Network layer cont. #
Switching fabrics #
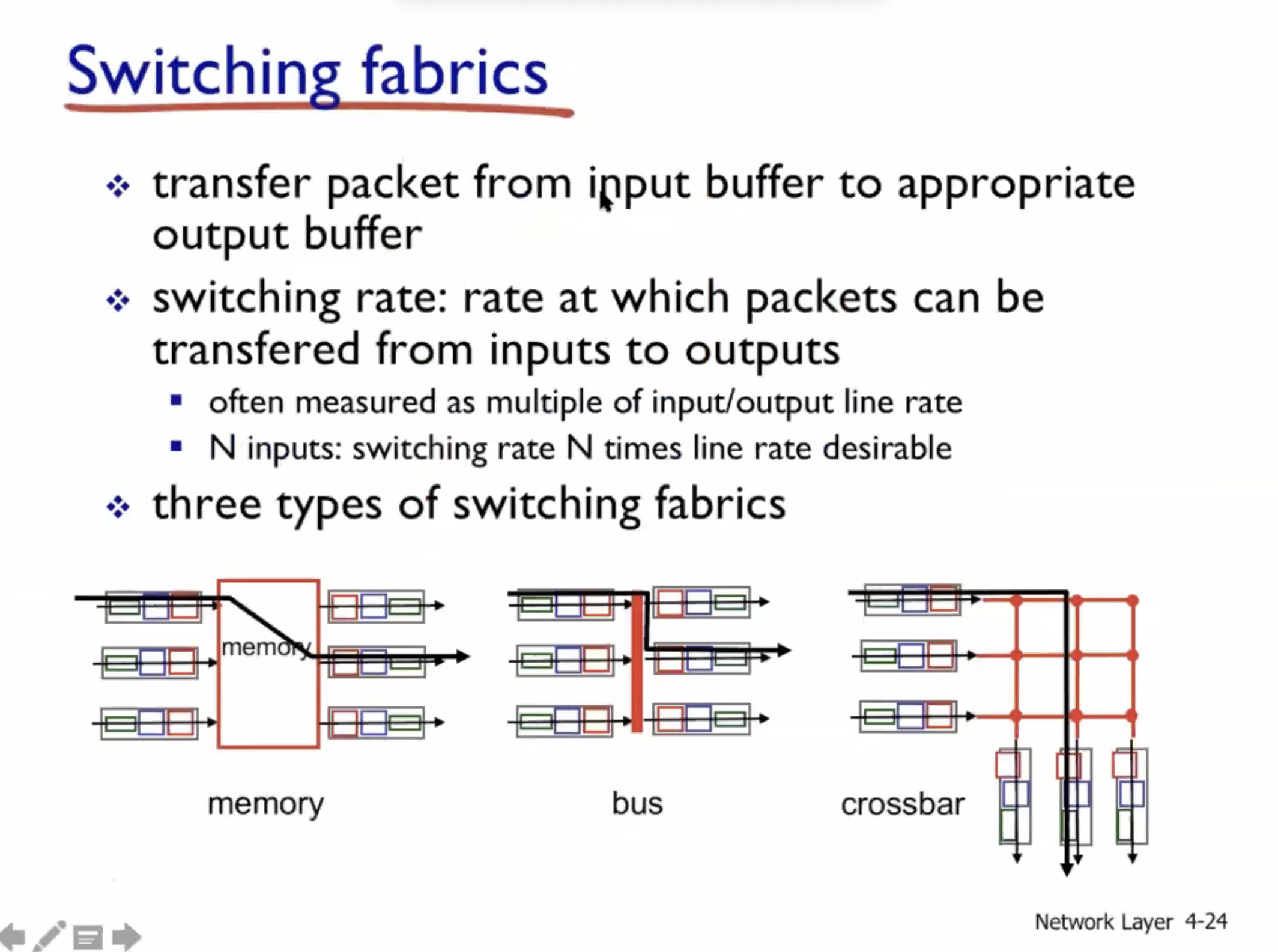
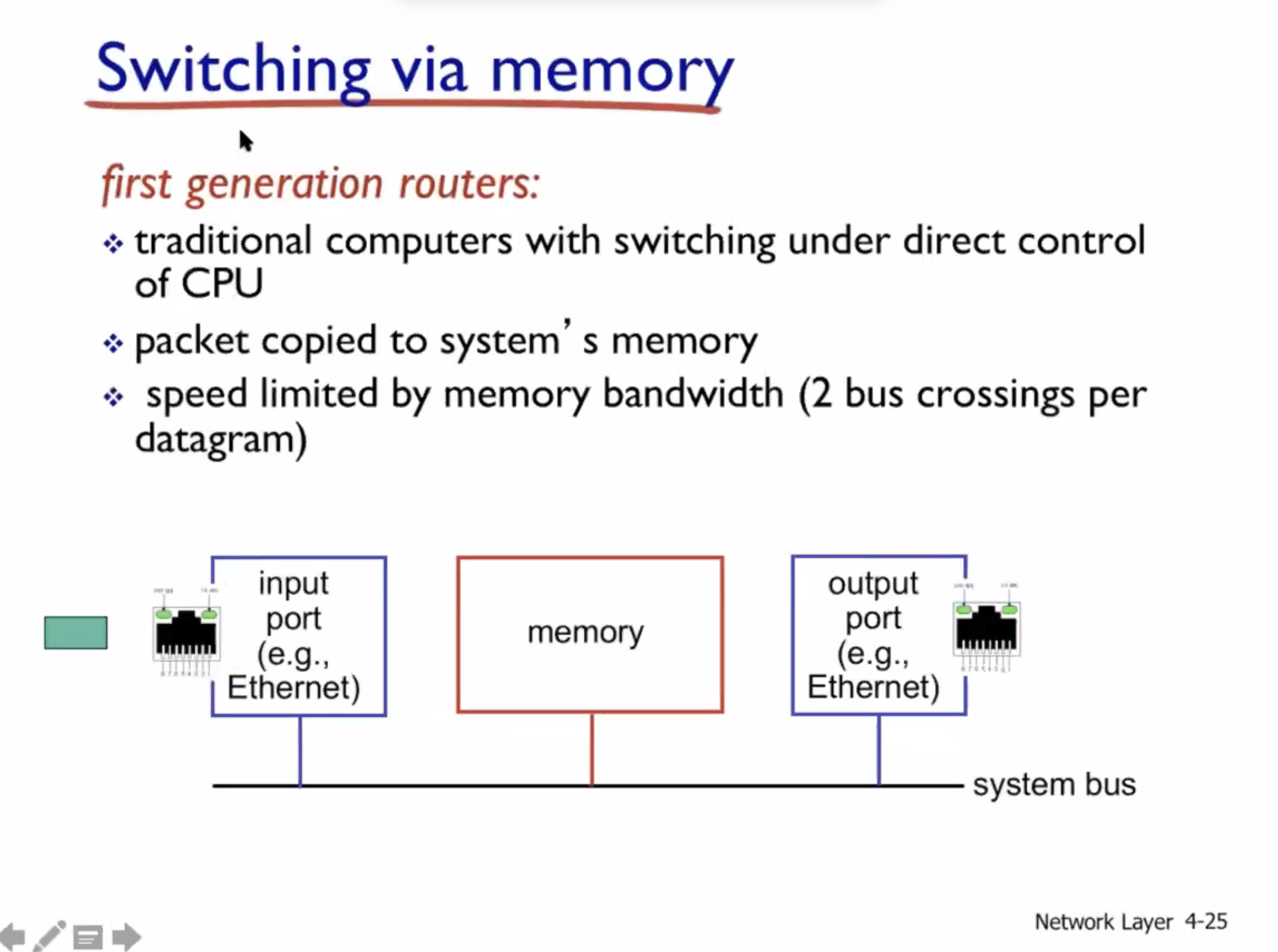
