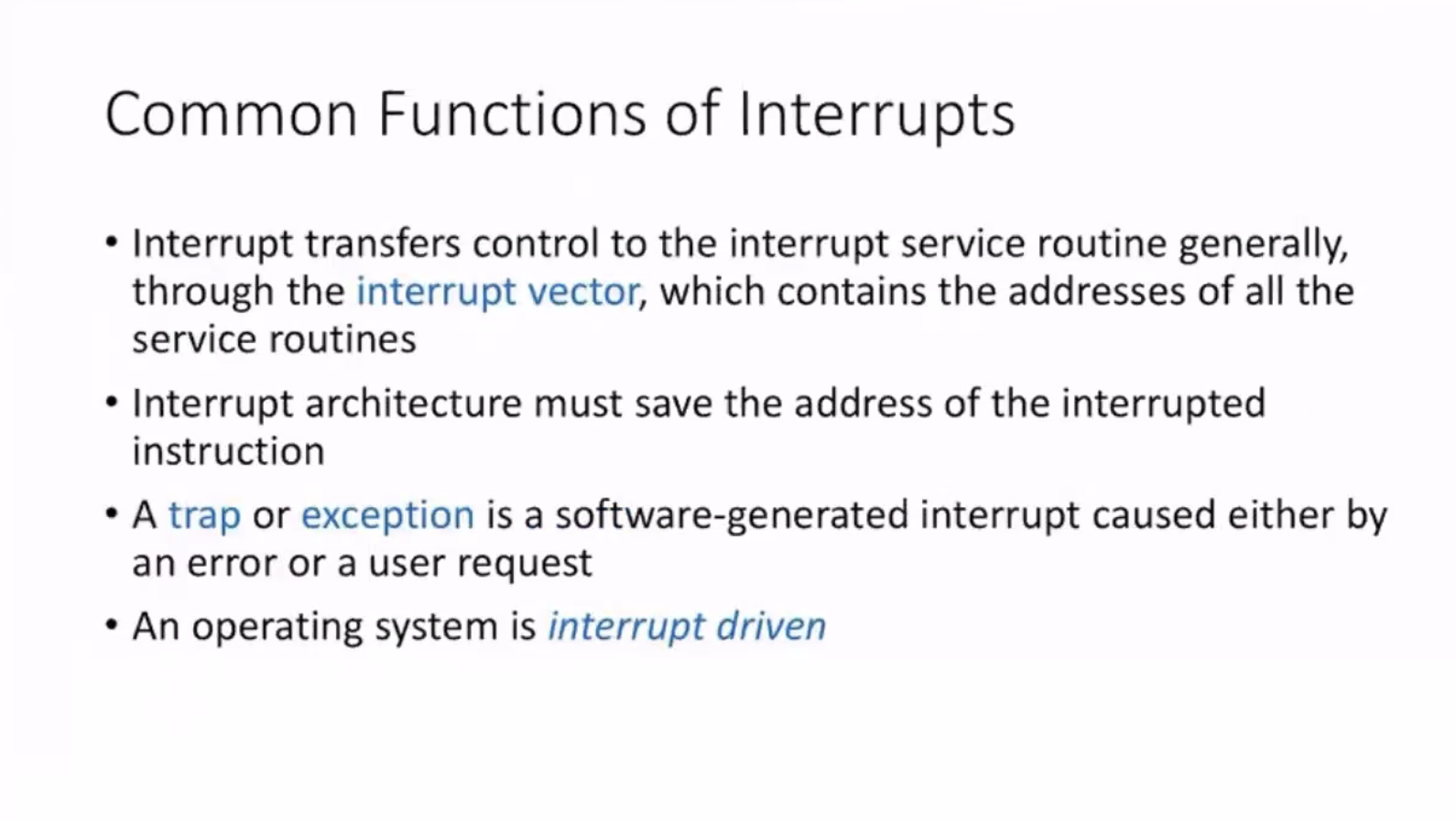
The interrupt vector is just a lookup table.

