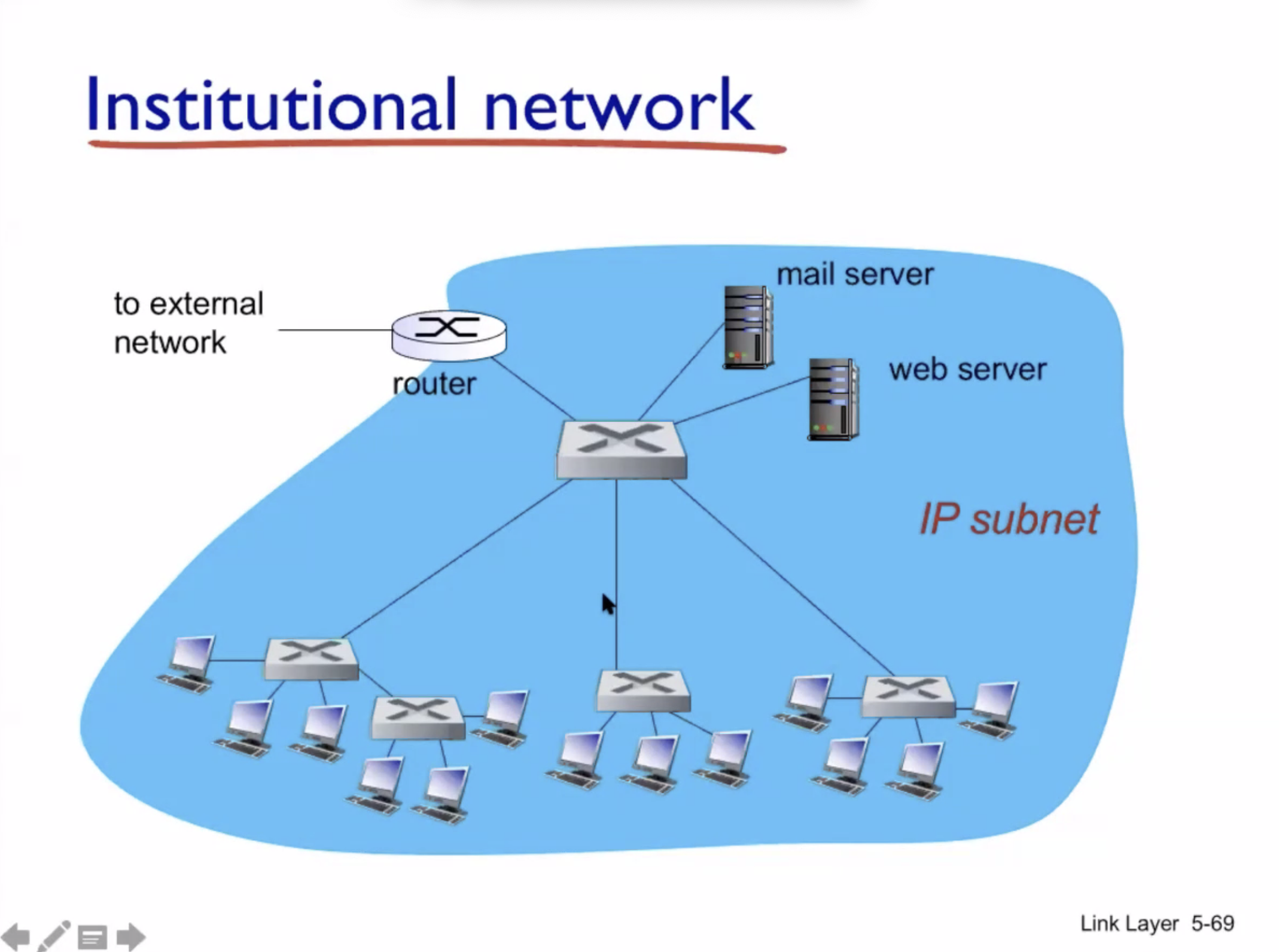
LAN cont. #
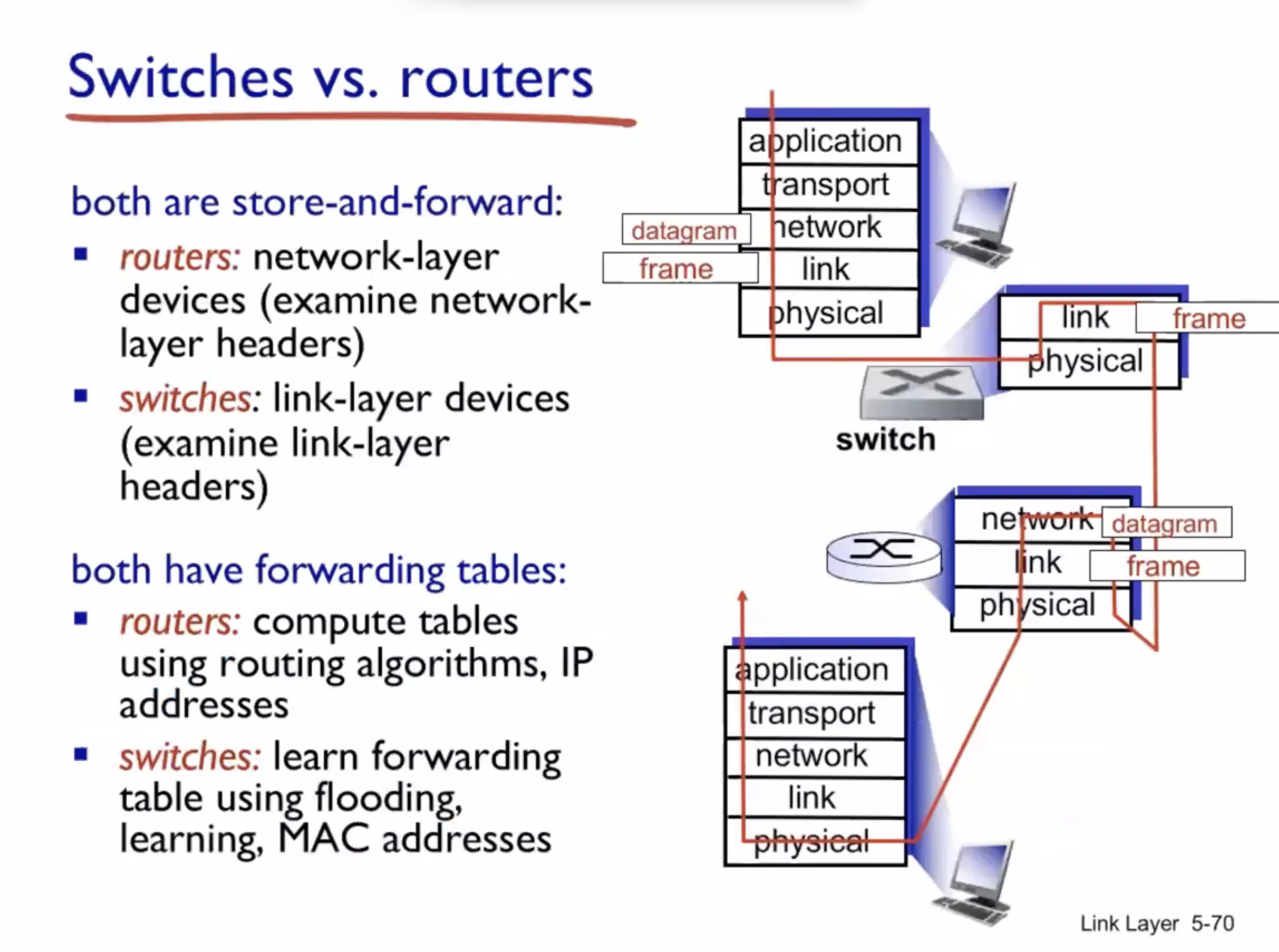
Switches vs routers #
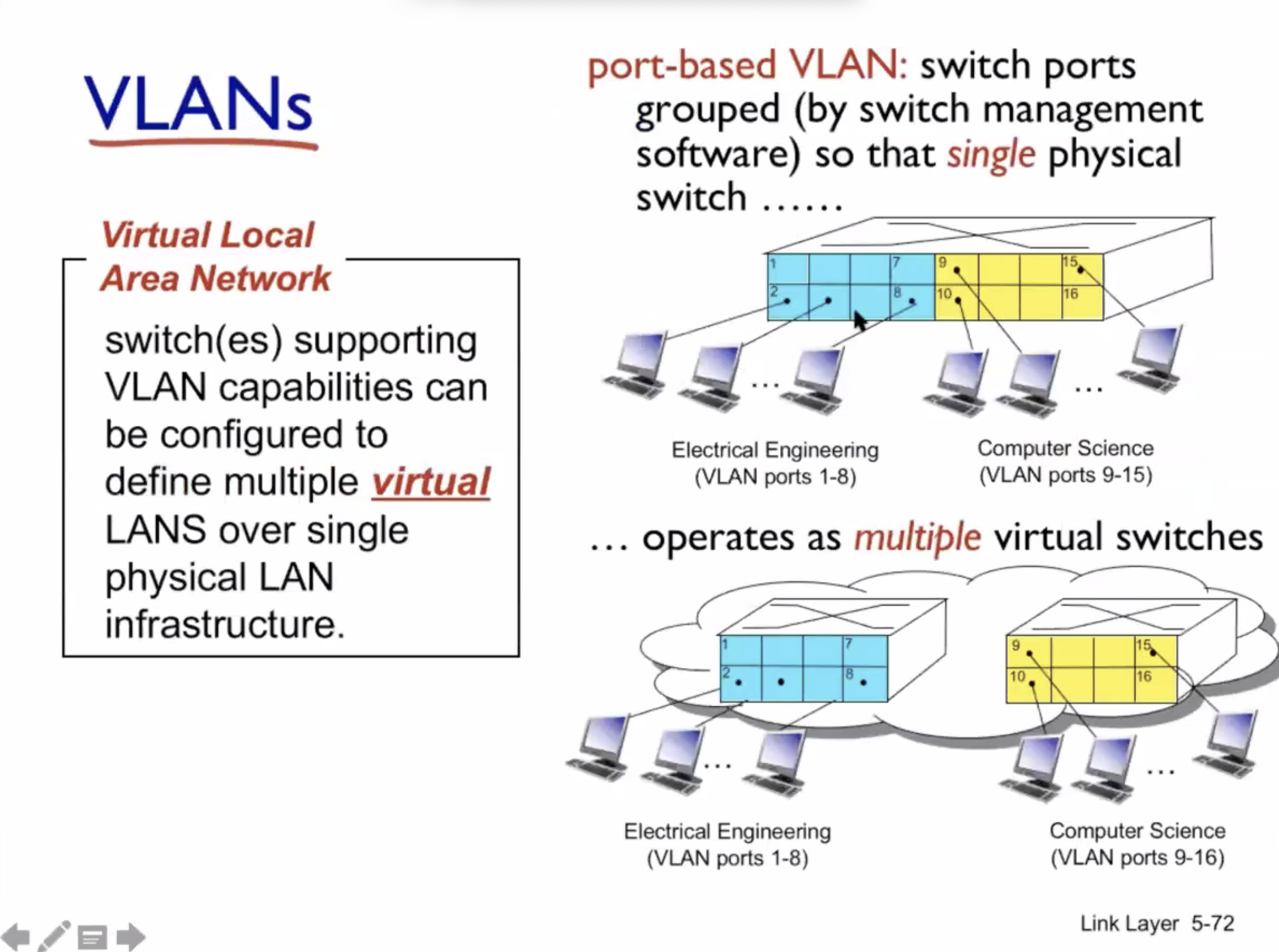
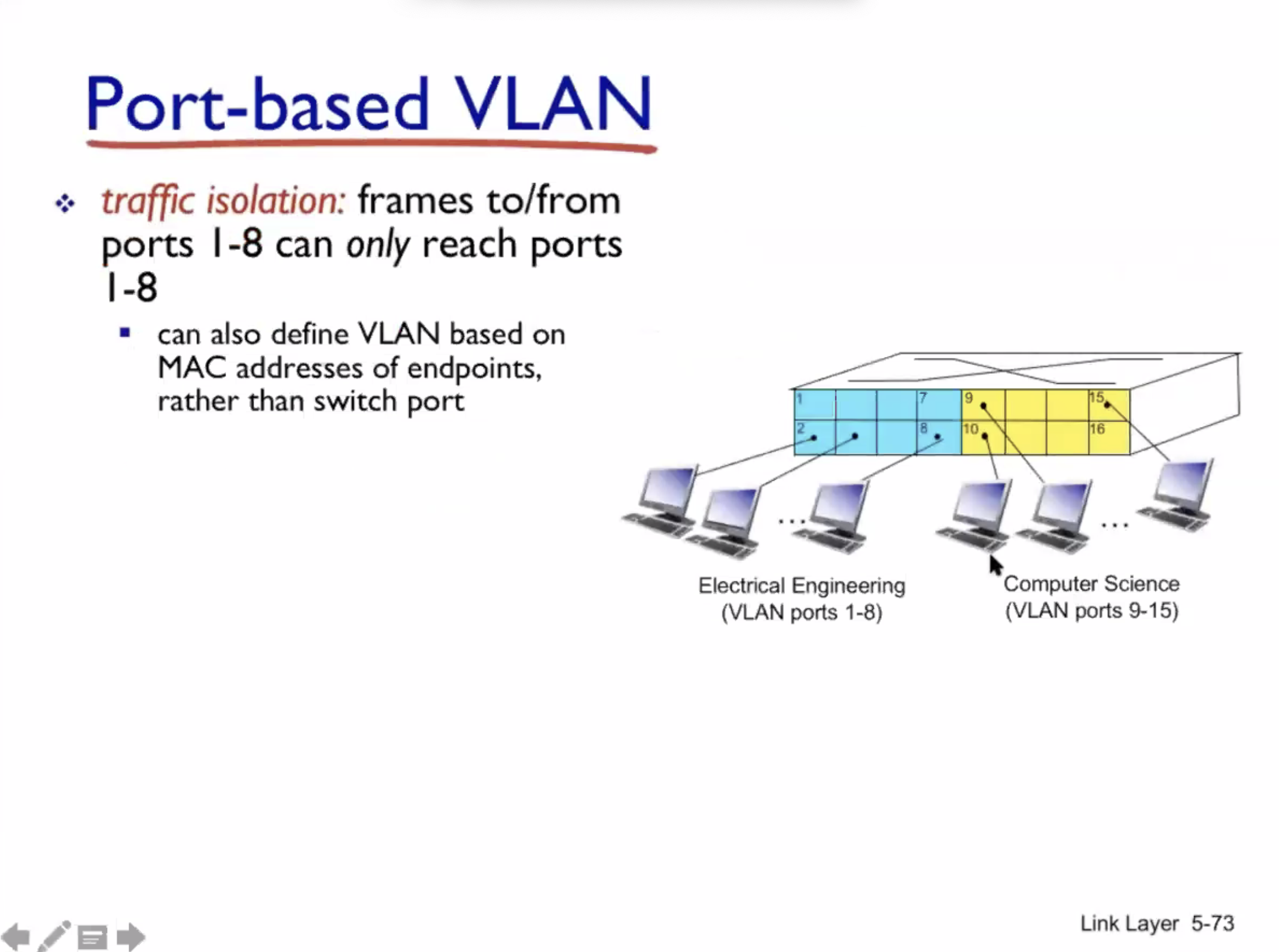
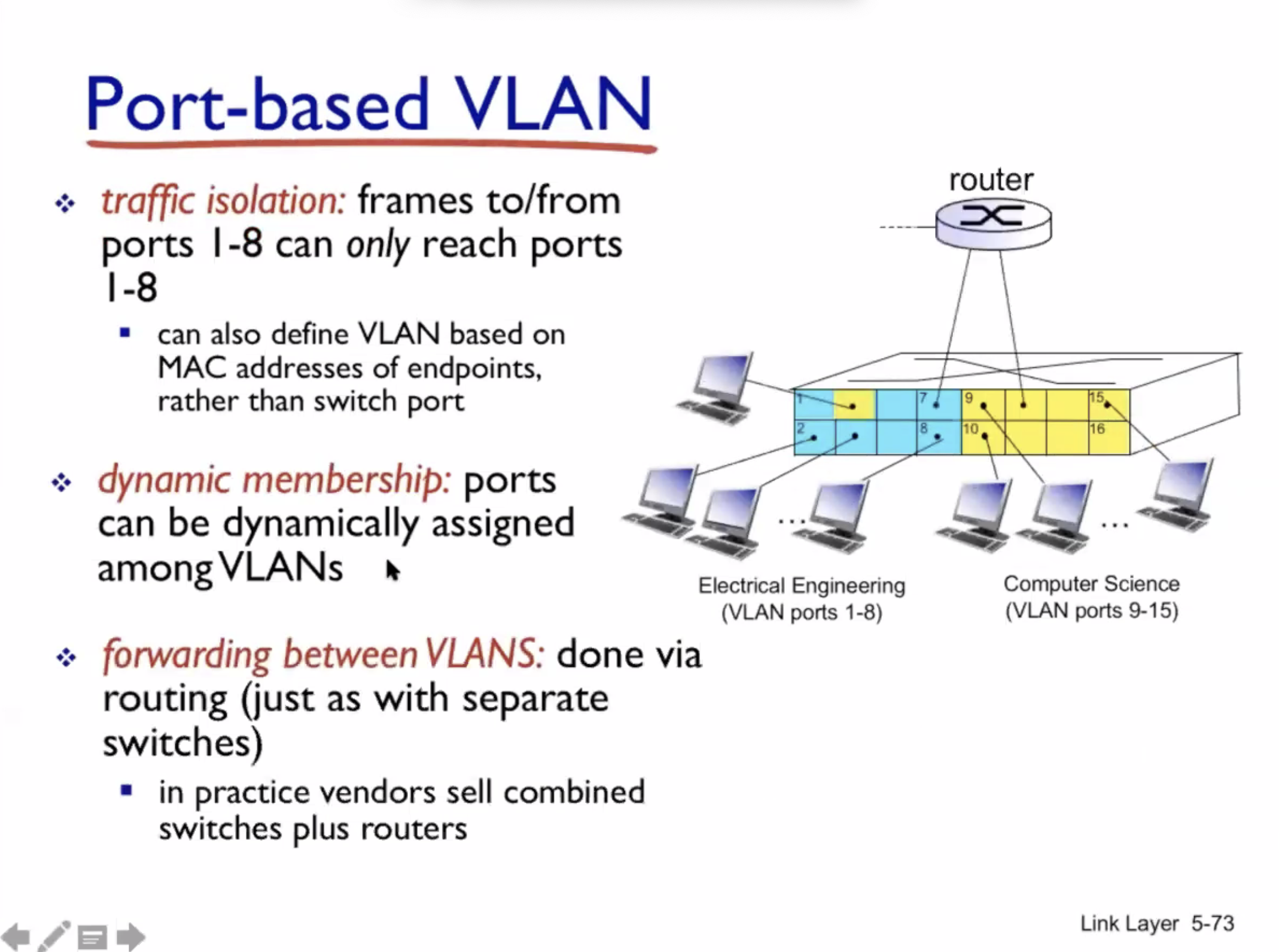
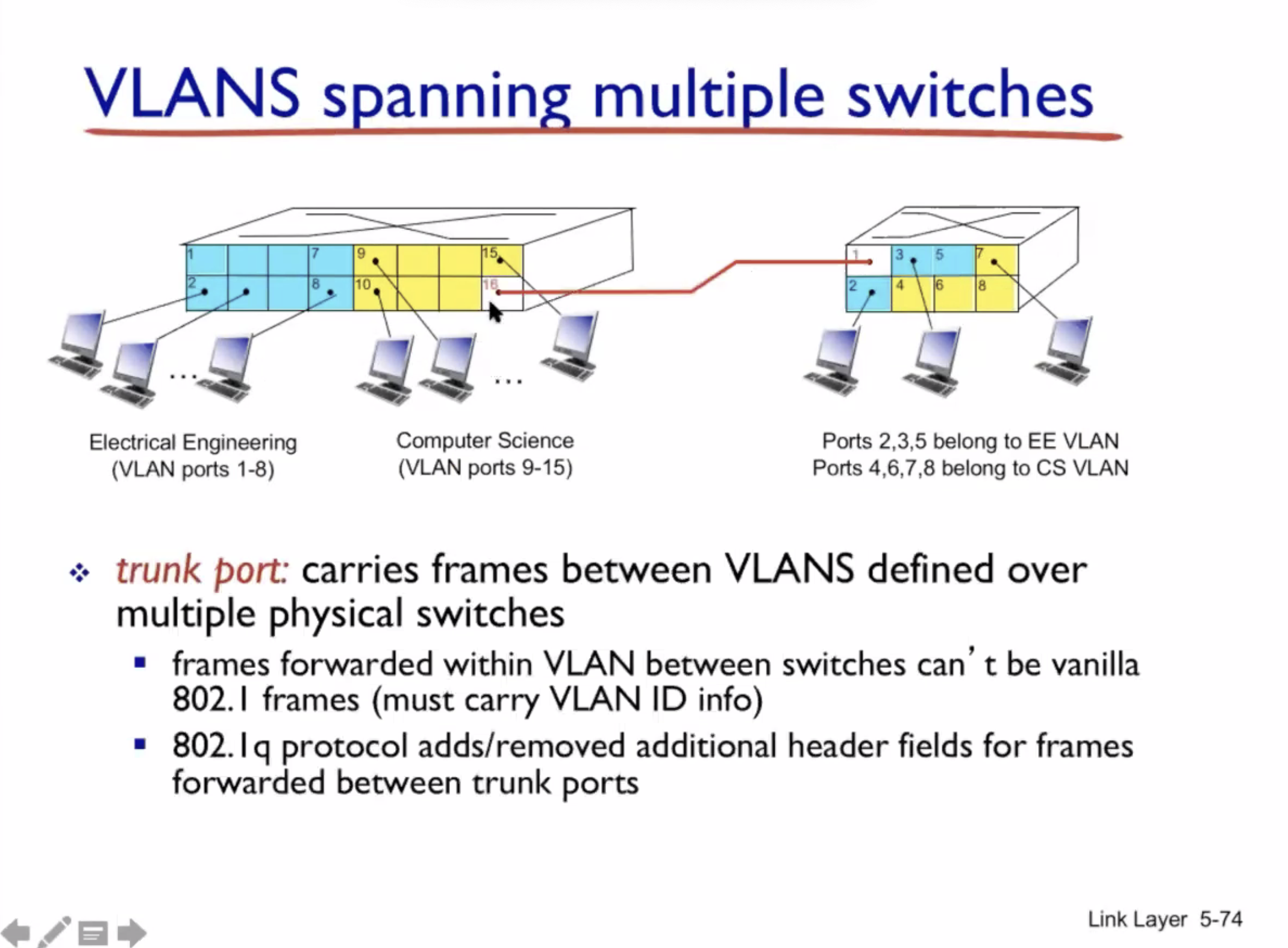
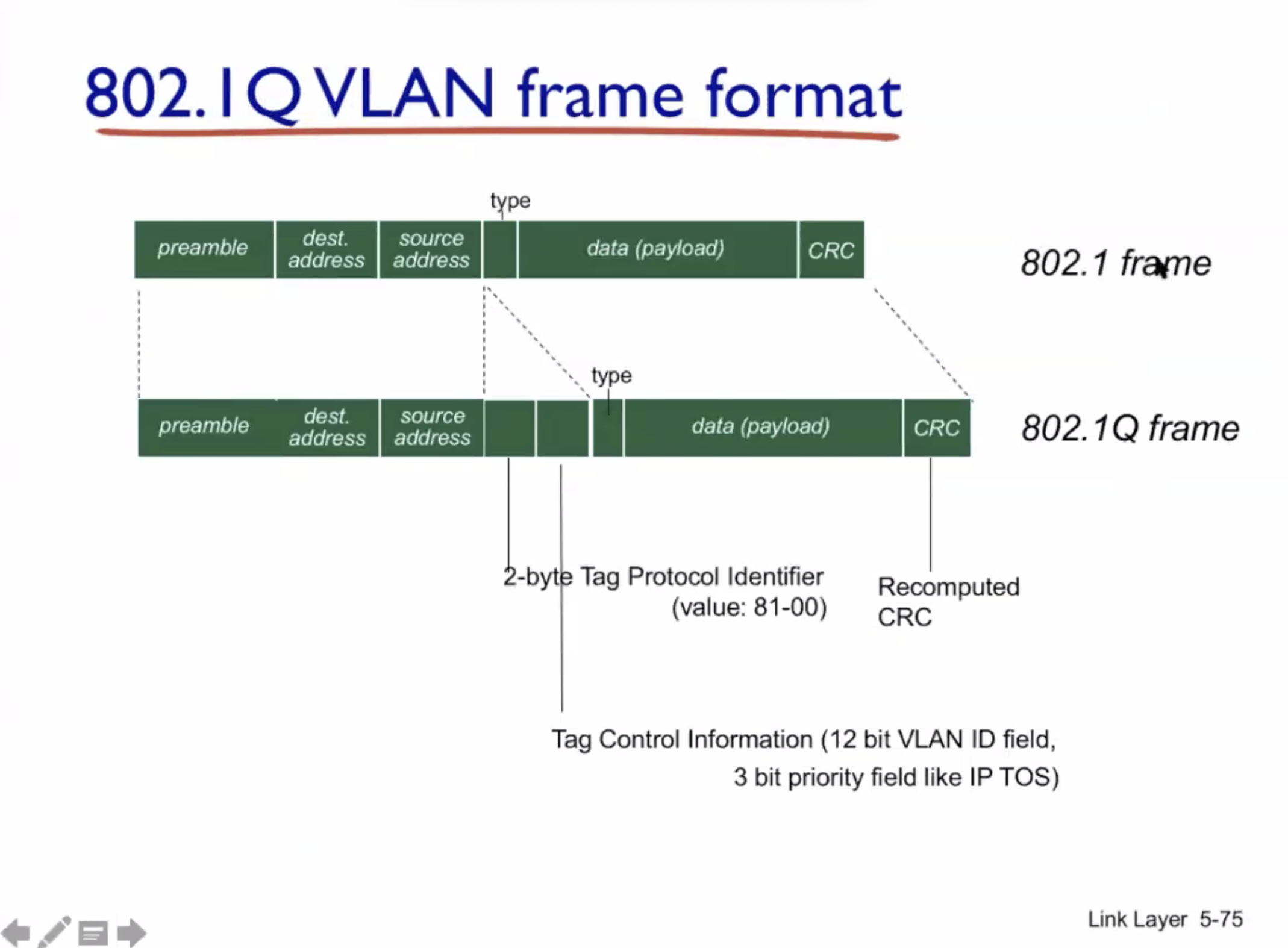
VLAN #
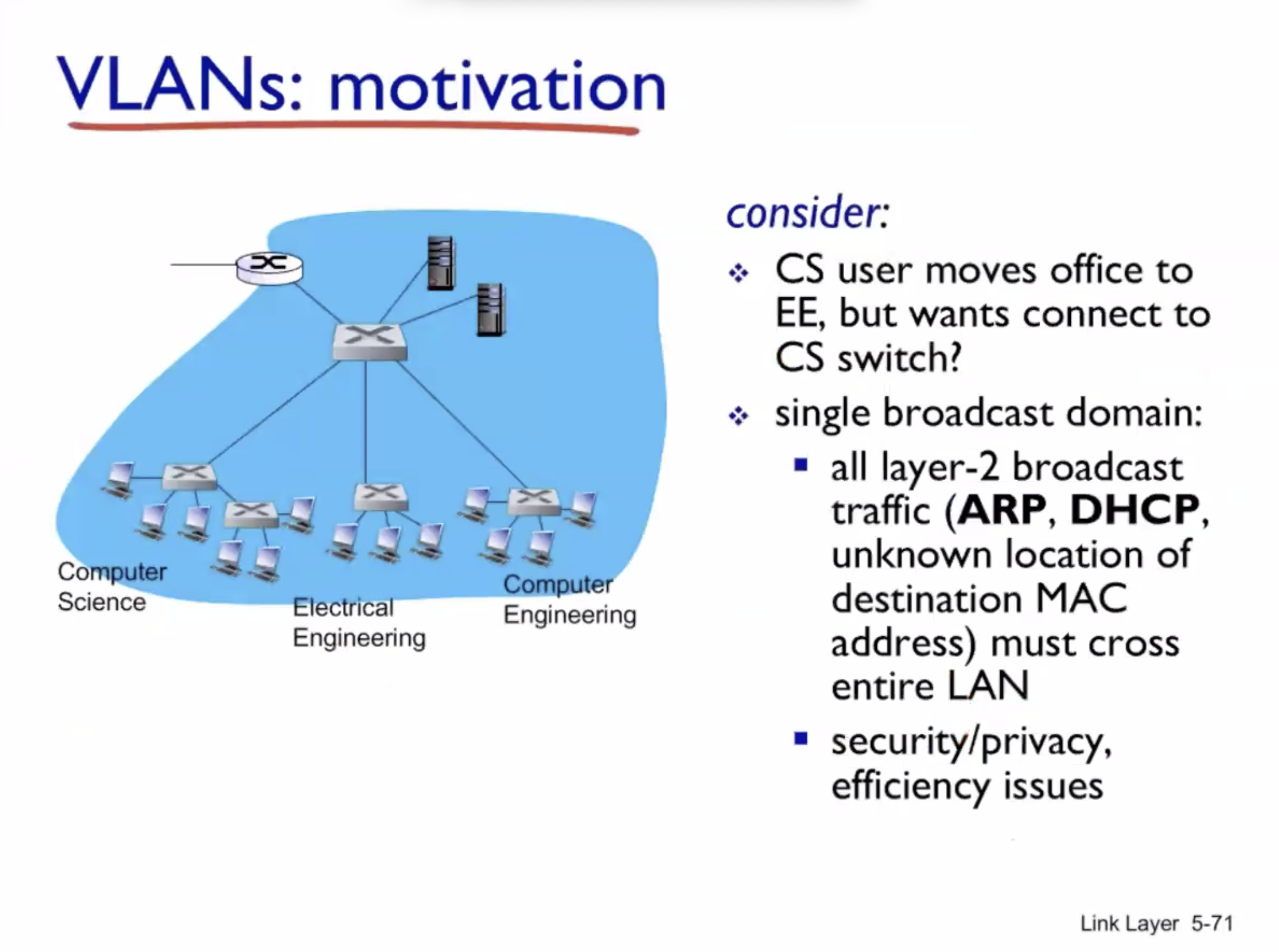
VLAN = virtual local area network
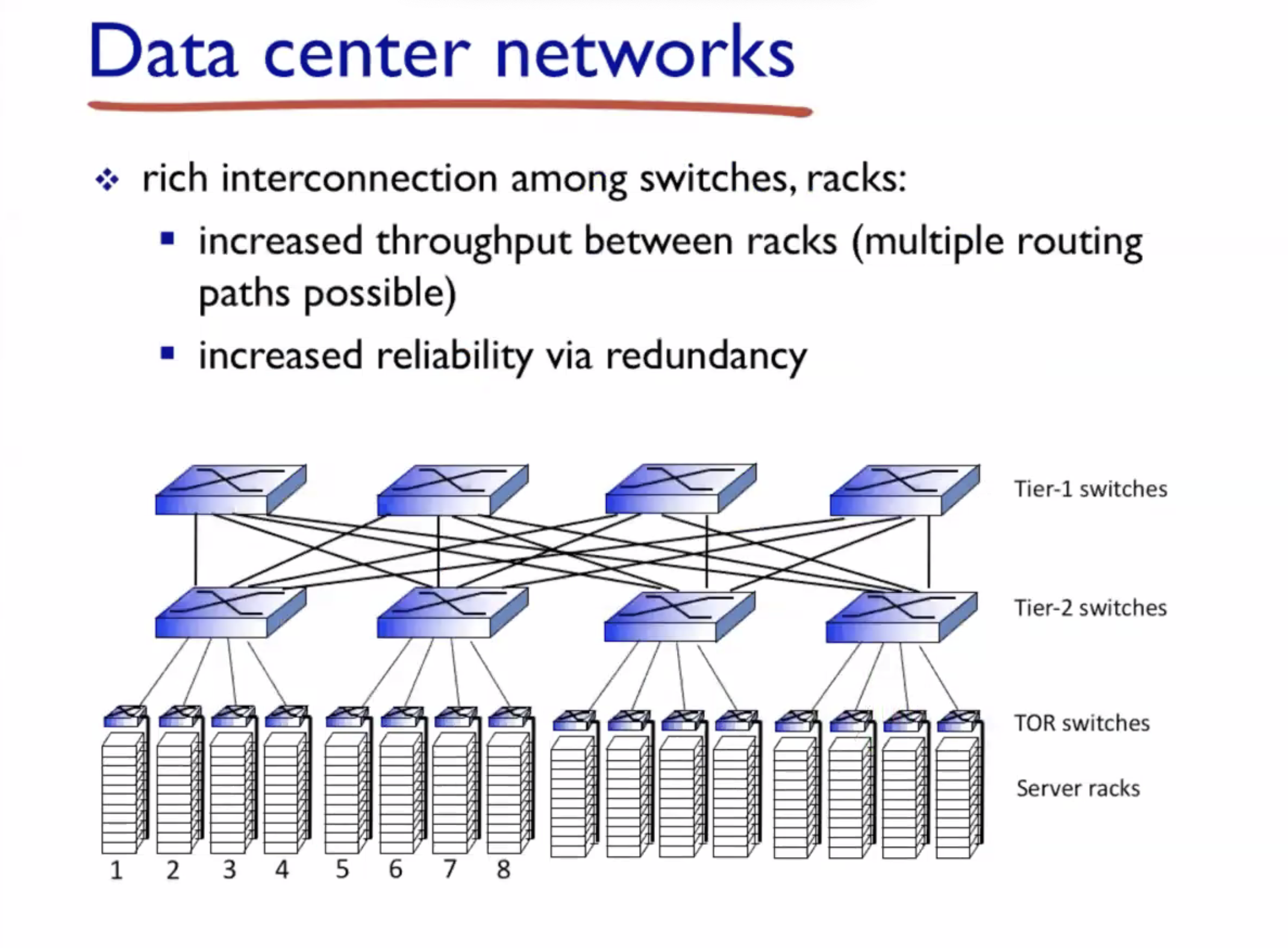
Data center networks #
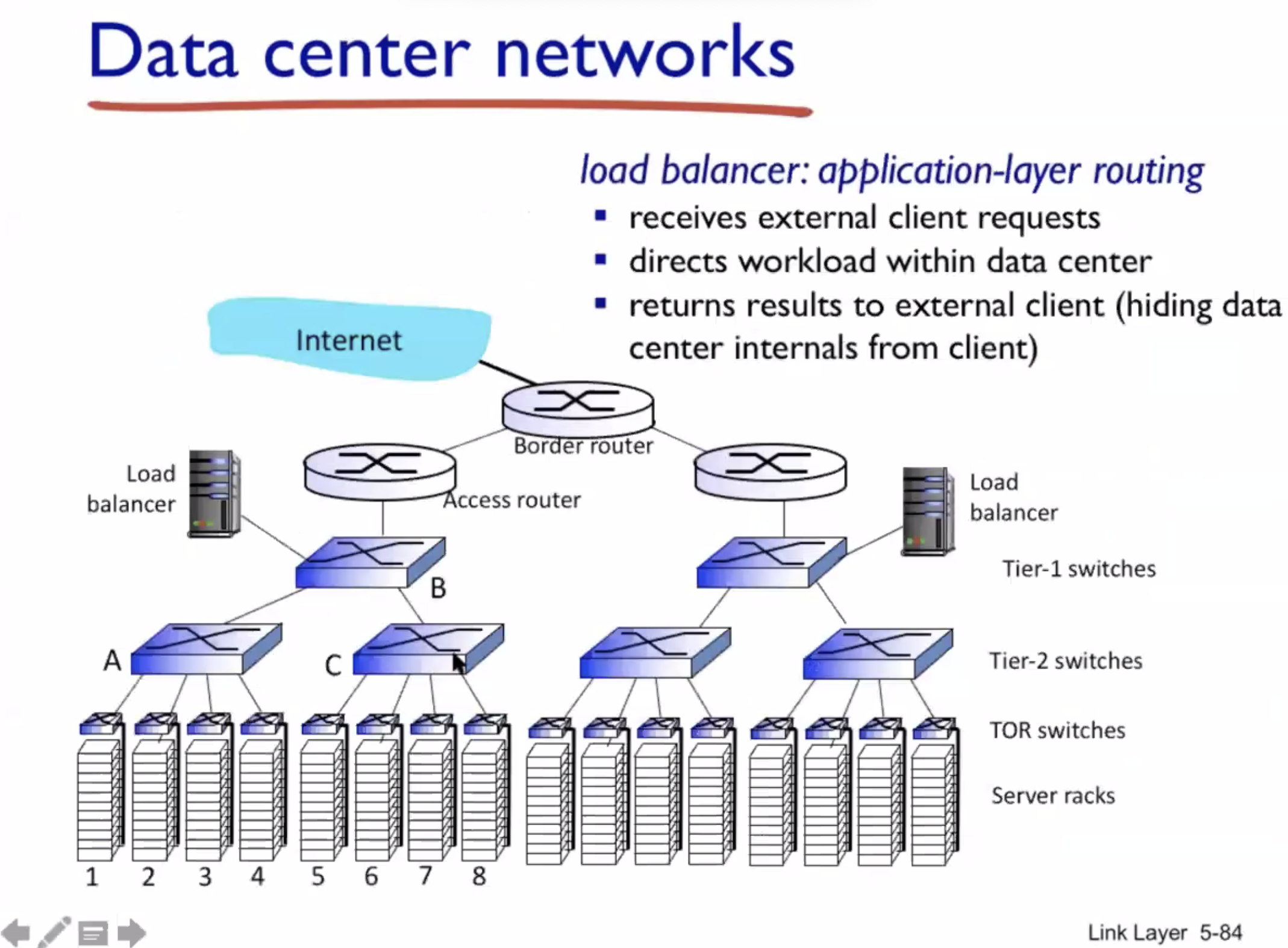
TOR = top of rack
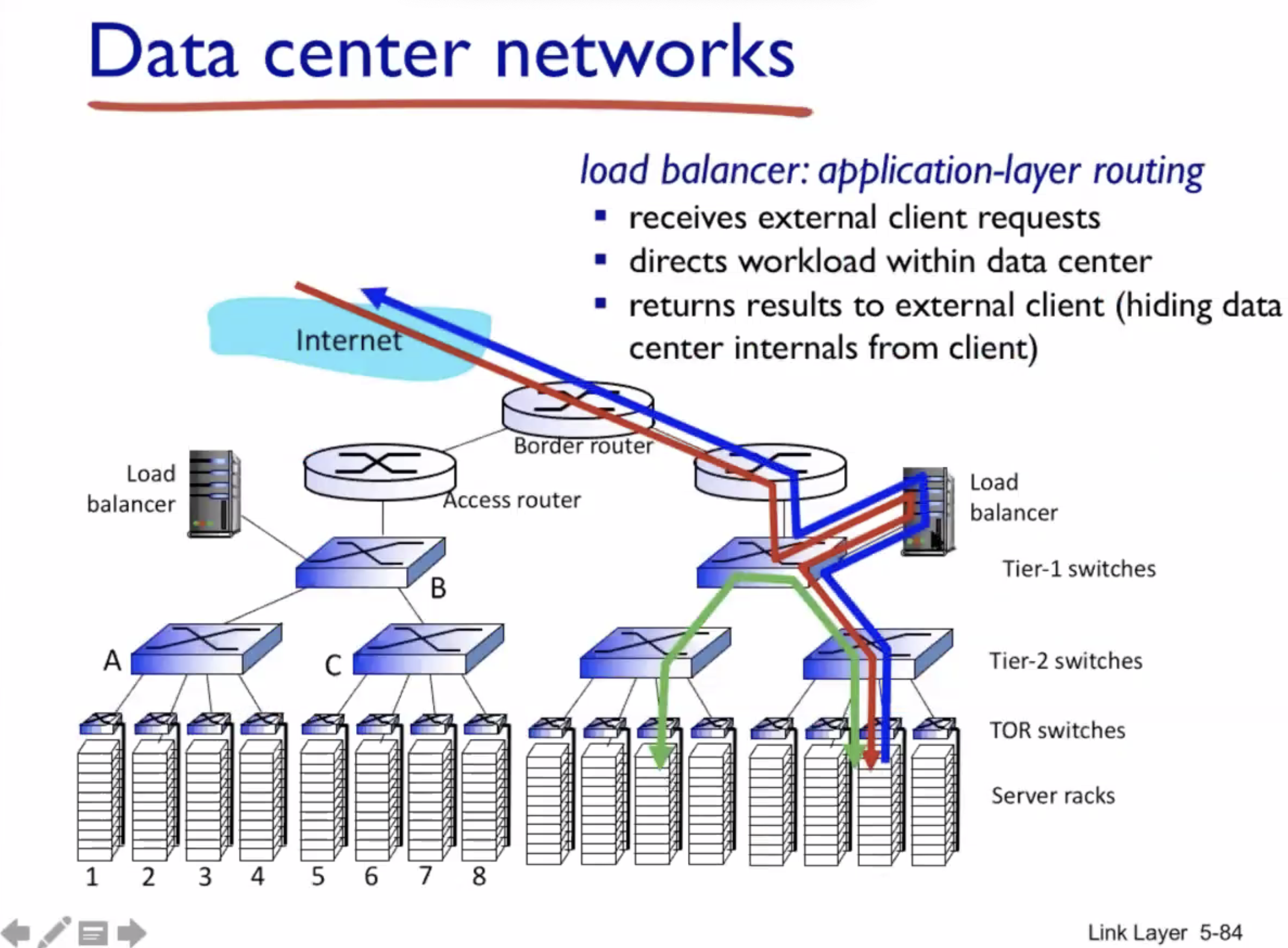
A day in the life of a web request #

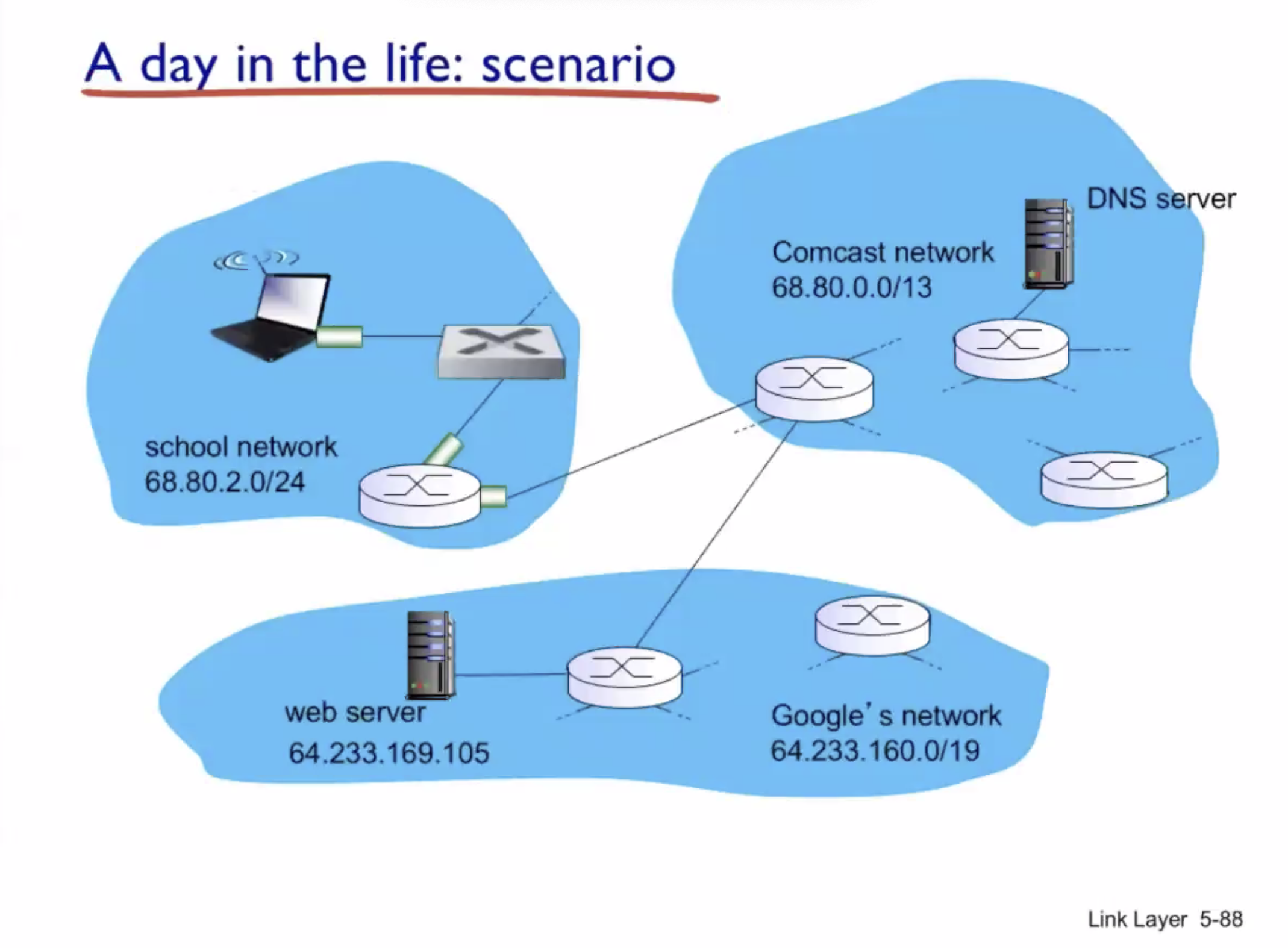