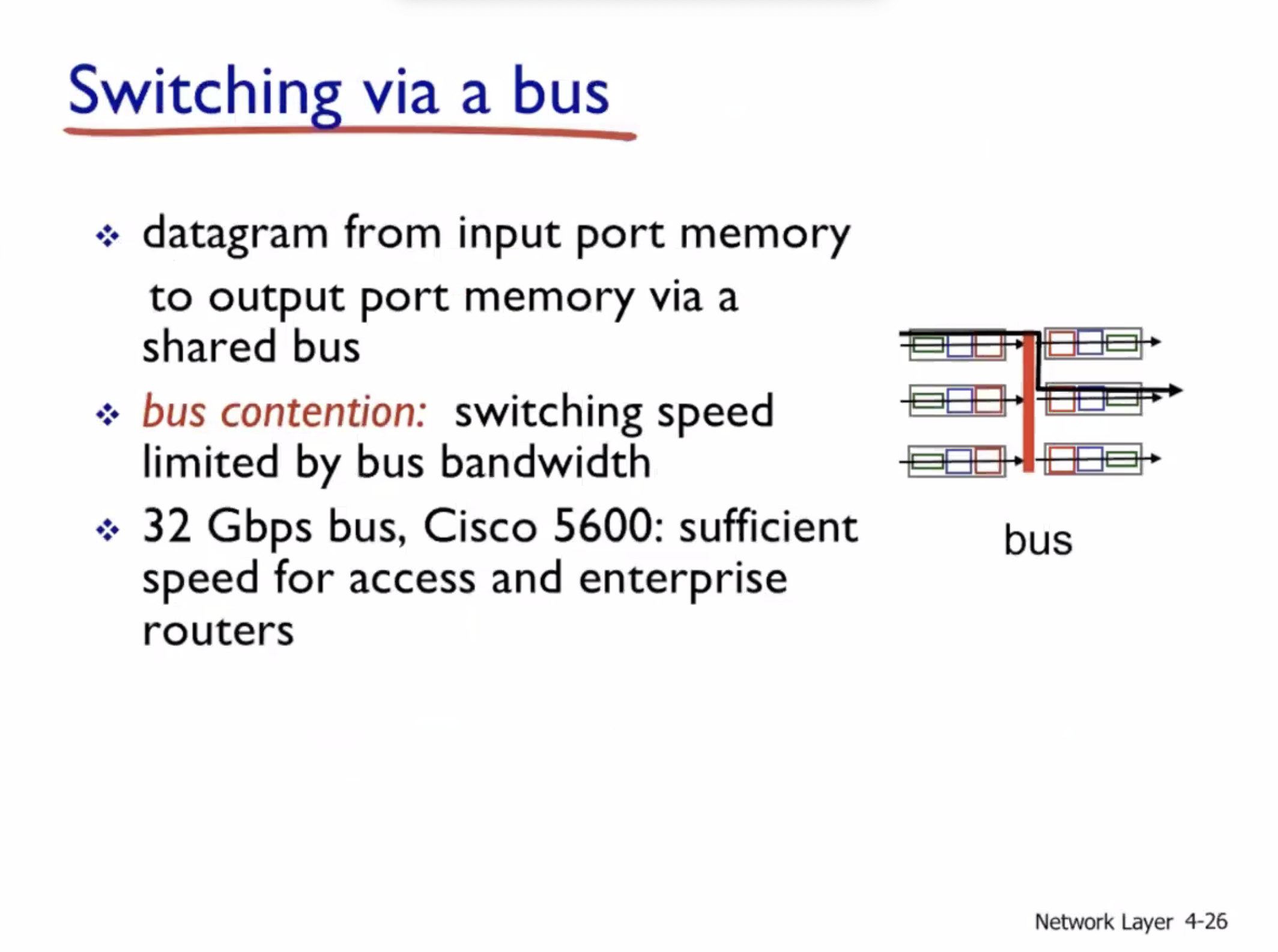
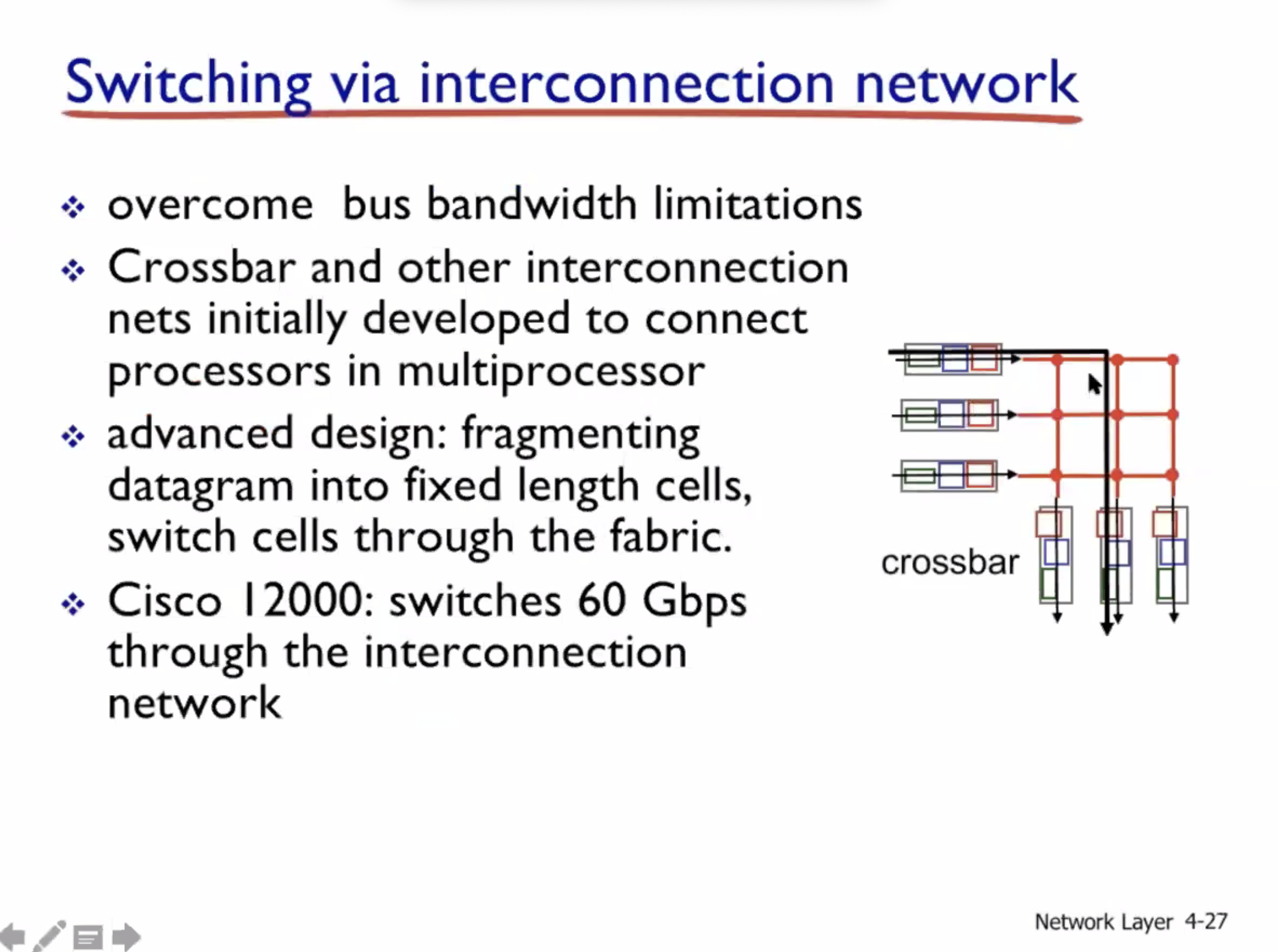
Since data can flow bidirectionally, inputs can become outputs, and vice versa.