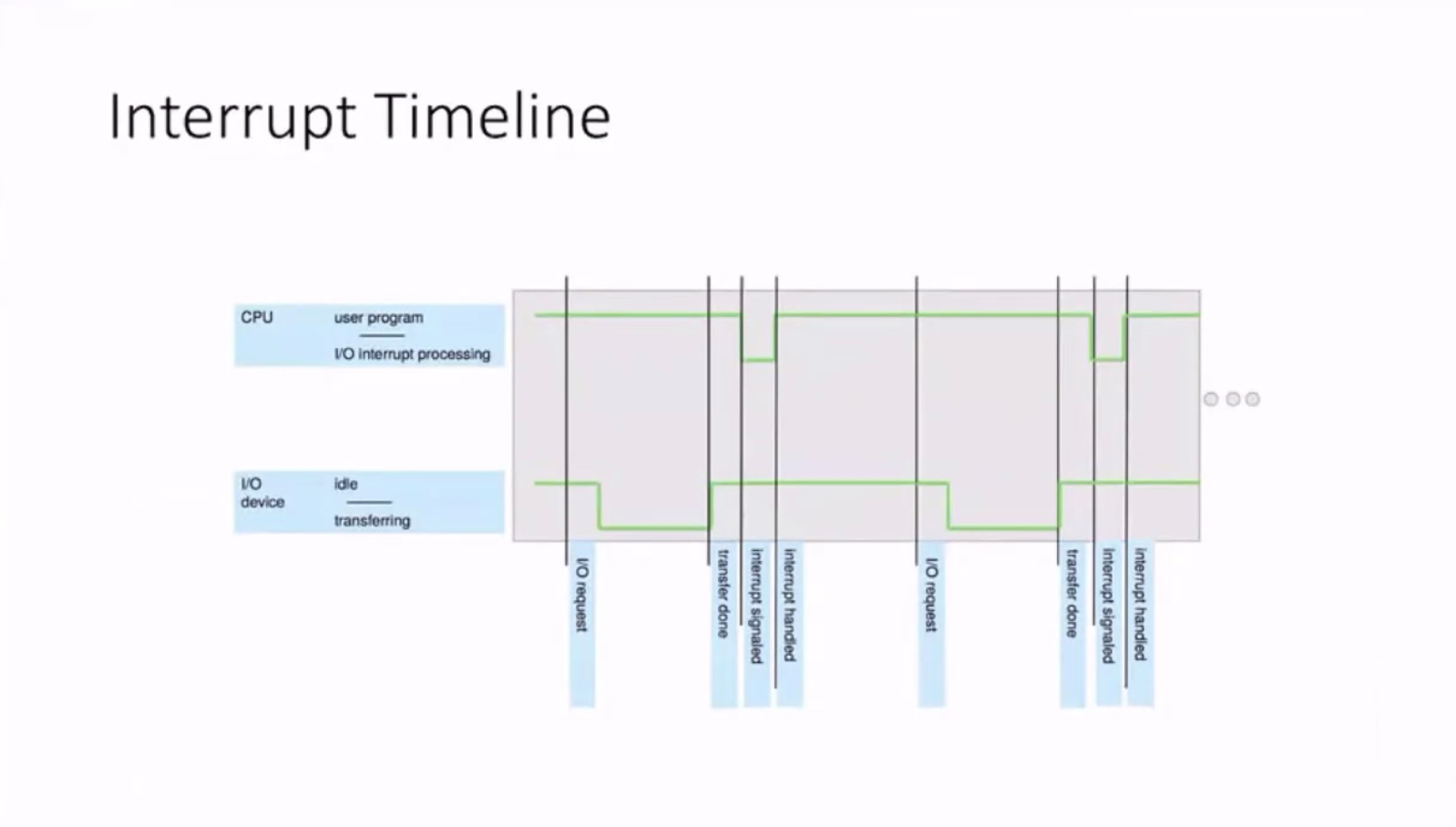
We allow the overlap of CPU and IO operations.