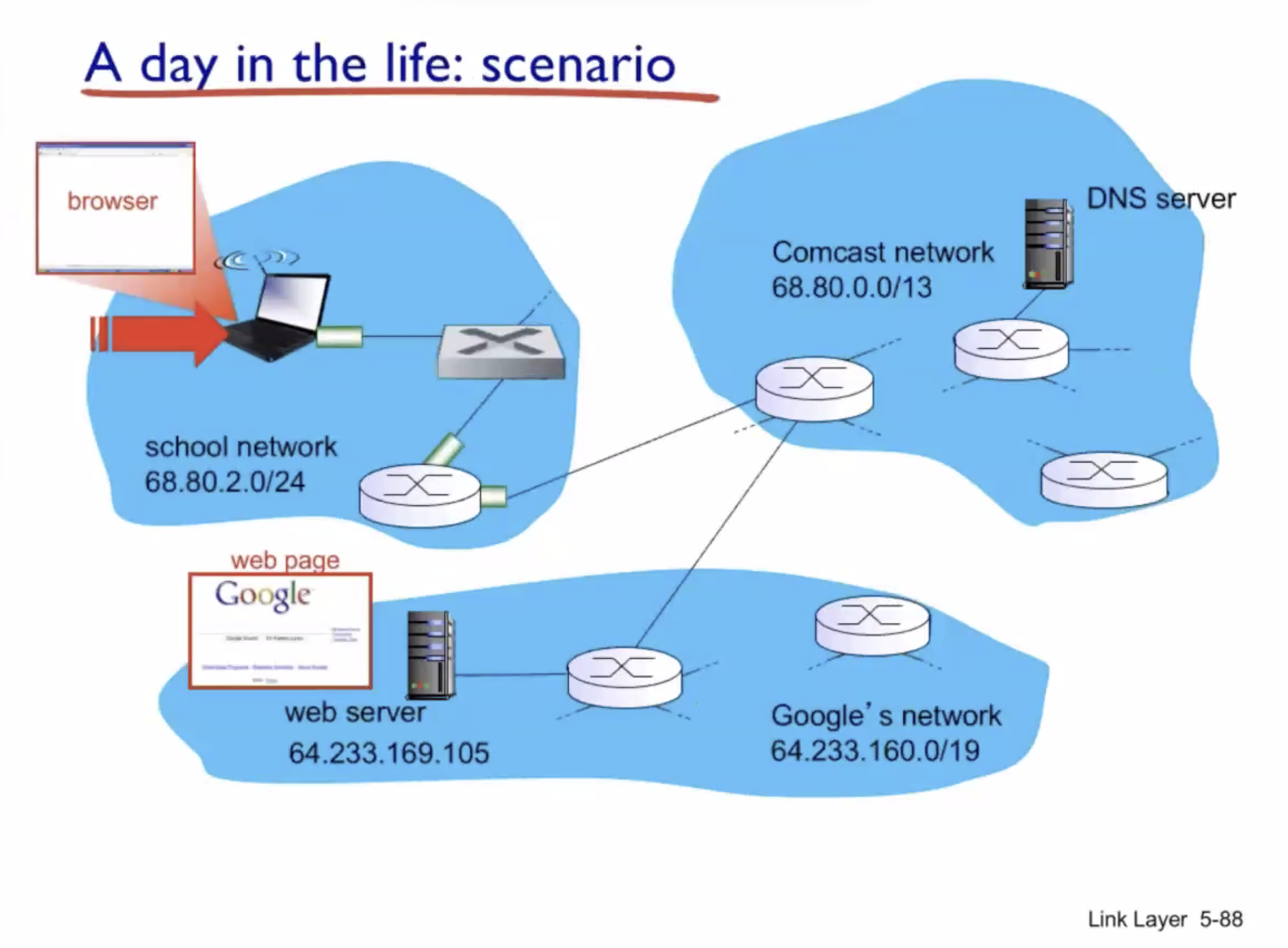
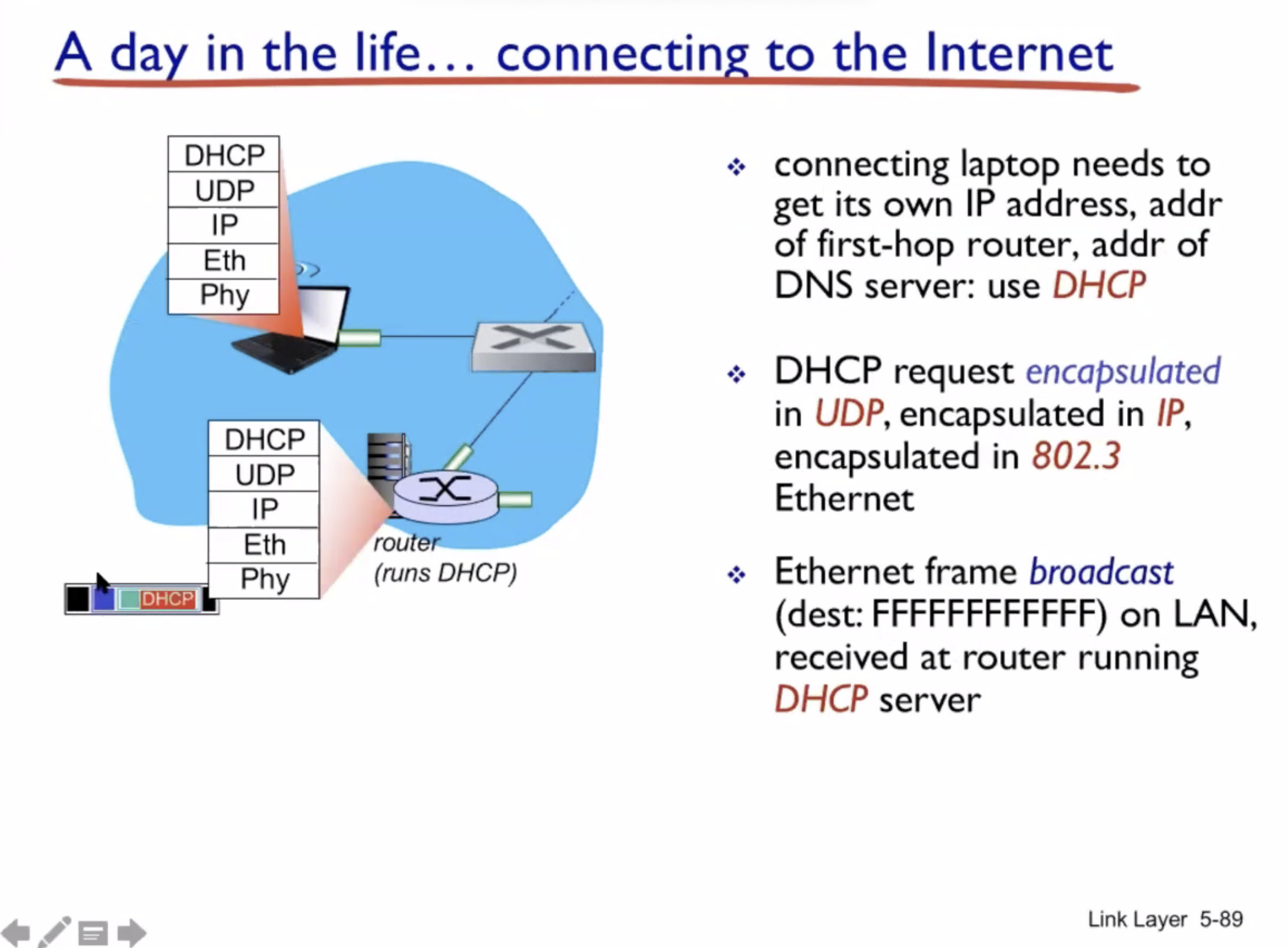
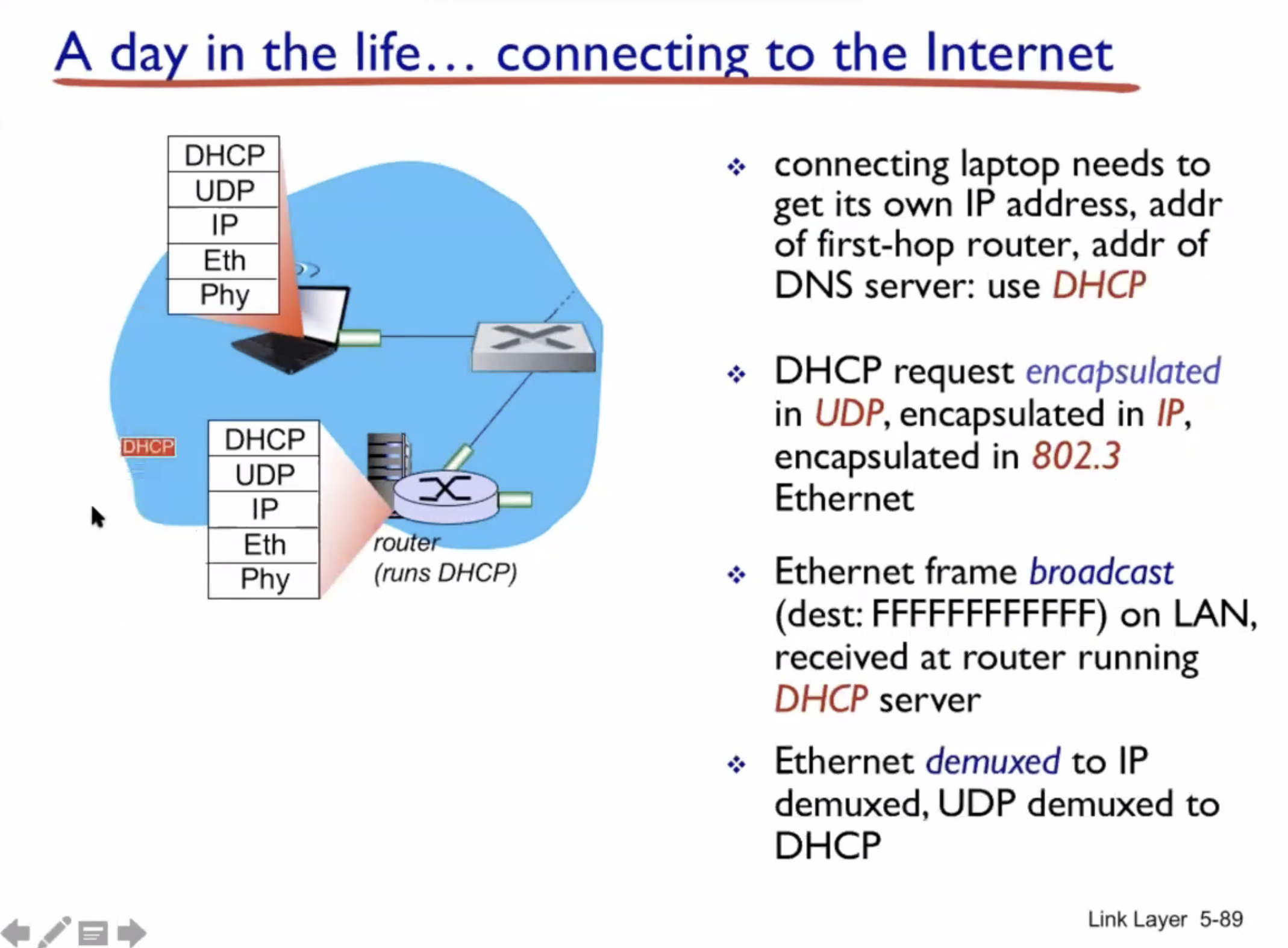
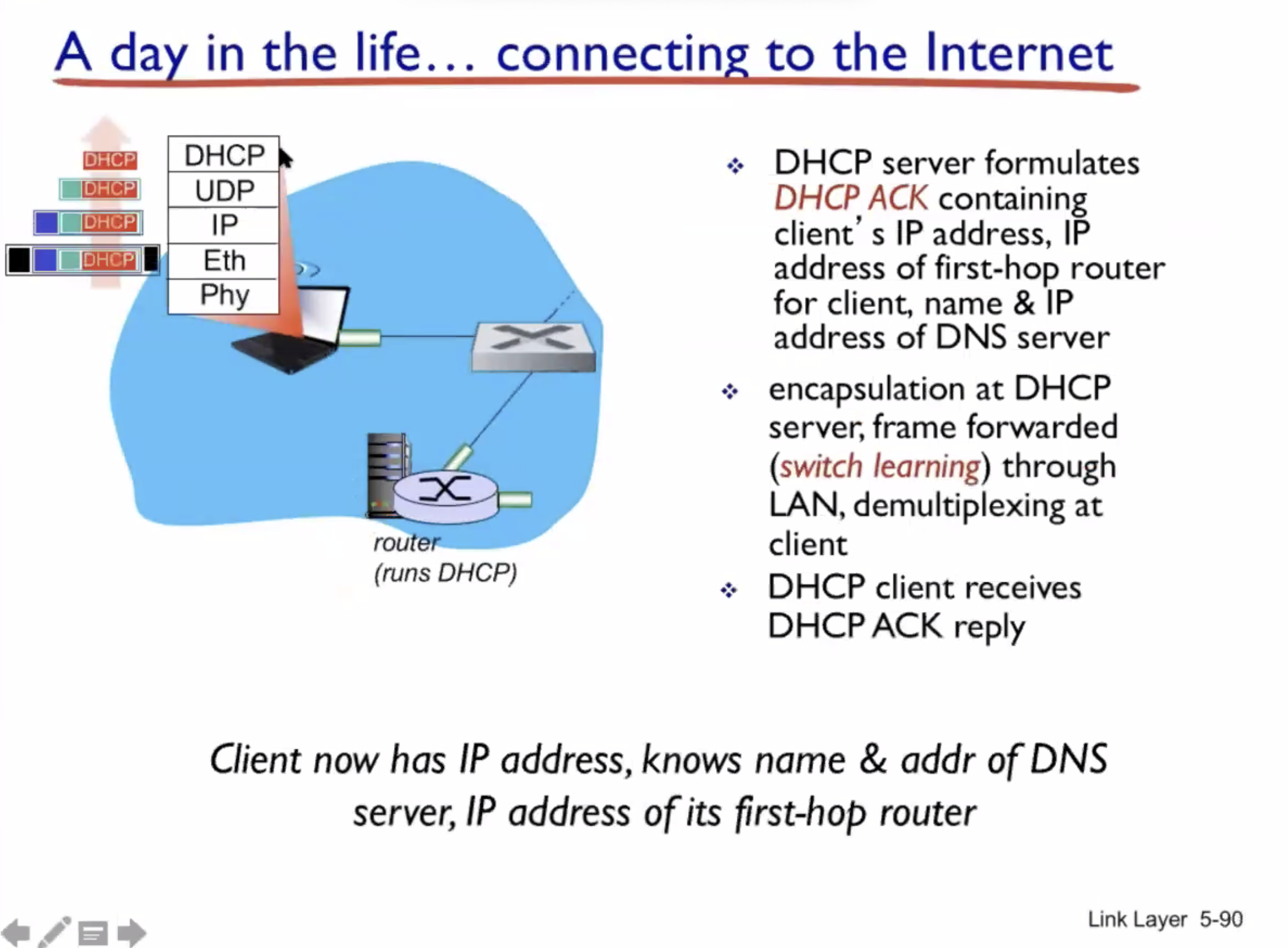
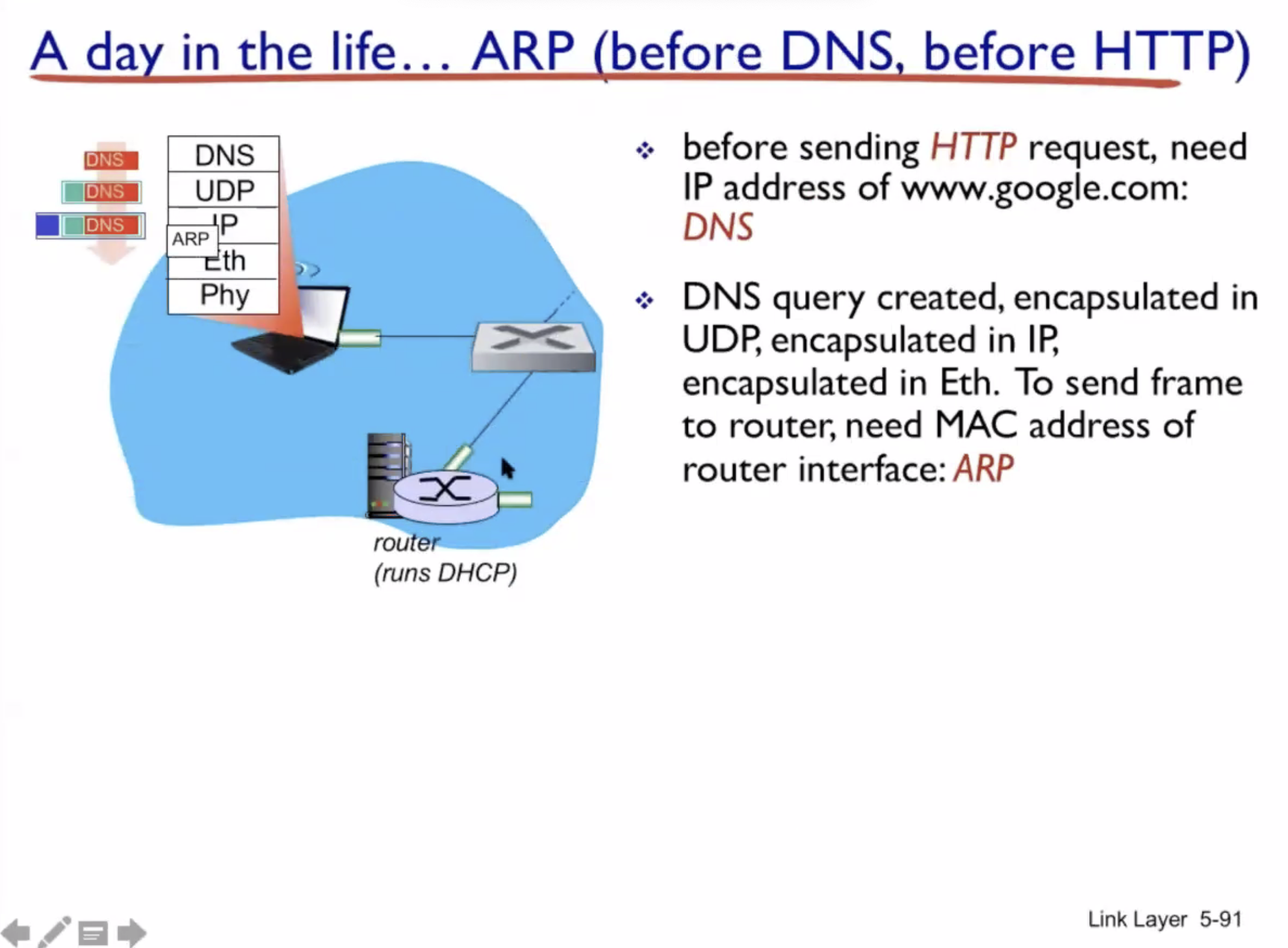
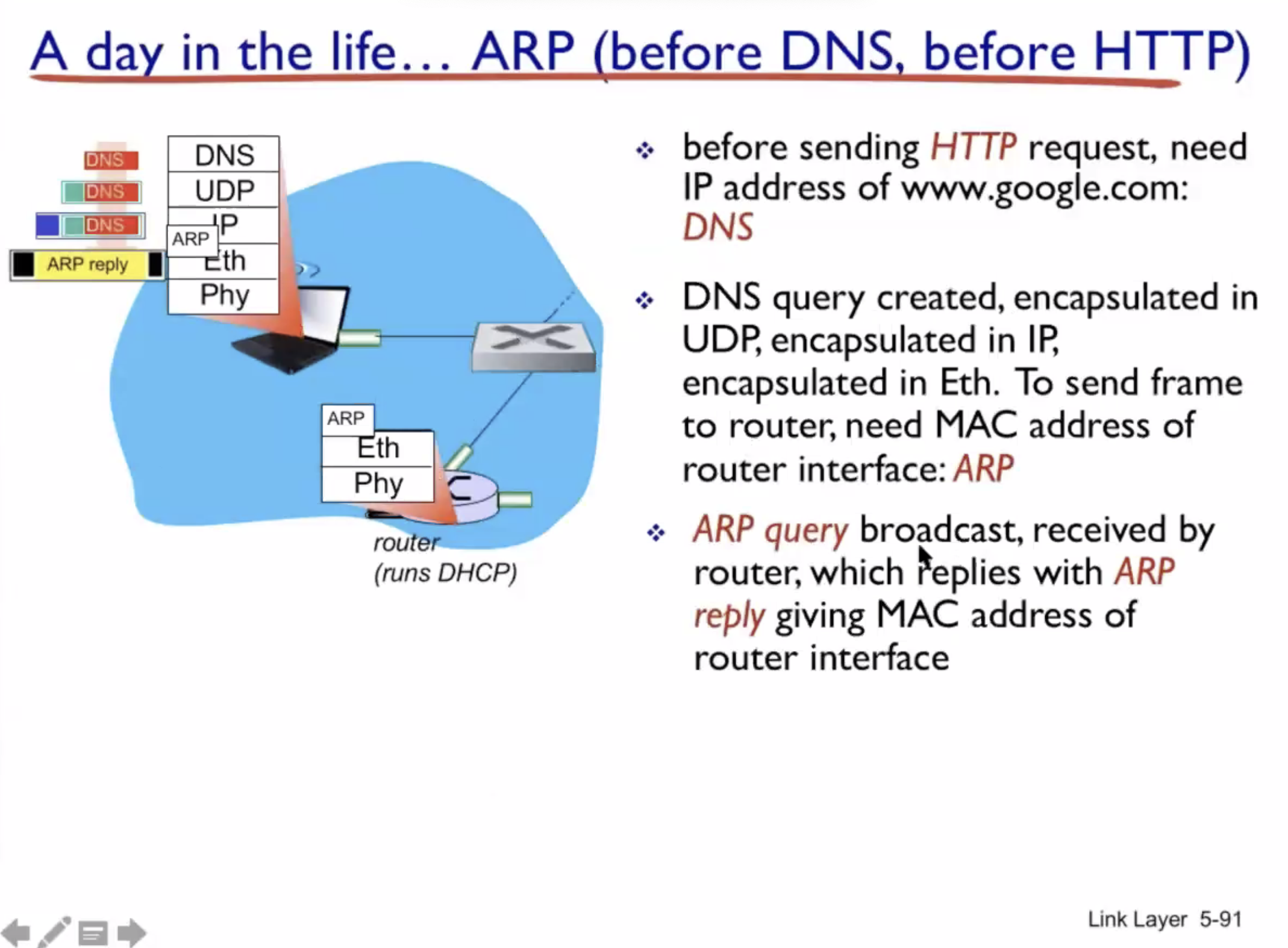
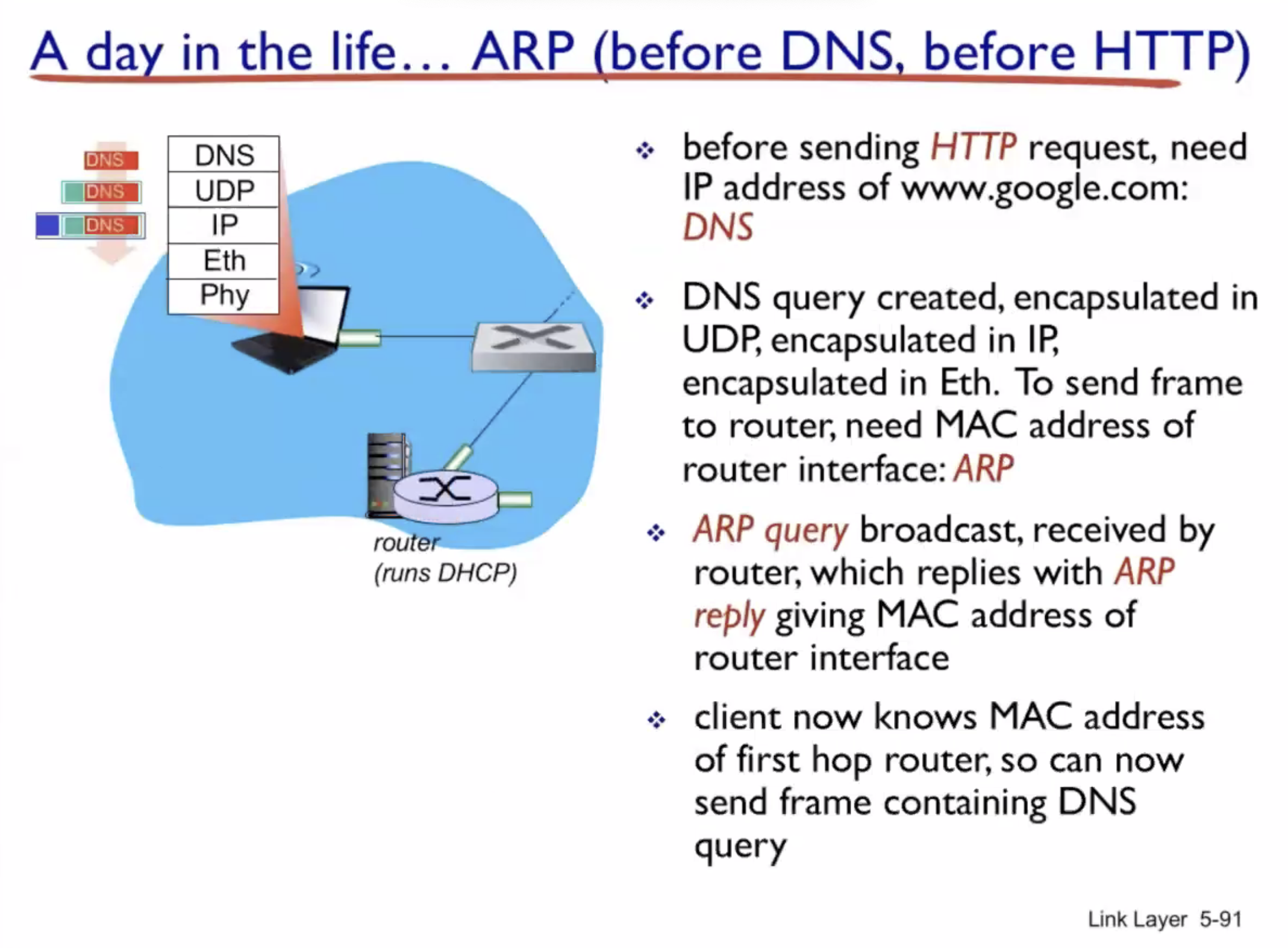
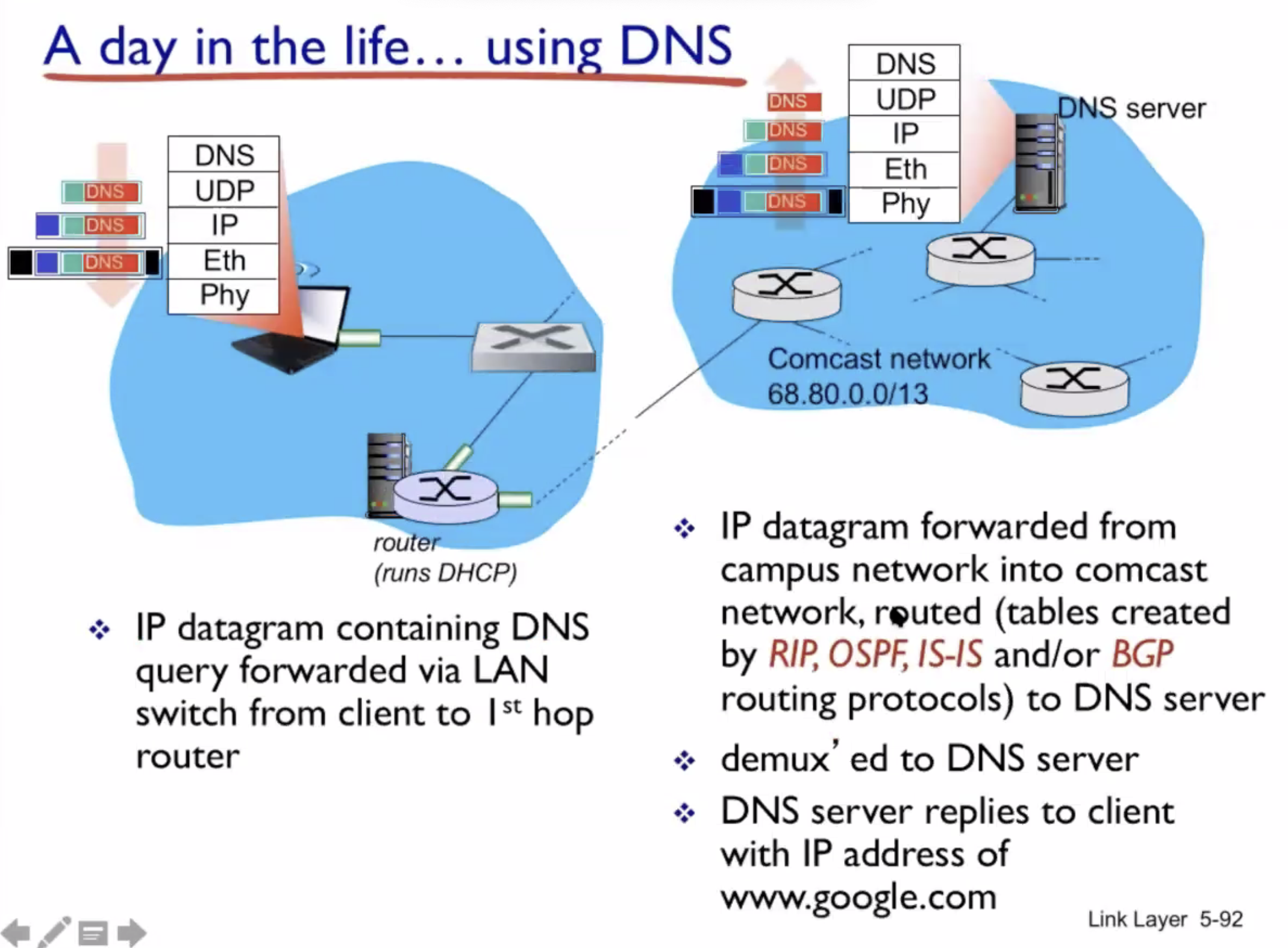
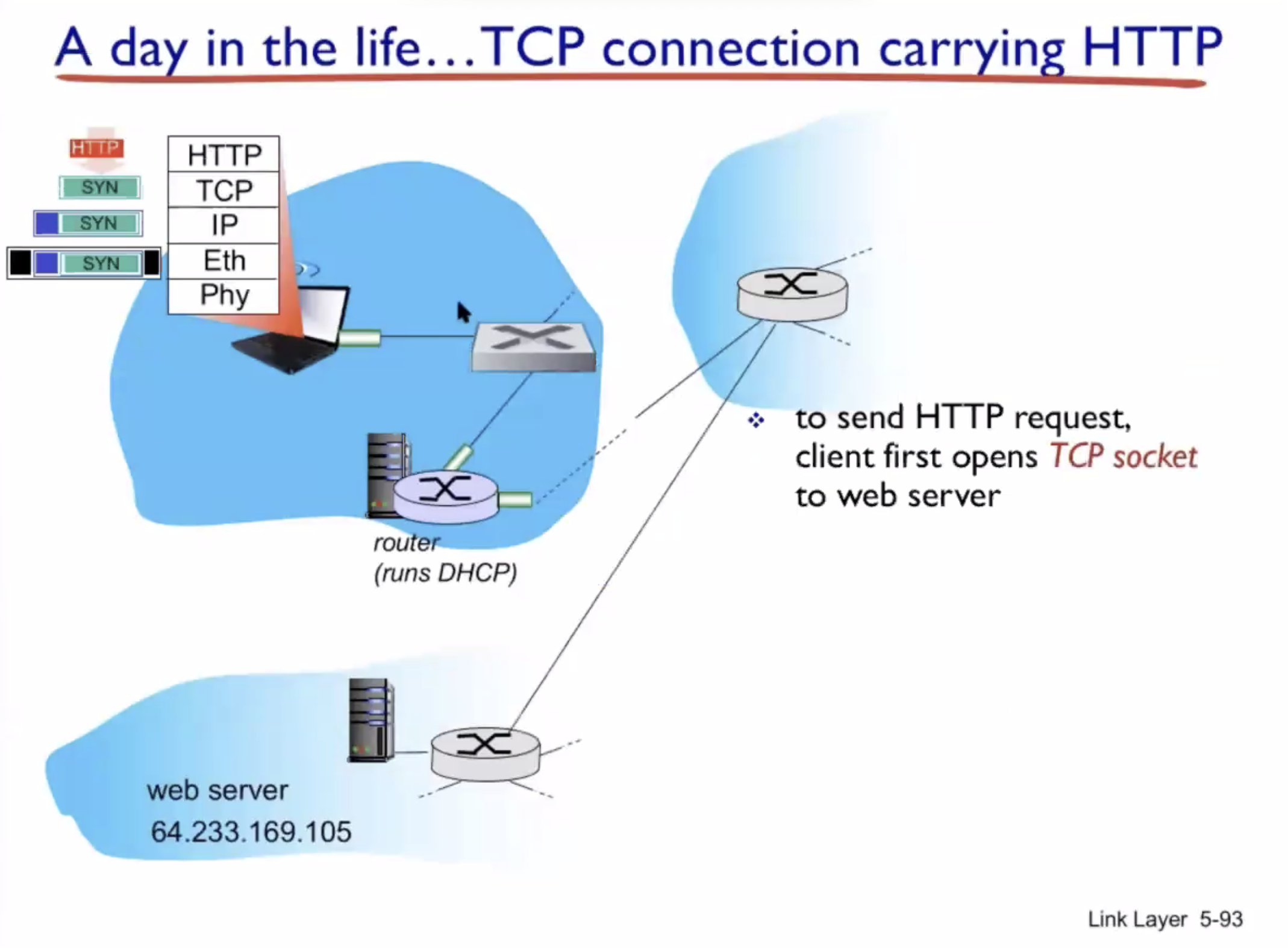
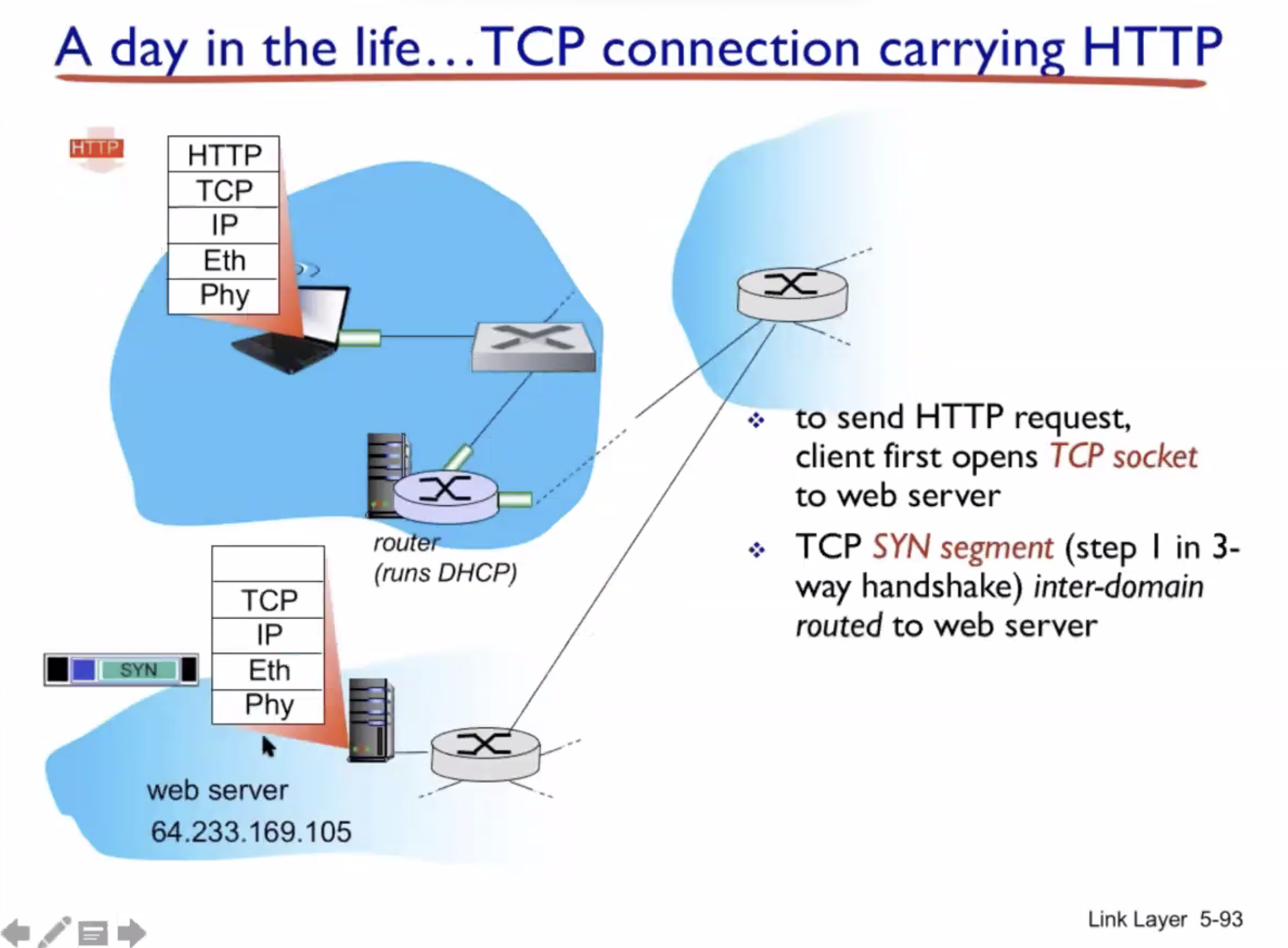
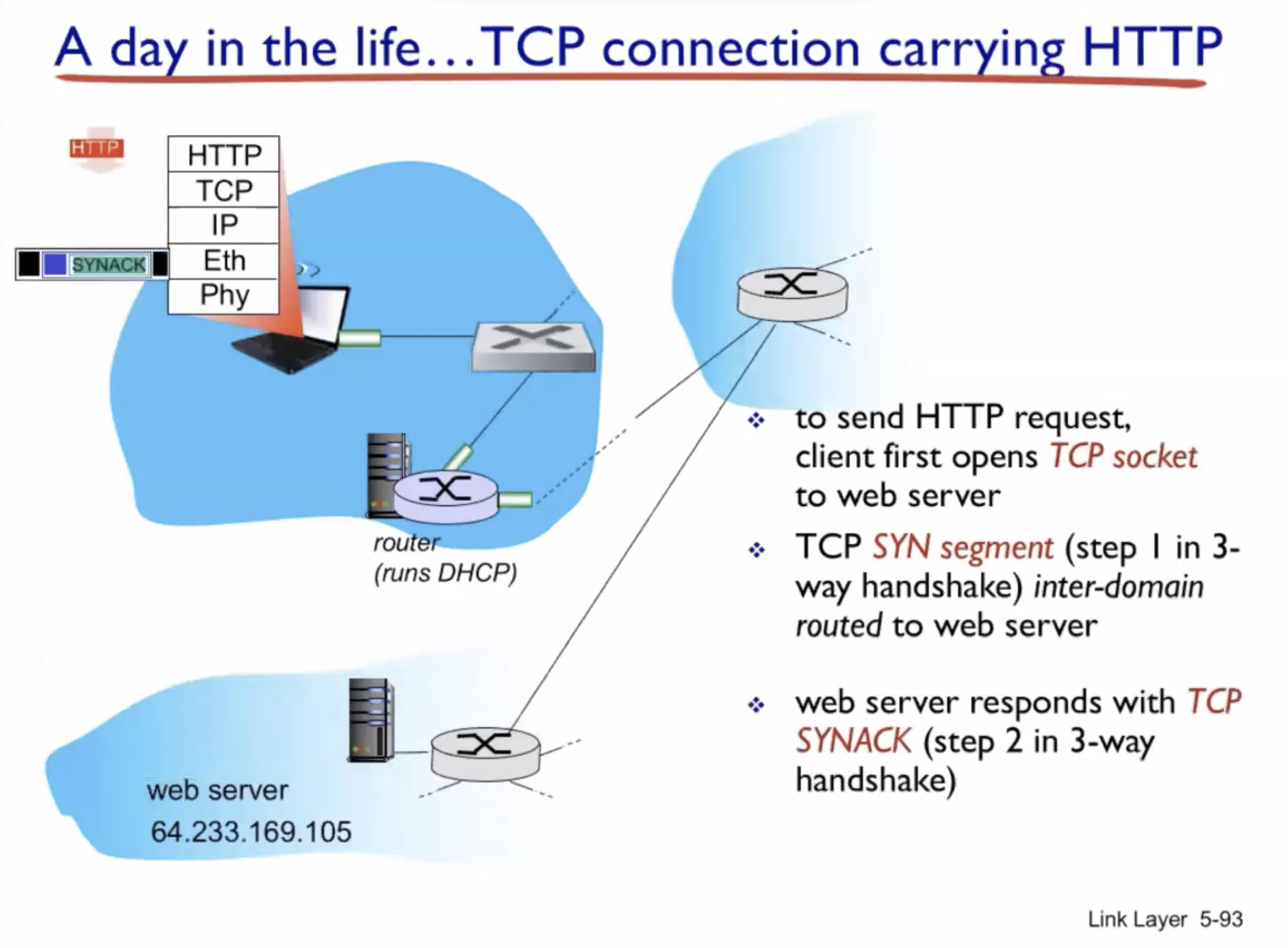
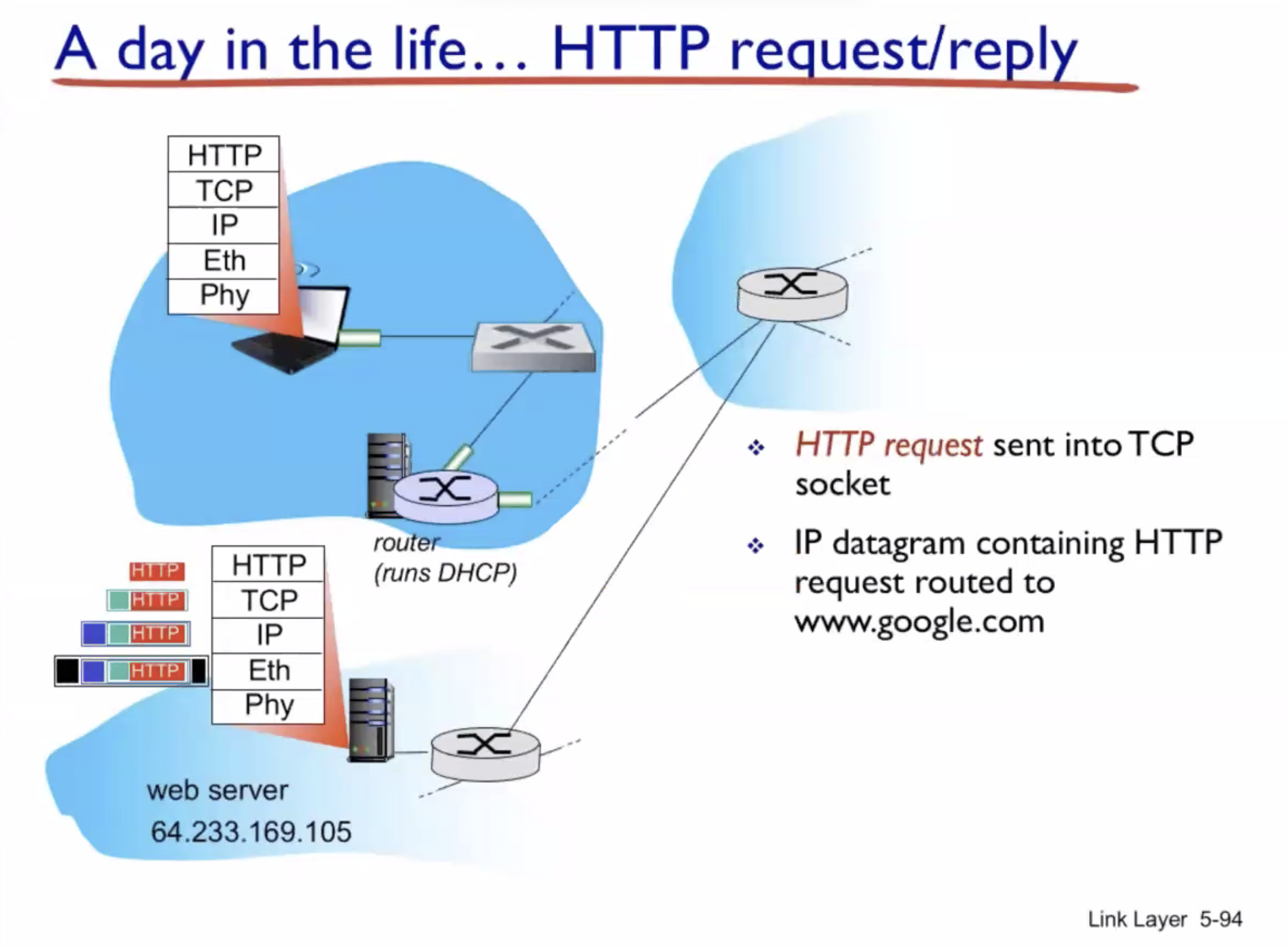
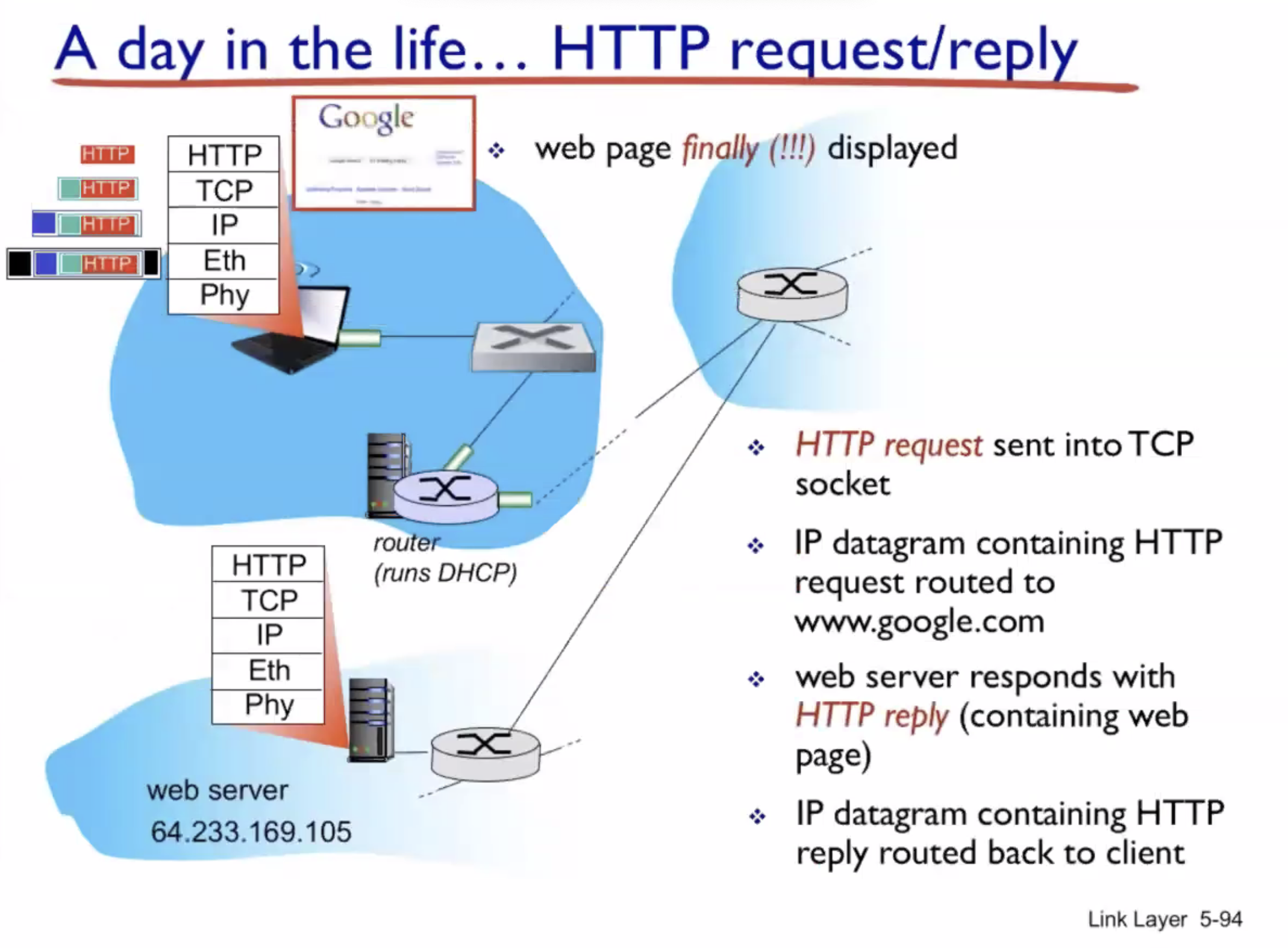
DHCP (UDP) > ARP (BGP) > DNS > HTTP (TCP)
Summary #

Review #
-
What is the difference between network and transport layer? Network is machine to machine, transport is process to process