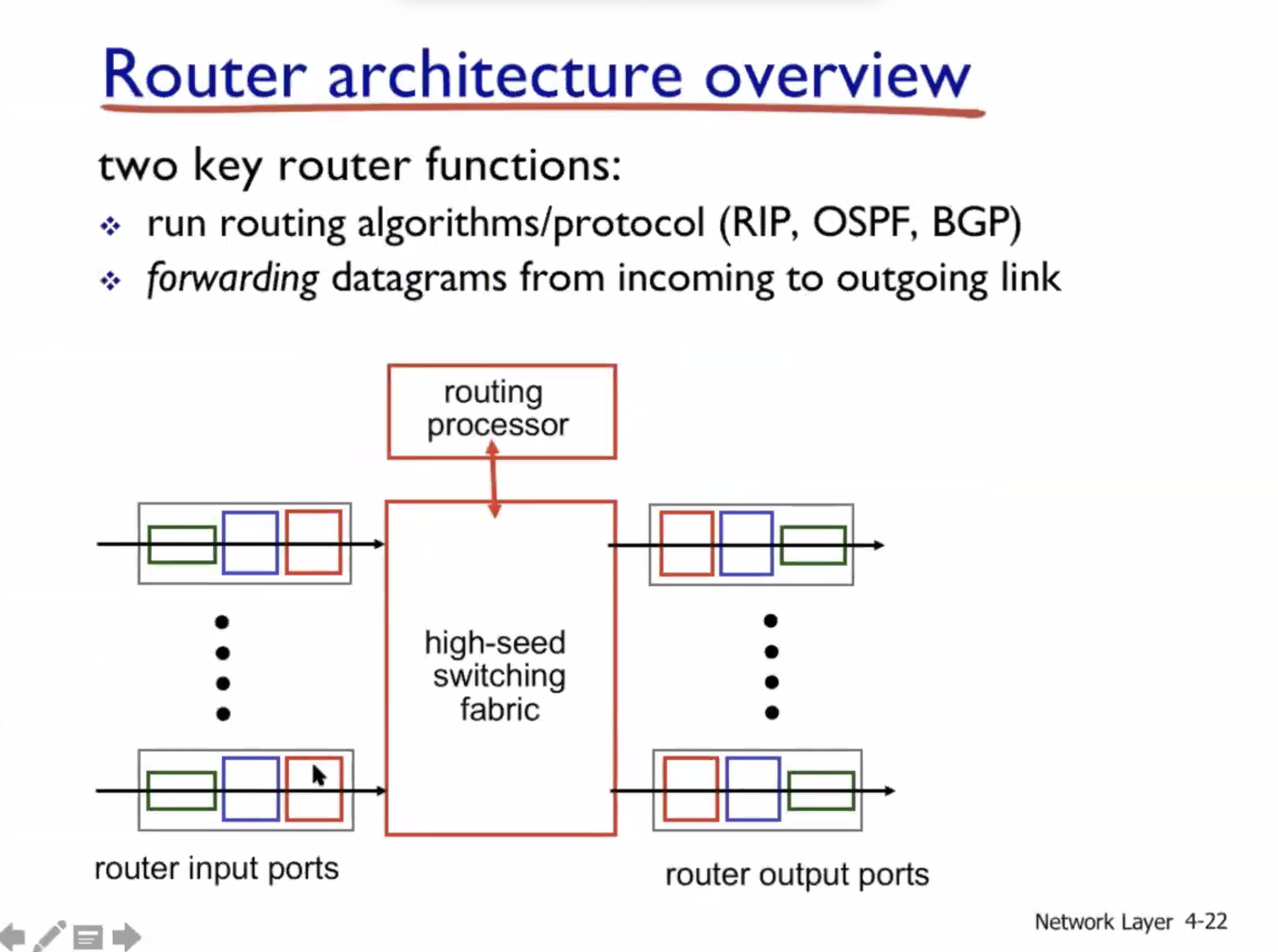
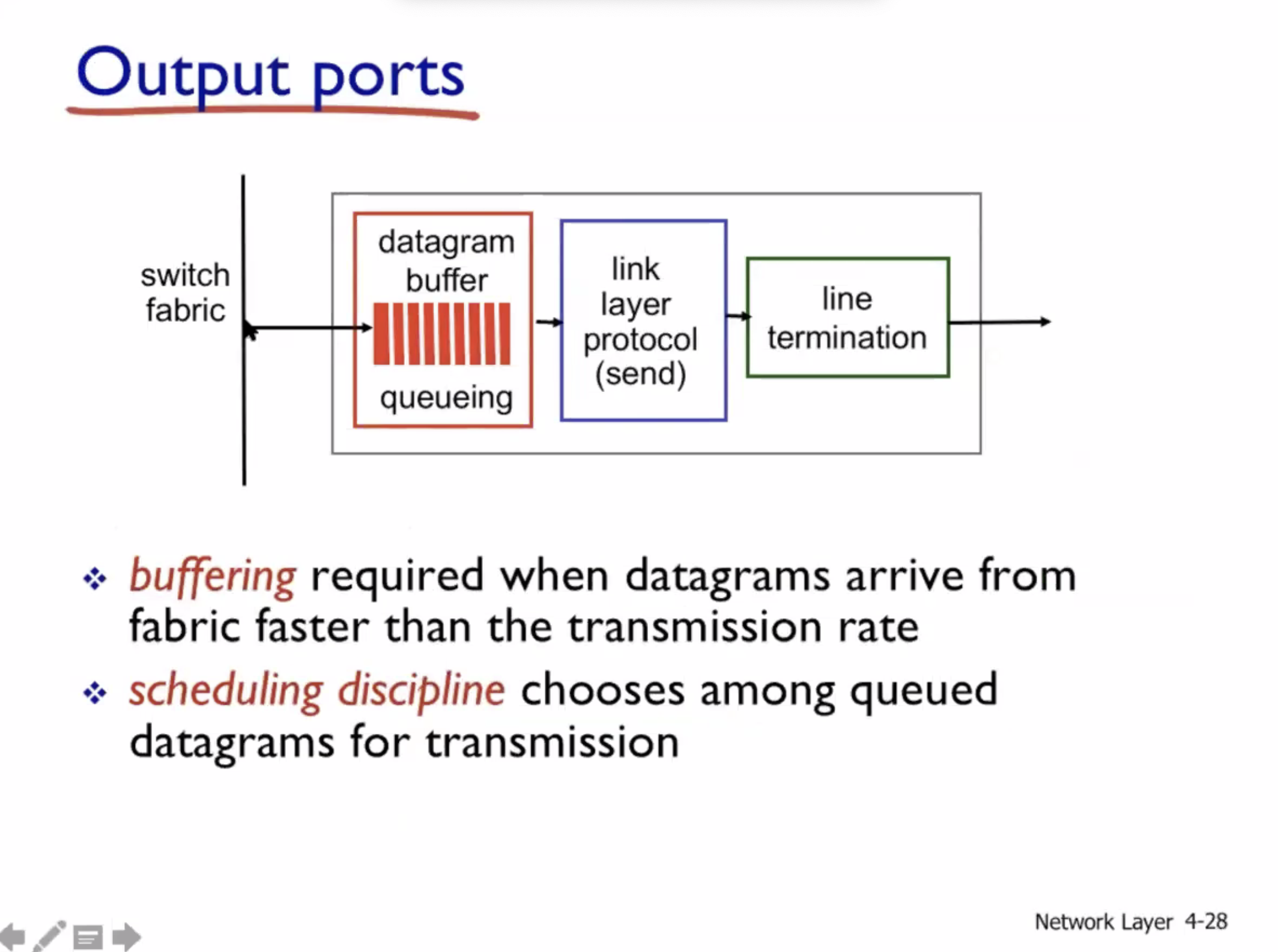
Output ports #
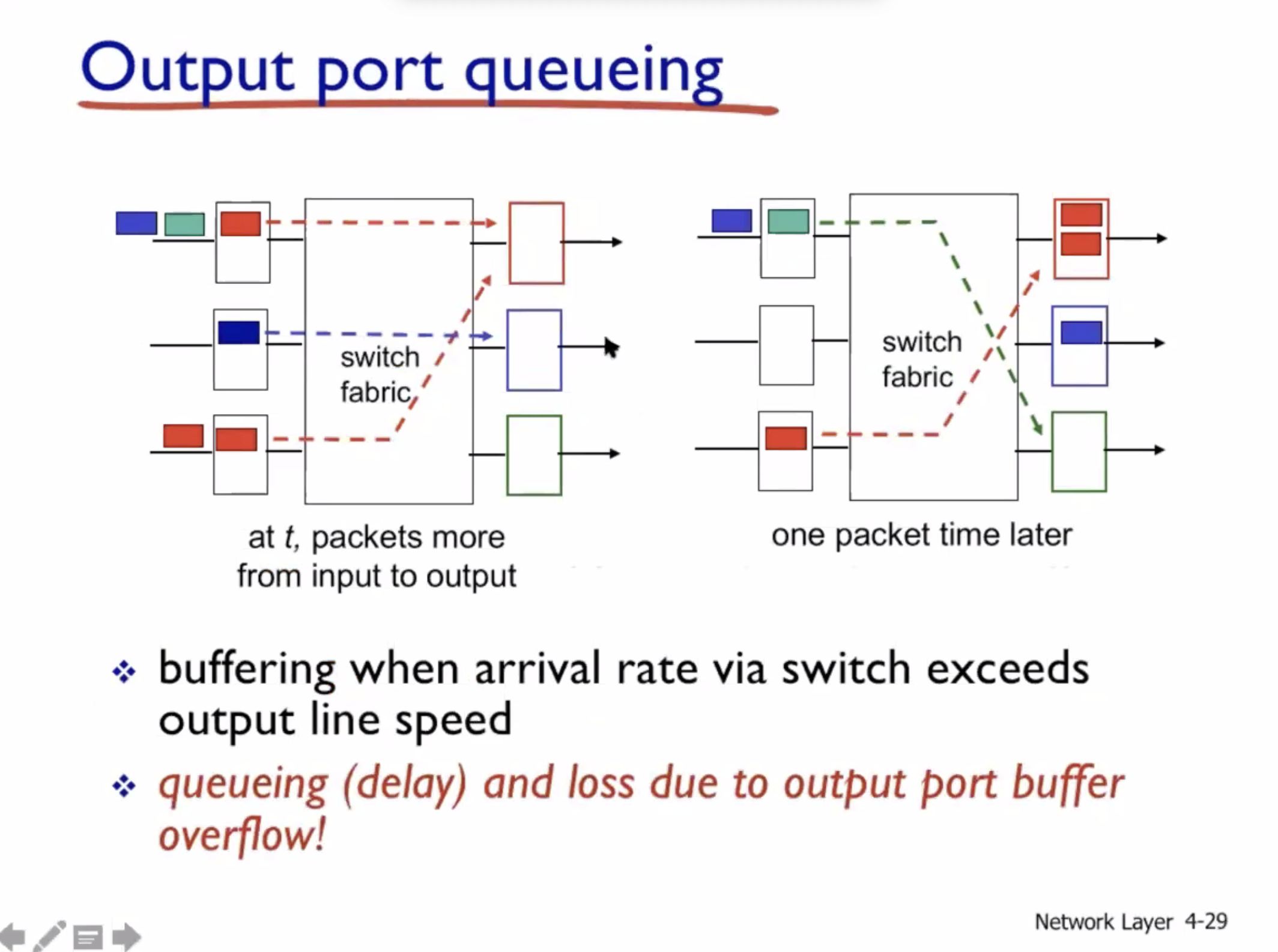
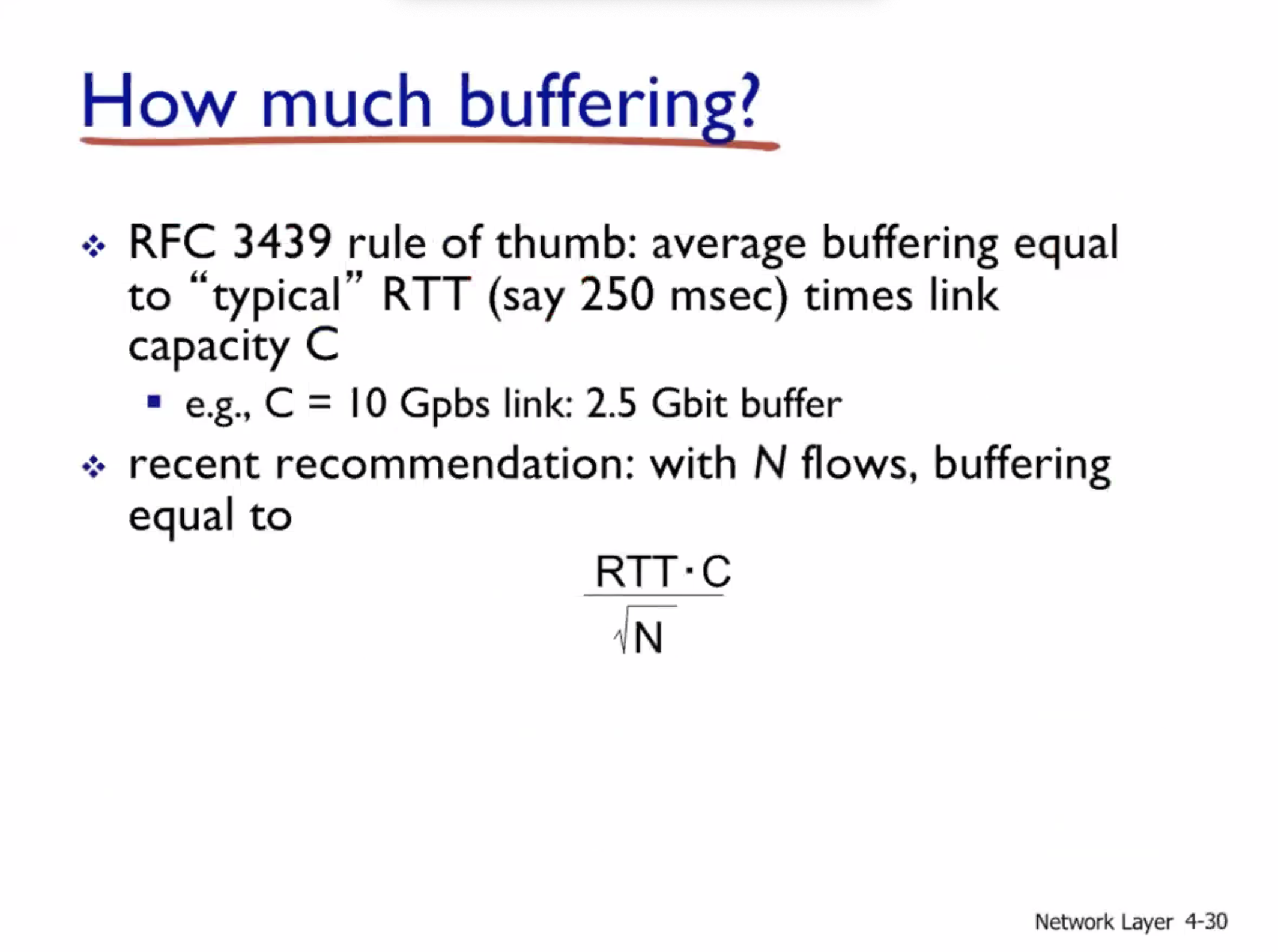
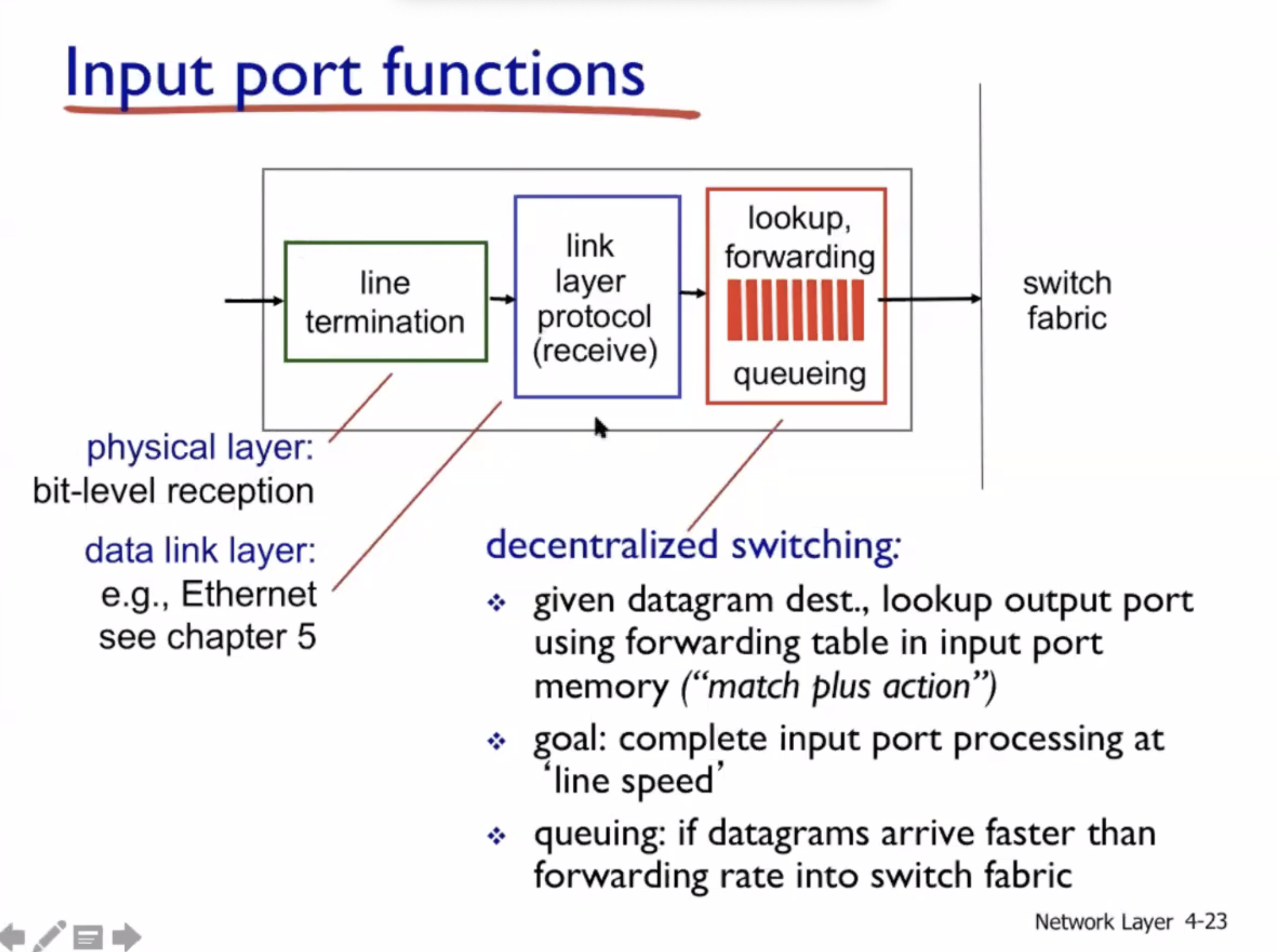
