Connection oriented transport: TCP #
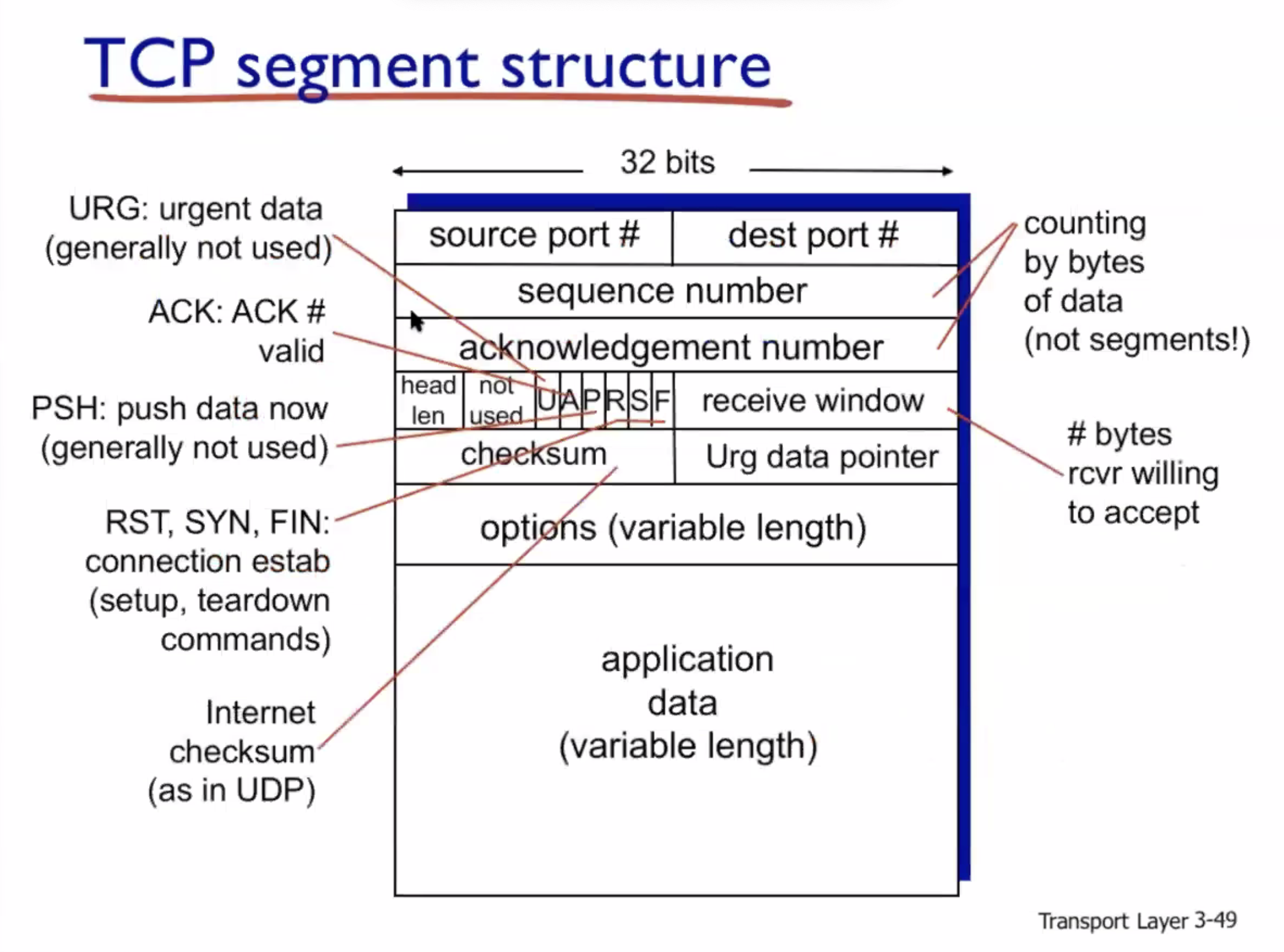
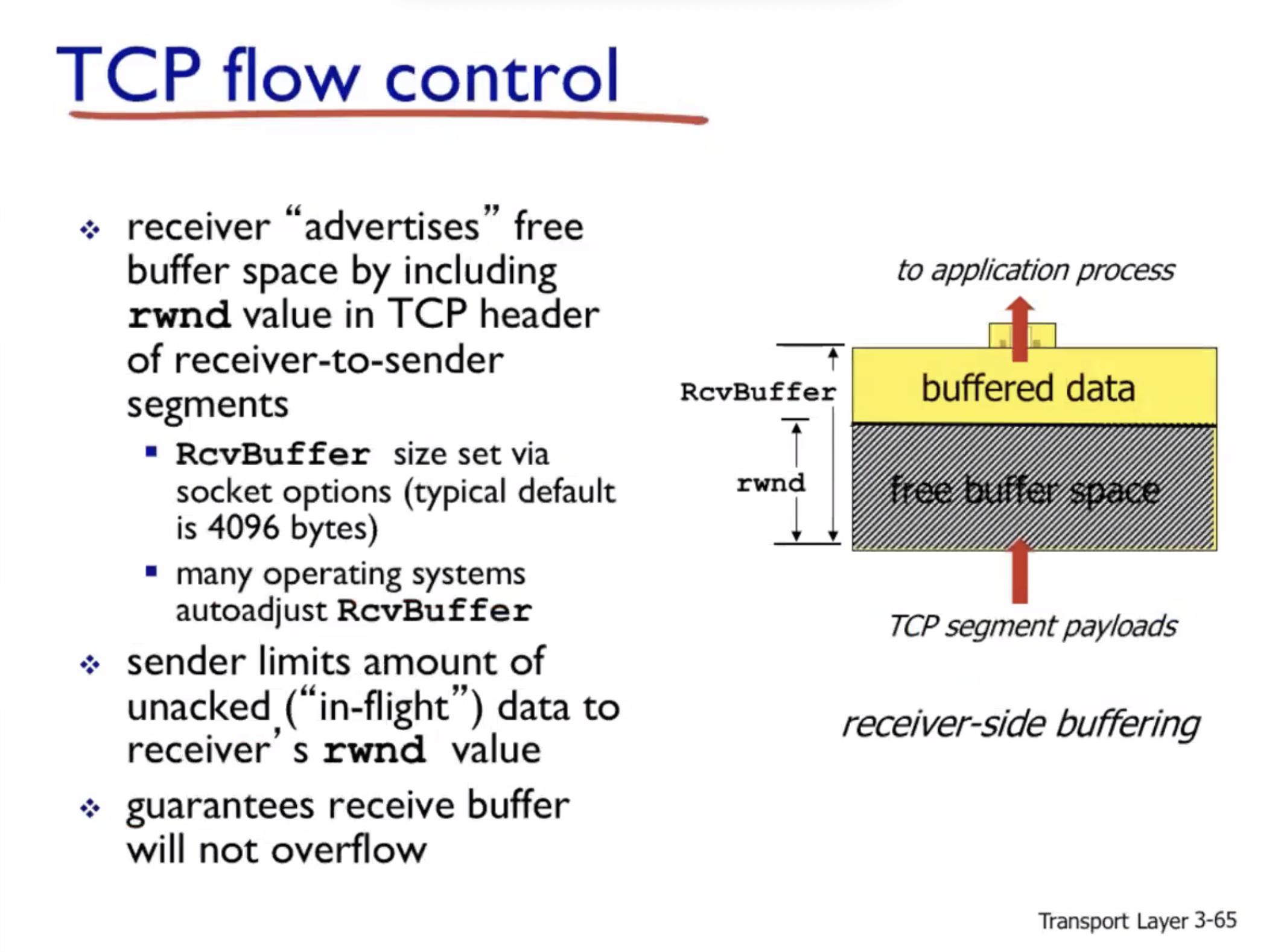
Entire header size is \( 32 \text{ bits } \cdot 5 = 160 \text{ bits } = 20 \text{ bytes } \) . The receive window is used for flow control.