-
Differences between TCP and UDP TCP is reliable, UDP is not
-
What is multiplex at sender? What is demultiplex at sender? View slides
-
What is different between UDP socket and TCP socket? UDP is
SOCK_DGRAMand TCP isSOCK_STREAM, and different respective functions. -
What is the usual size of UDP header? 8 bytes
-
What is the usual size of IPv4 header? 20 bytes
-
What is the purpose of UDP checksum? Error detection
-
What is the problem and solution in rdt 2.0, 2.1, 3.0? View slides
-
For non-pipelined protocols, why does sequence number surface (0,1) suffice? We only send 1 packet at a time
-
What is the difference between stop-and-wait protocols and pipelined protocols?/ Stop and wait only send 1 packet each time, pipelined send multiple
-
What is cumulative ACK? Cumulative ACK will confirm success for multiple packets
-
Why does selective repeat have a dilemma when sequence numbers 0,1,2,3 and window size = 3? View slides
-
For k-bit sequence number, what is the window size for GBN and selective repeat respectively? GBN is 2^k and selective repeat is 2^(k-1)
-
Name 5 features TCP has that UDP doesn’t.
- Reliability
- flow control
- Congestion control
- handshake
- connection management
-
What is called TCP fast retransmit? If the sender got triple duplicate it will retransmit