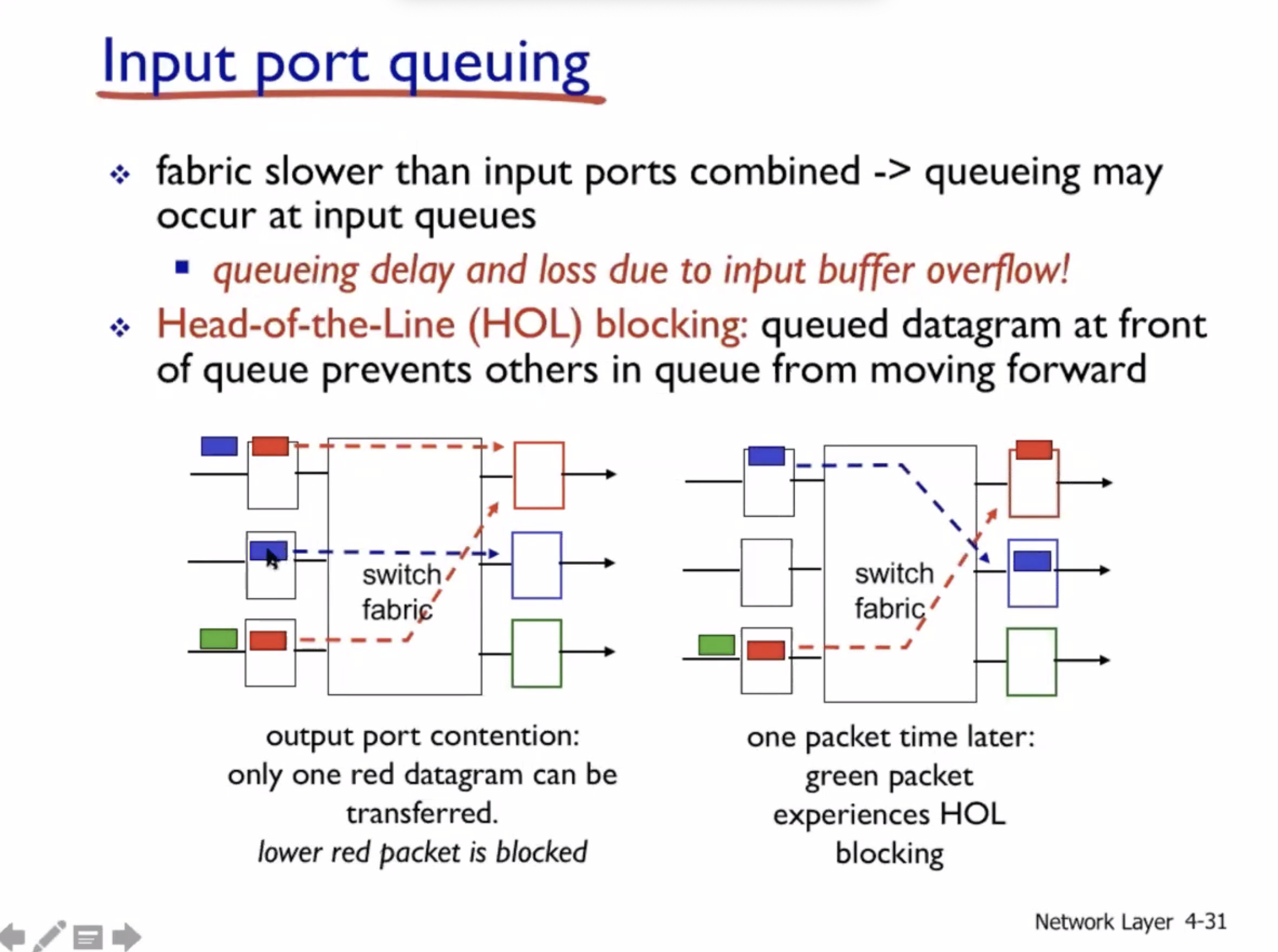
Input port queueing #
IP: Internet Protocol #

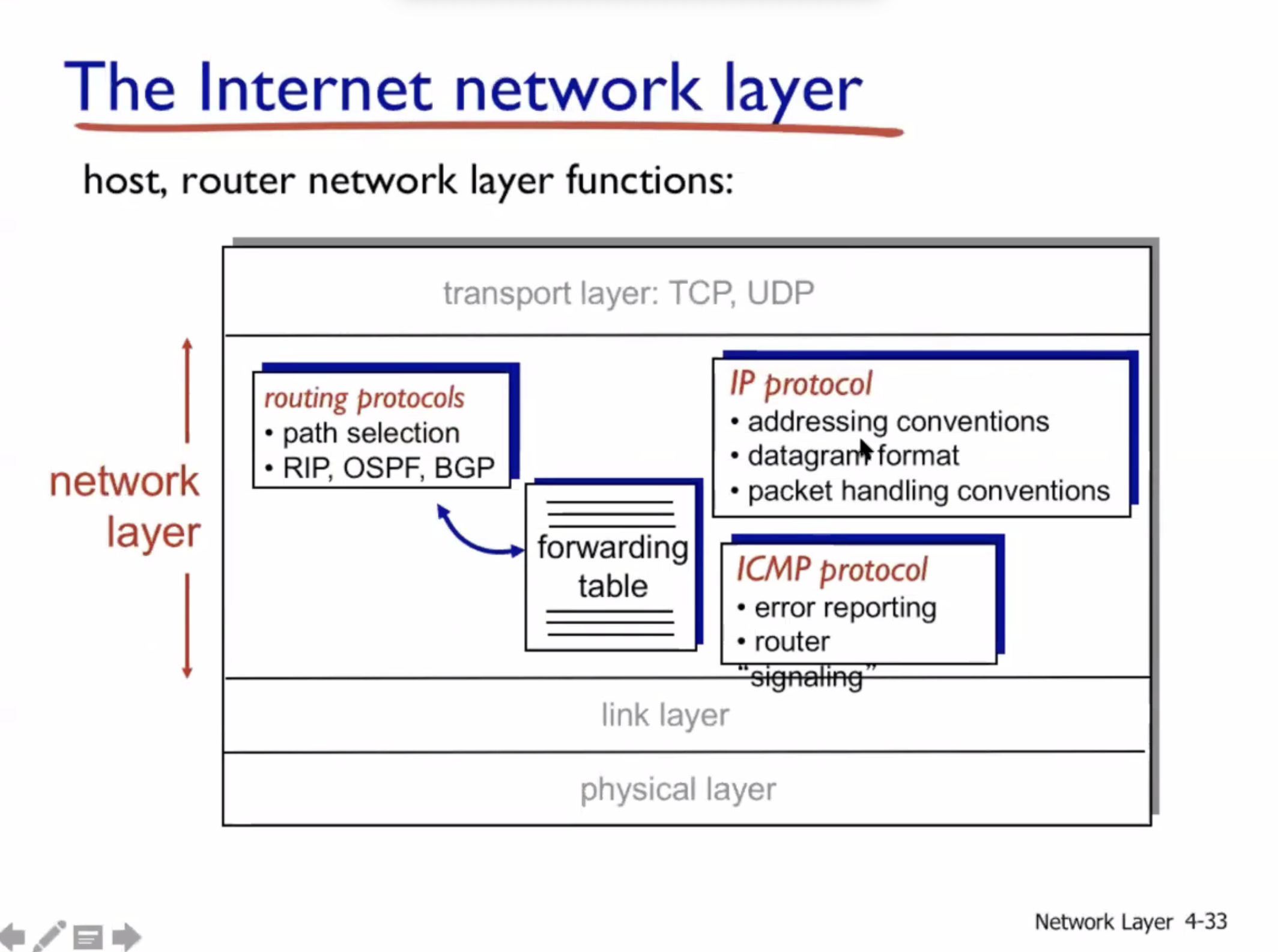
ICMP = internet control message protocol
Datagram format #
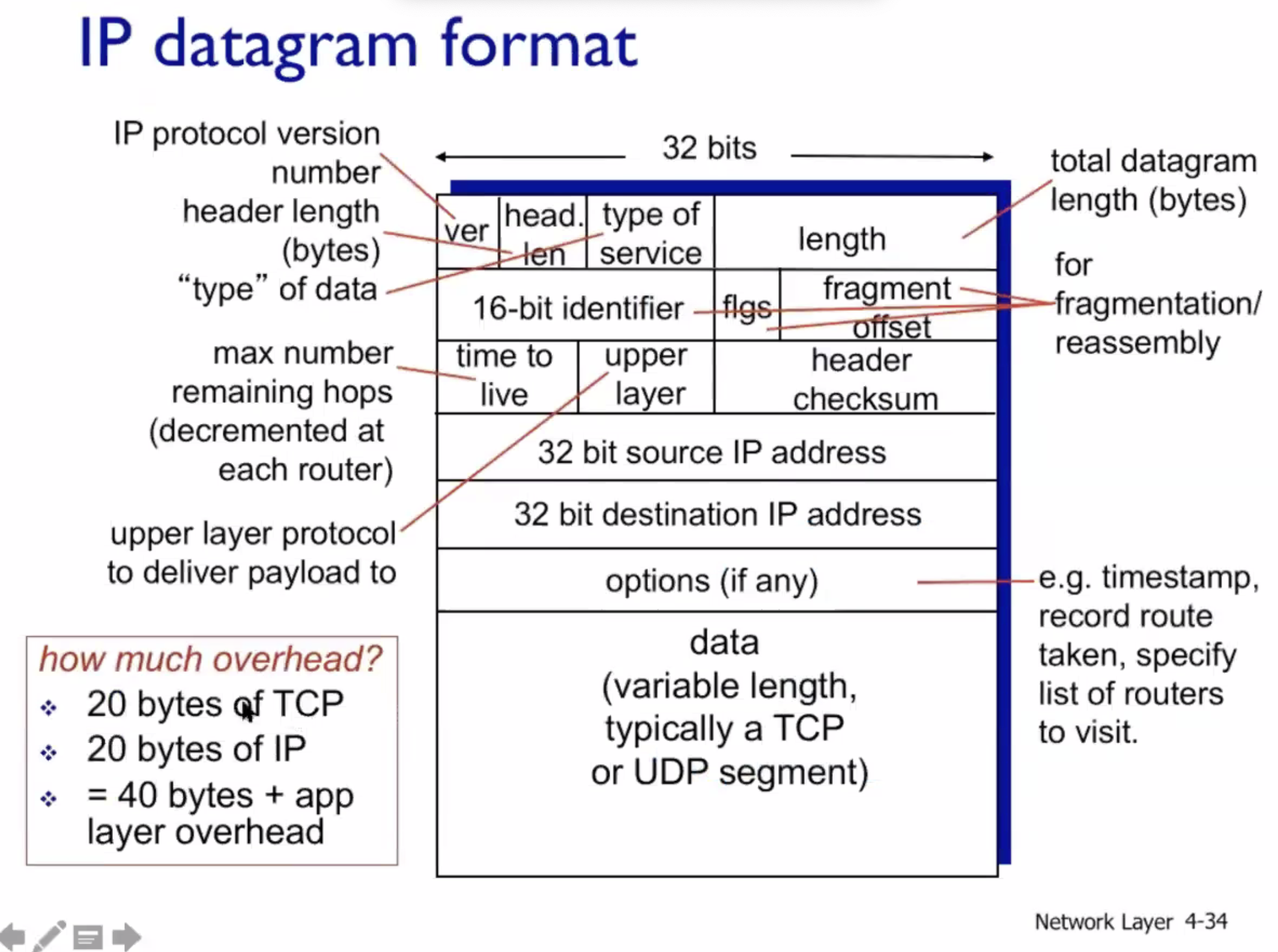