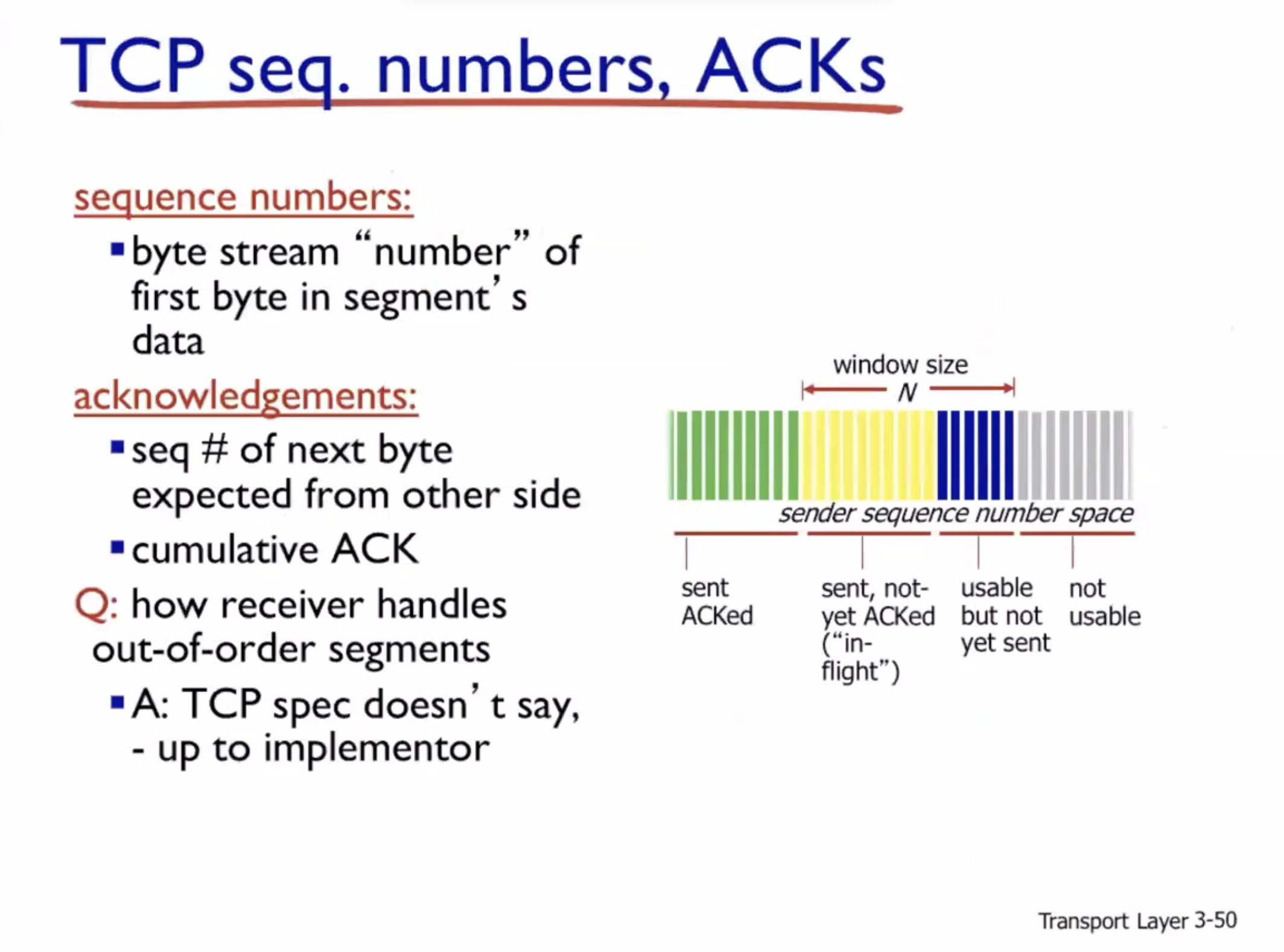
Sequence number example:

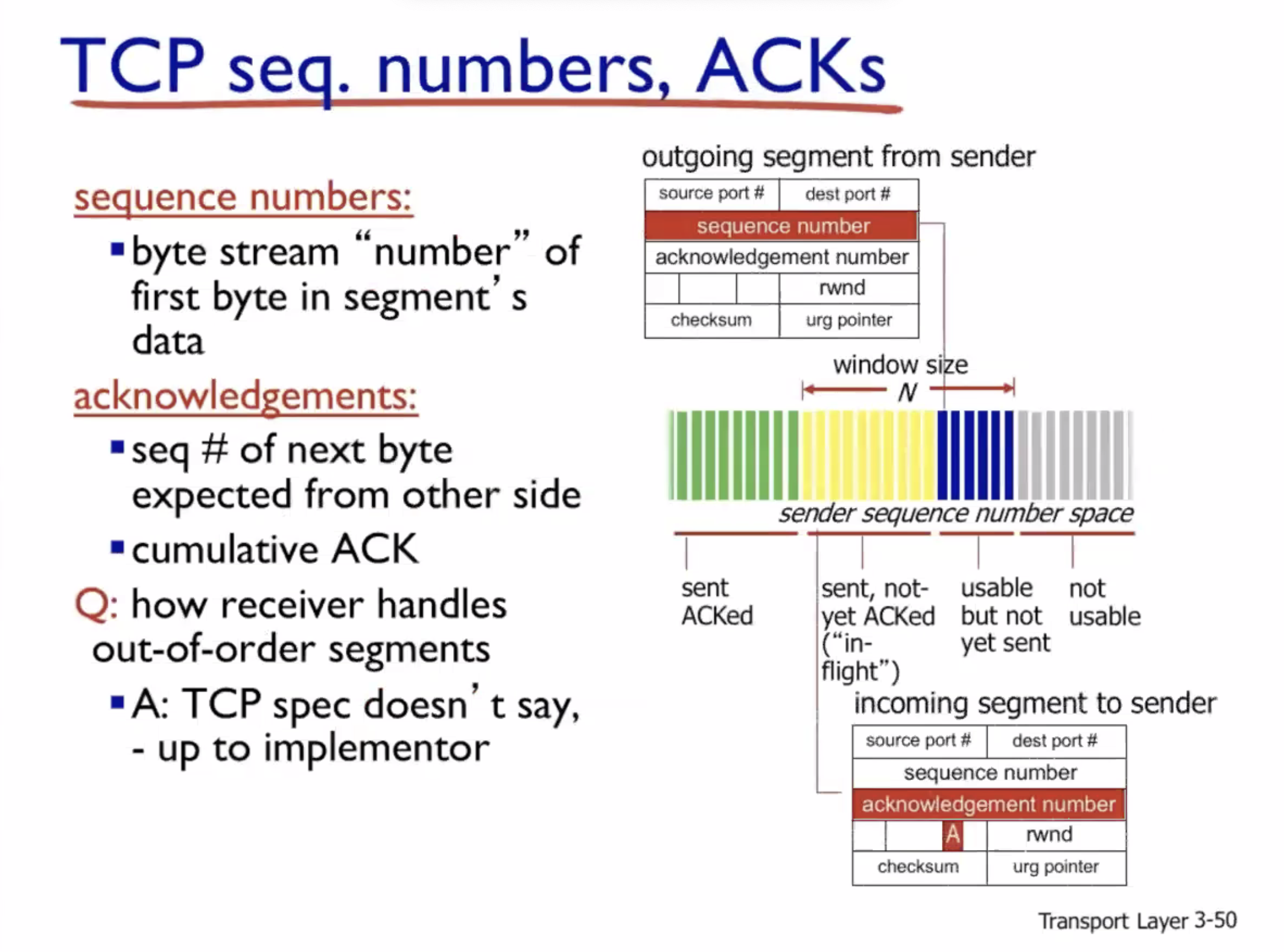
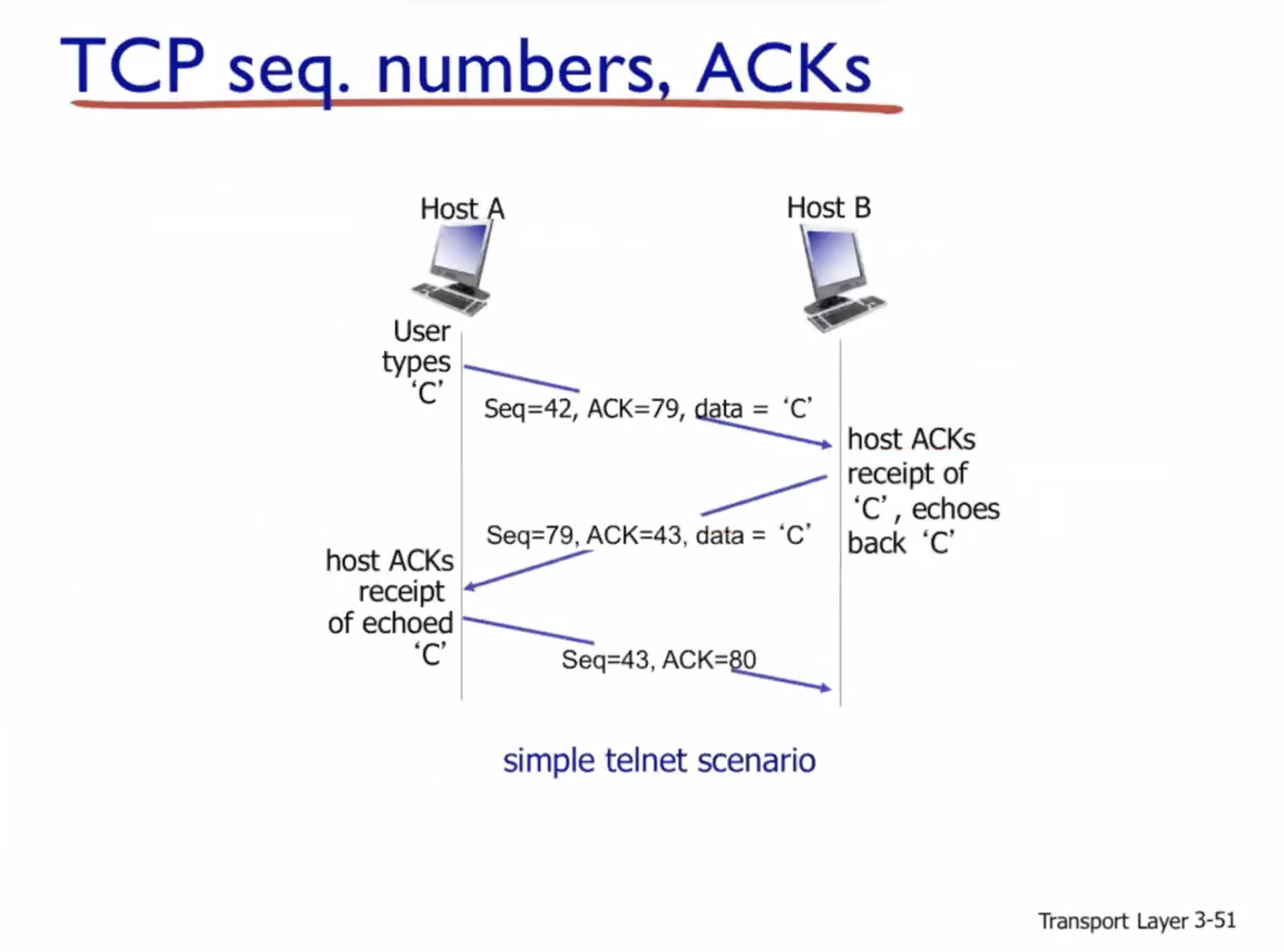
Both sides randomize the sequence number they will use at the beginning.