-
Two indicates of data loss. Count down timer, triple duplicate
-
What is ddefinition of sequence number and ack number for TCP? View slides
-
Among packet headers, which layer header contains port number?
-
What is diff between TCP flow control and congestion control? Flow control protects receiver, congestion control protects the network
-
How does receiver advertise free buffer space in TCP header? View slides.
-
Why do we need preamble in packet format? synchronization, or recognize start of new packet
-
3 costs of congestion
- data retranmission due to loss
- retransmission due to premature timeout
- Network resources allocated to dropped packet
-
Why does TCP have fairness? Because for all machines involved, each connection will have additive increase multiplicative decrease
-
What is called longest prefix matching? Selecting the longest matching IP, view slides.
-
IP: What is subset part and host part? A.B.C.D/X, the a-d is host, x is subnet mask
-
NAT, why can internal computers use private addresses? The private address is translated on its way out
-
What is the difference between inter-as and intra-as protocols? Inter is handling tasks between regions, and intra handles only the tasks inside the same region.
-
What is the functionality of inter-as? Advertise reachability information
-
Hot potatoe routing is to select which router when multiple choices are present
-
What is difference between eBGP and iBGP. External and internal
-
TDMA is time division, FDMA is frequency division
-
2 common drawbacks from “taking turns” MAC protocols? Token based has 1 point of failure, also delay
TRUE/FALSE
- Multiplexinf occurs at receiver and demultiplexing at sender. FALSE
- UDP ssocket is identified by 4 tuple: FALSE
- Checksum can be used to detect transmission error 100% correct. FALSE
- rdt 3.0 is pipelined: FALSE
- Stop and wait protocols are better than pipelined: FALSE
- Selective repeat utilizes cumulative ACK: FALSE
- GBN has buffers at receivers side: FALSE
- Forwarding and routing are independent: FASLE
- Forwarding table uses individual IP addresses as indexes, FALSE
- Internet is based on datagram network: FALSE
- IP address if flat: FALSE
- Like TCP and UDP, ICMP is transport layer: FALSE
- In tunneling, IPv4 is carried as payload of IPv6: FALSE
- For broadcasting, innetwork duplicating is betteer than source duplication: TRUE
- What is called reverse path forwarding based controlled flooding.
- Data link layer studies logical communication between remote hosts or processes. FALSE
- Data link layer studies logical communication between hosts or processes: FALSE
- MAC is hierarchical: FALSE