The header is 20 bytes long.
Upper layer can be TCP or UDP, or ICMP
A type could be multimedia, satellite signal etc, used for priority.
IP Fragmentation #
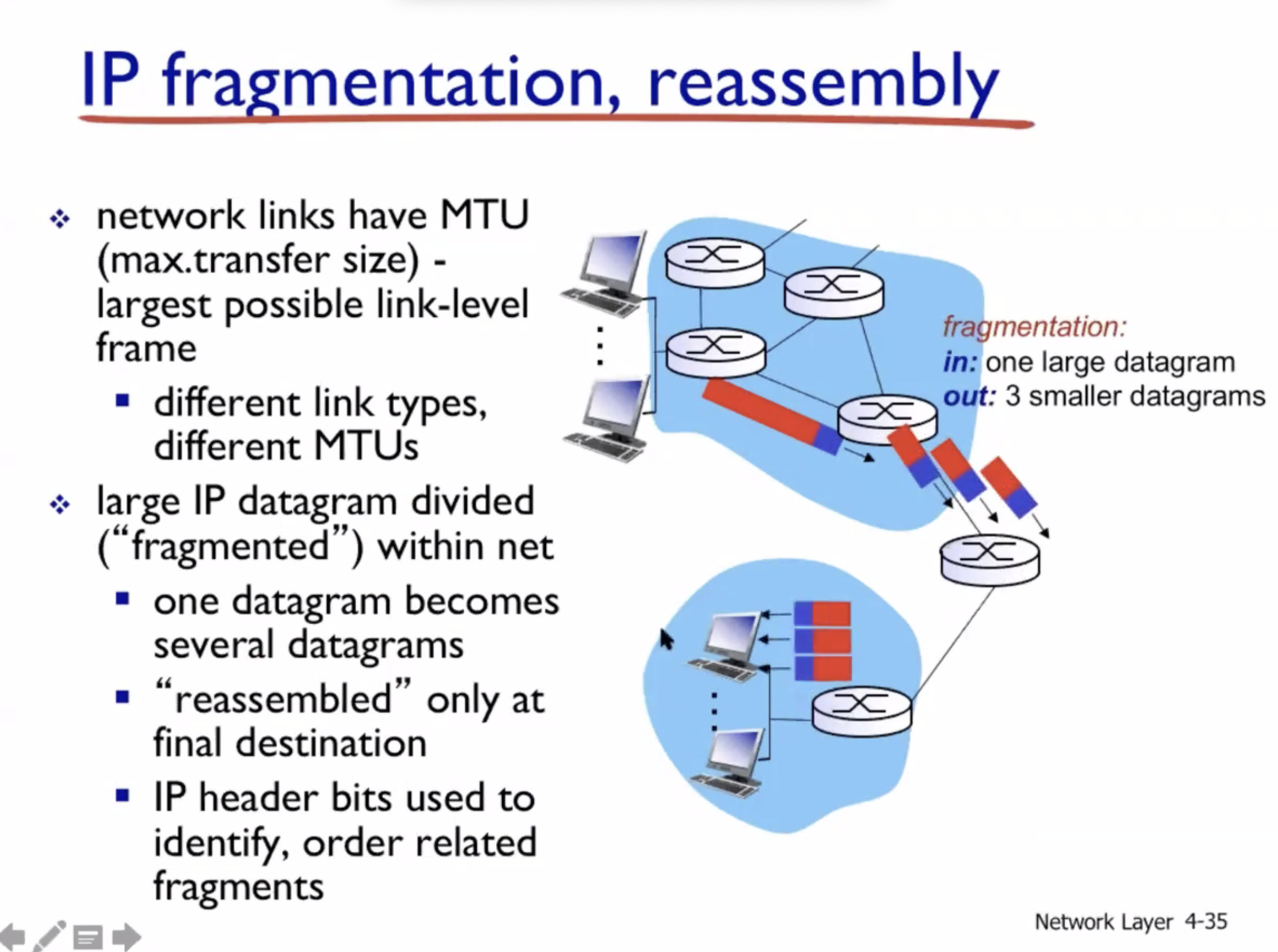
MTU = max transfer size