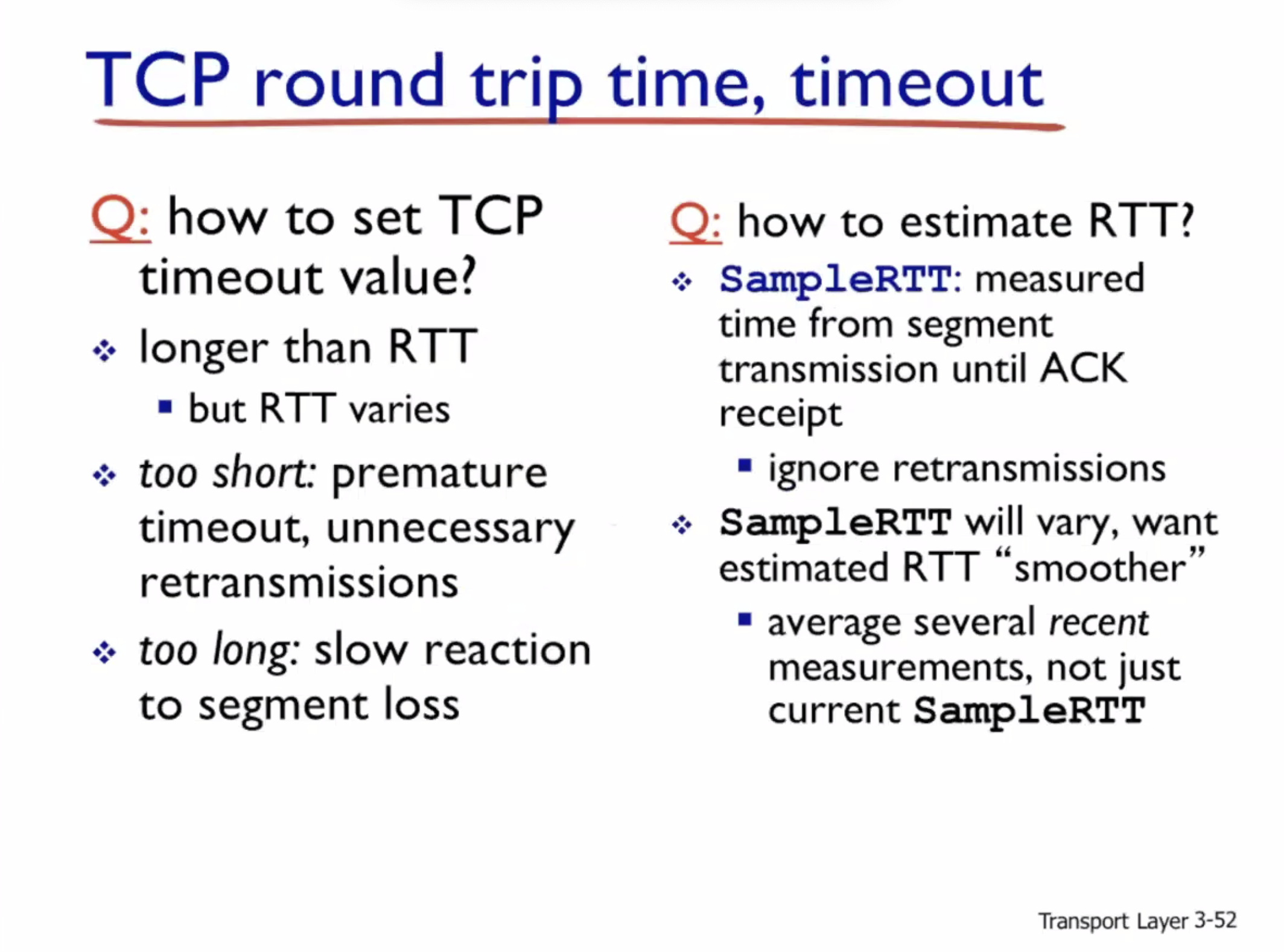