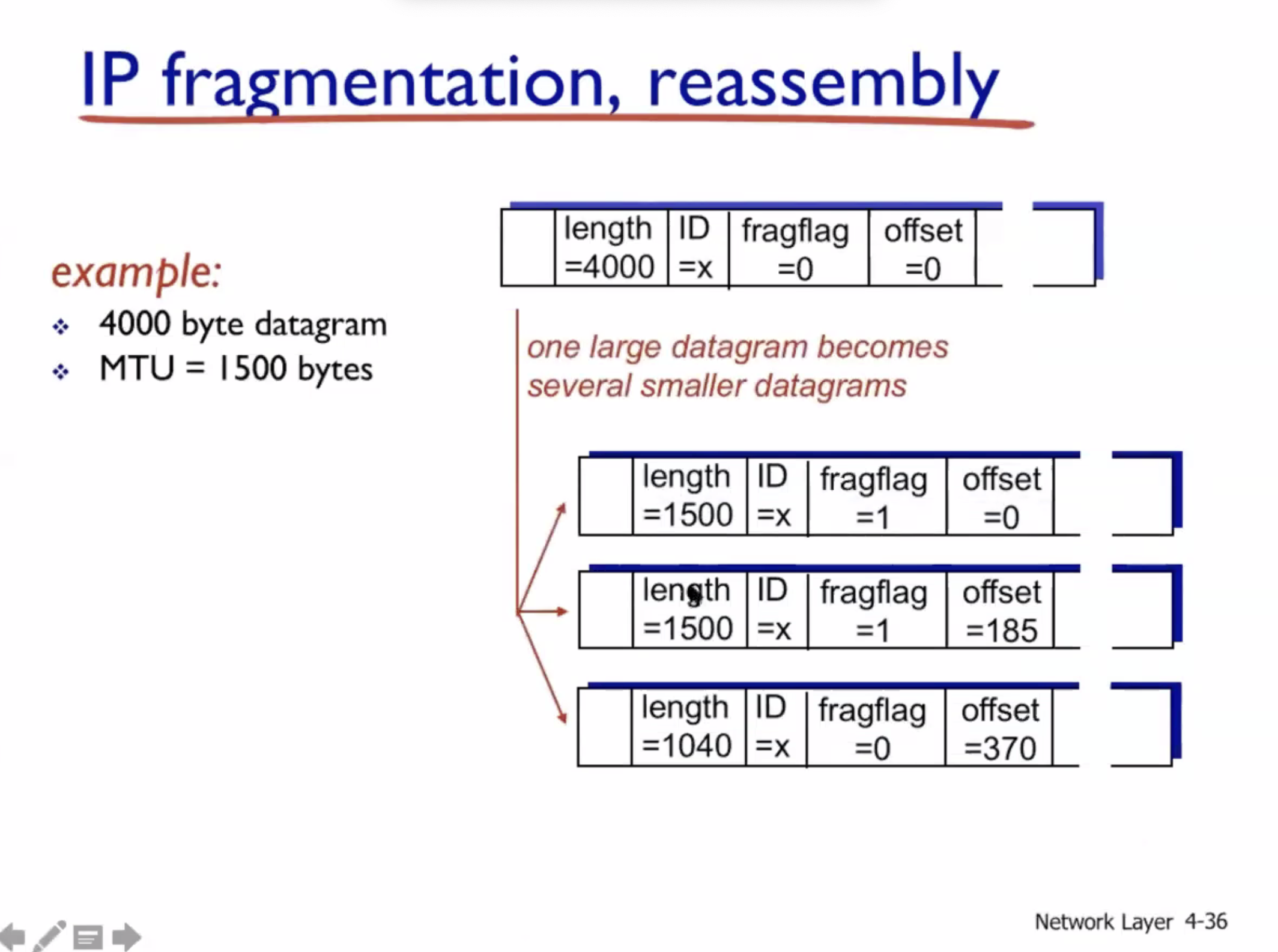
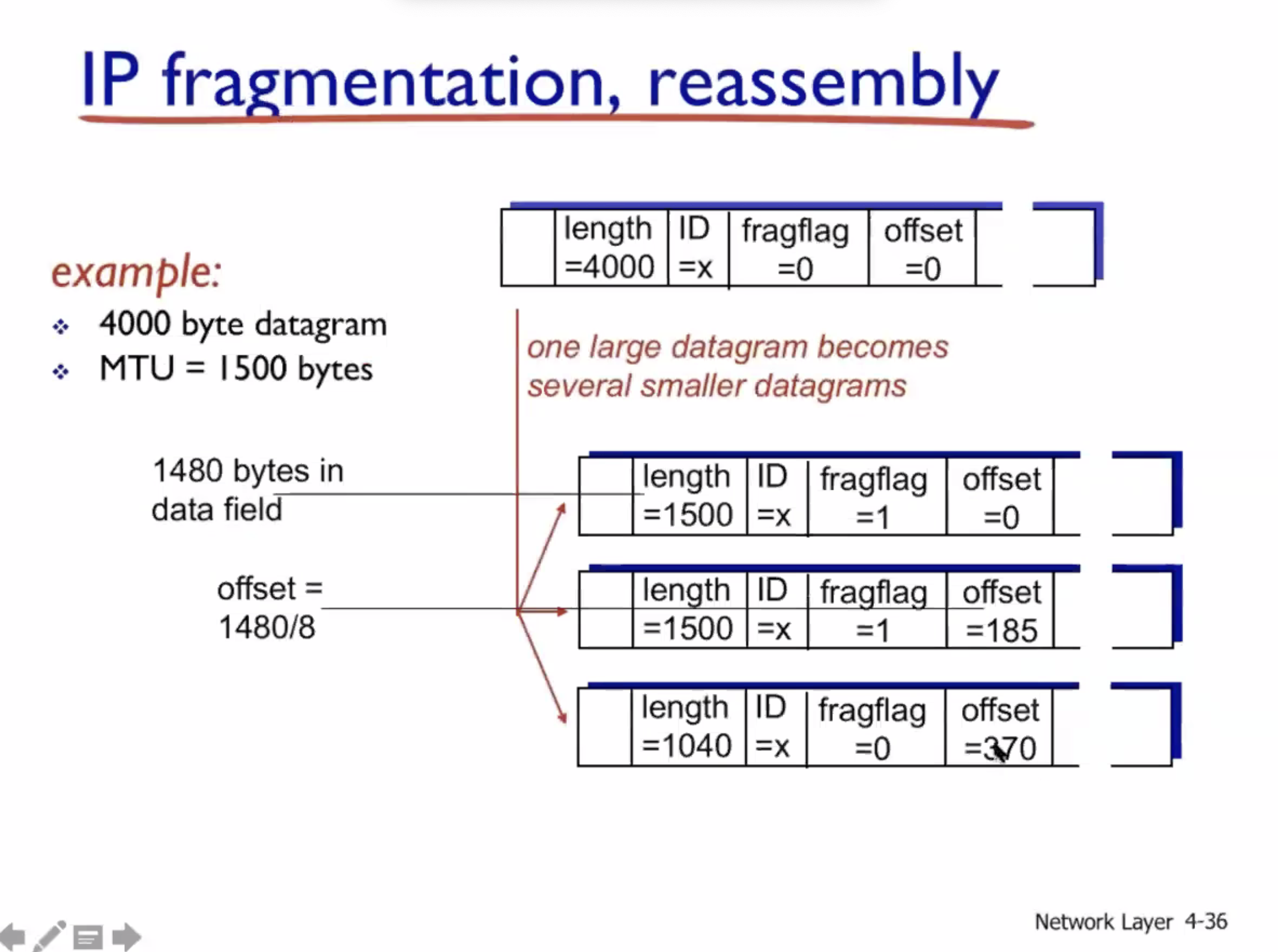
The original is 4000 bytes, but the MTU is 1500 bytes. So the original will be fragmented to accommodate the MTU.


Note: IP header is in every fragment, but the TCP header is only in the first. The TCP header is regarded as payload at the network layer.
IPv4 #
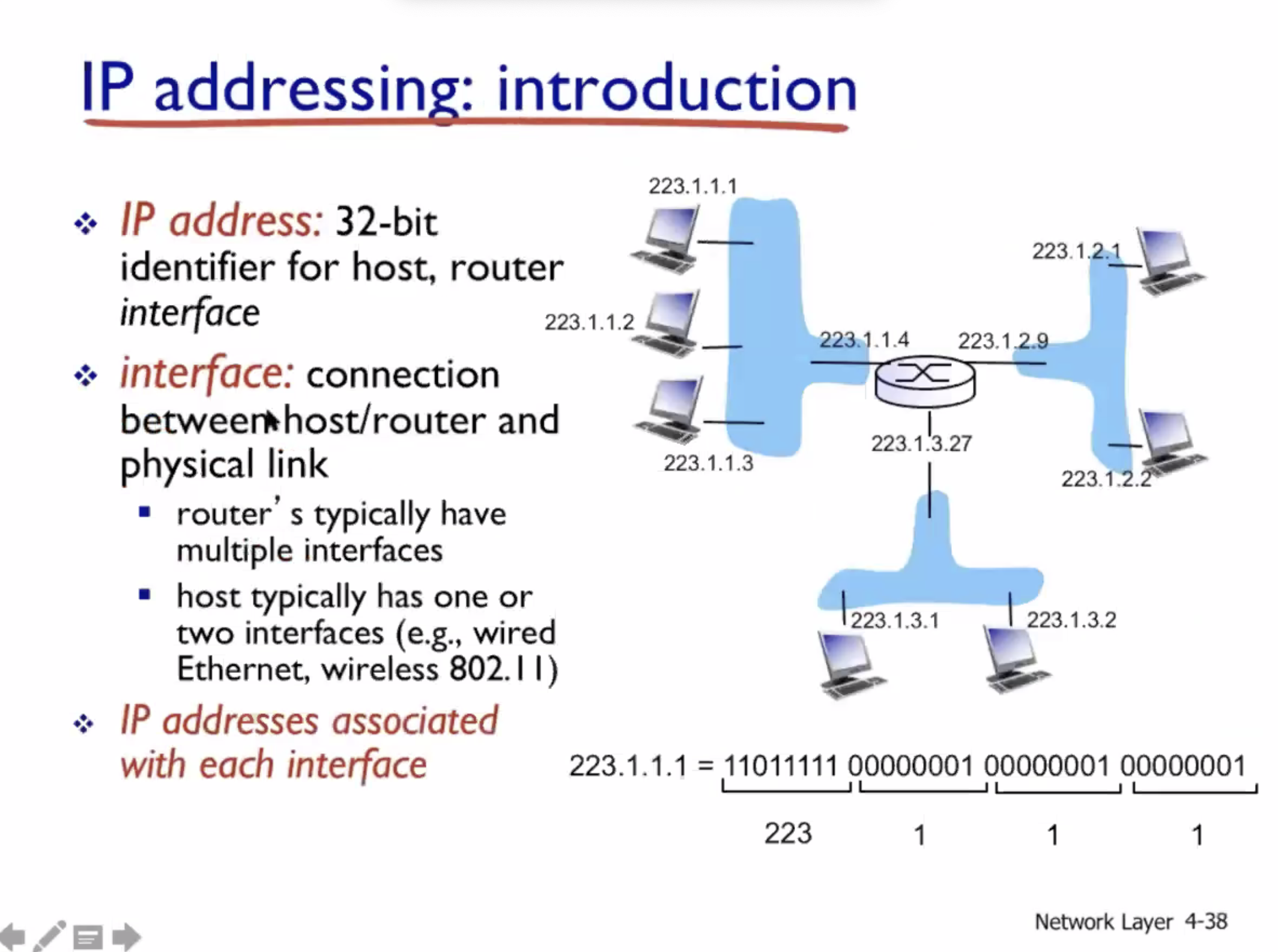
NIC = network interface card
A.B.C.D where each letter is 8 bits, so 32 bits total.