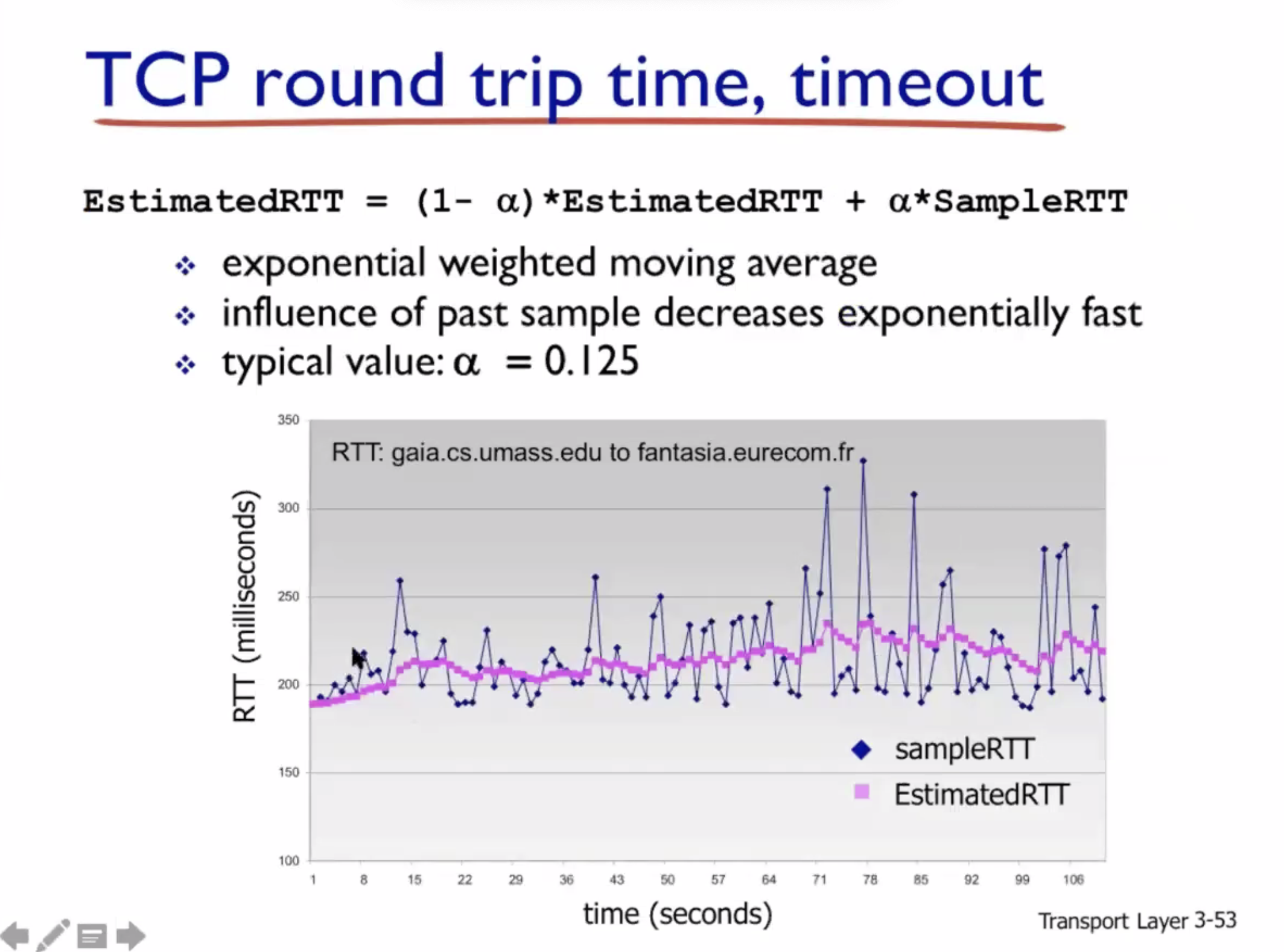