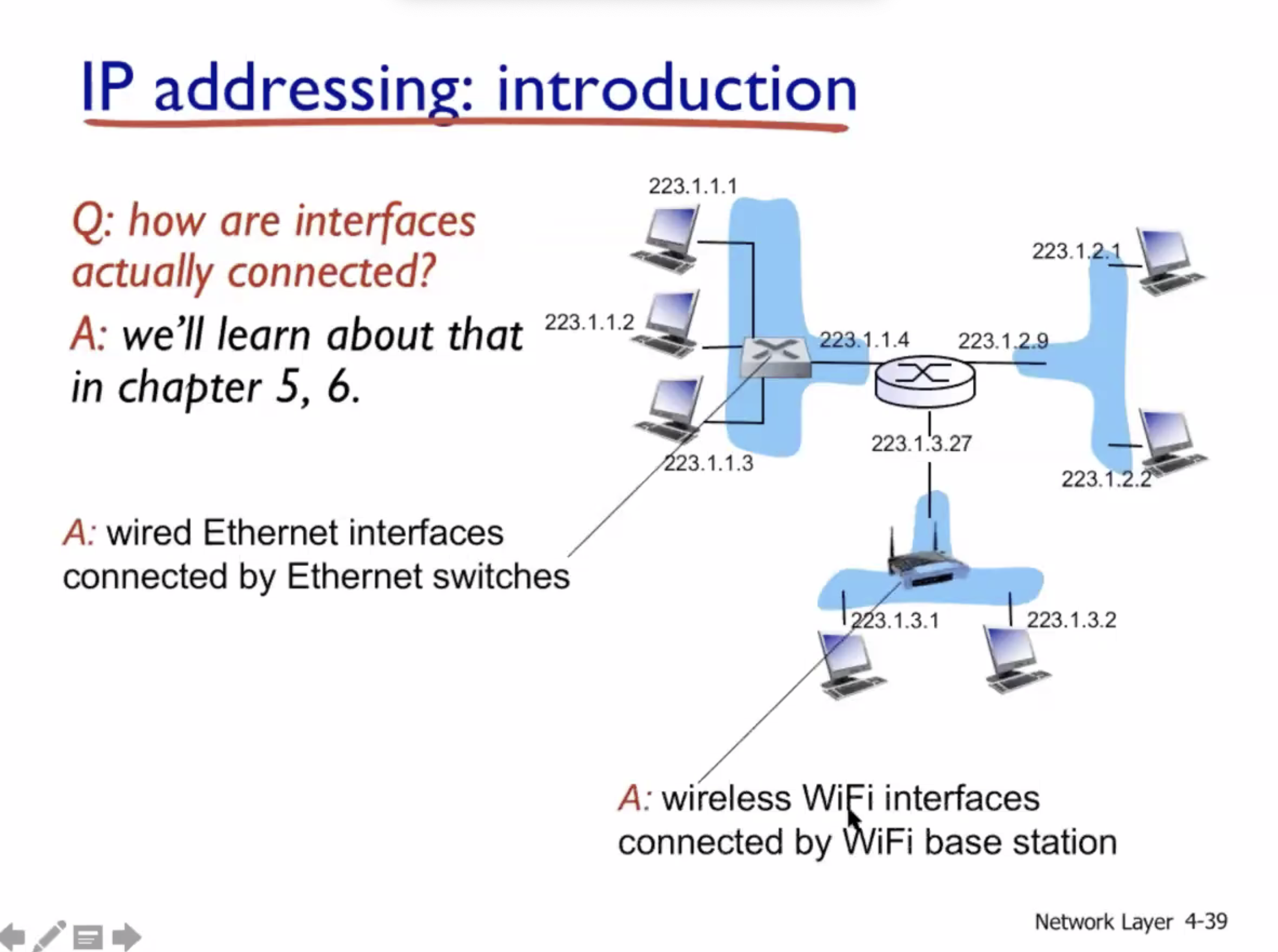
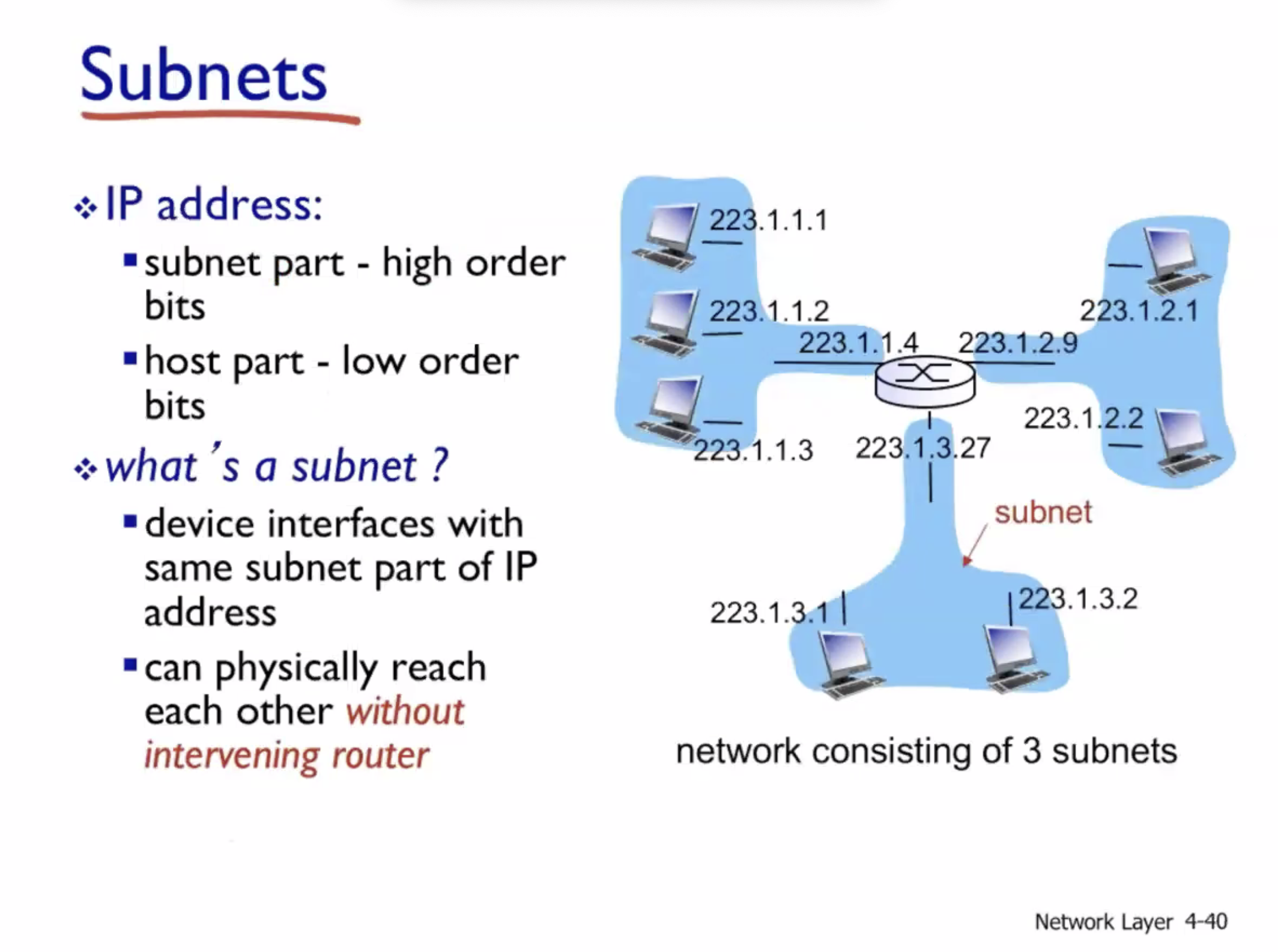
Subnets #