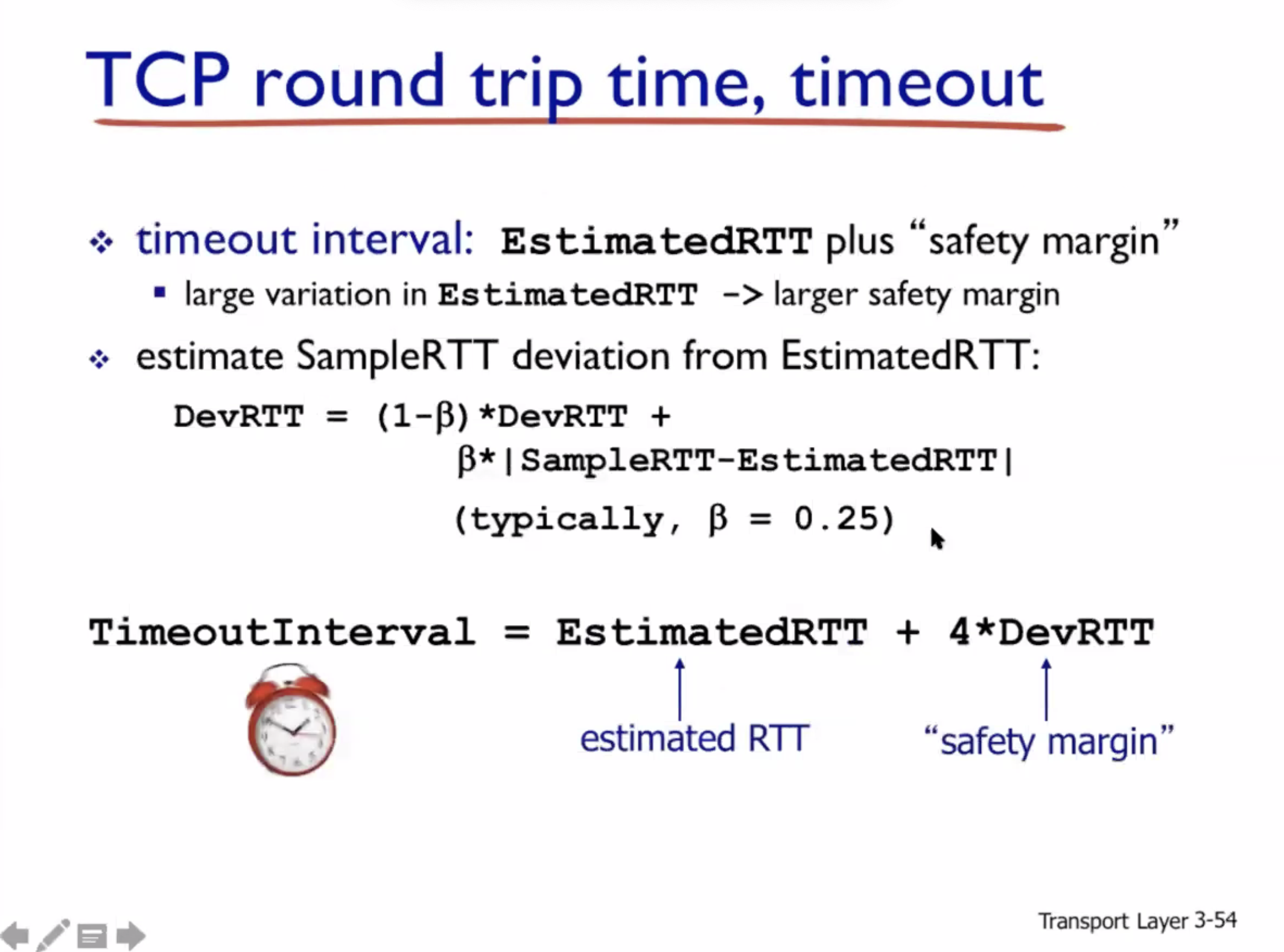
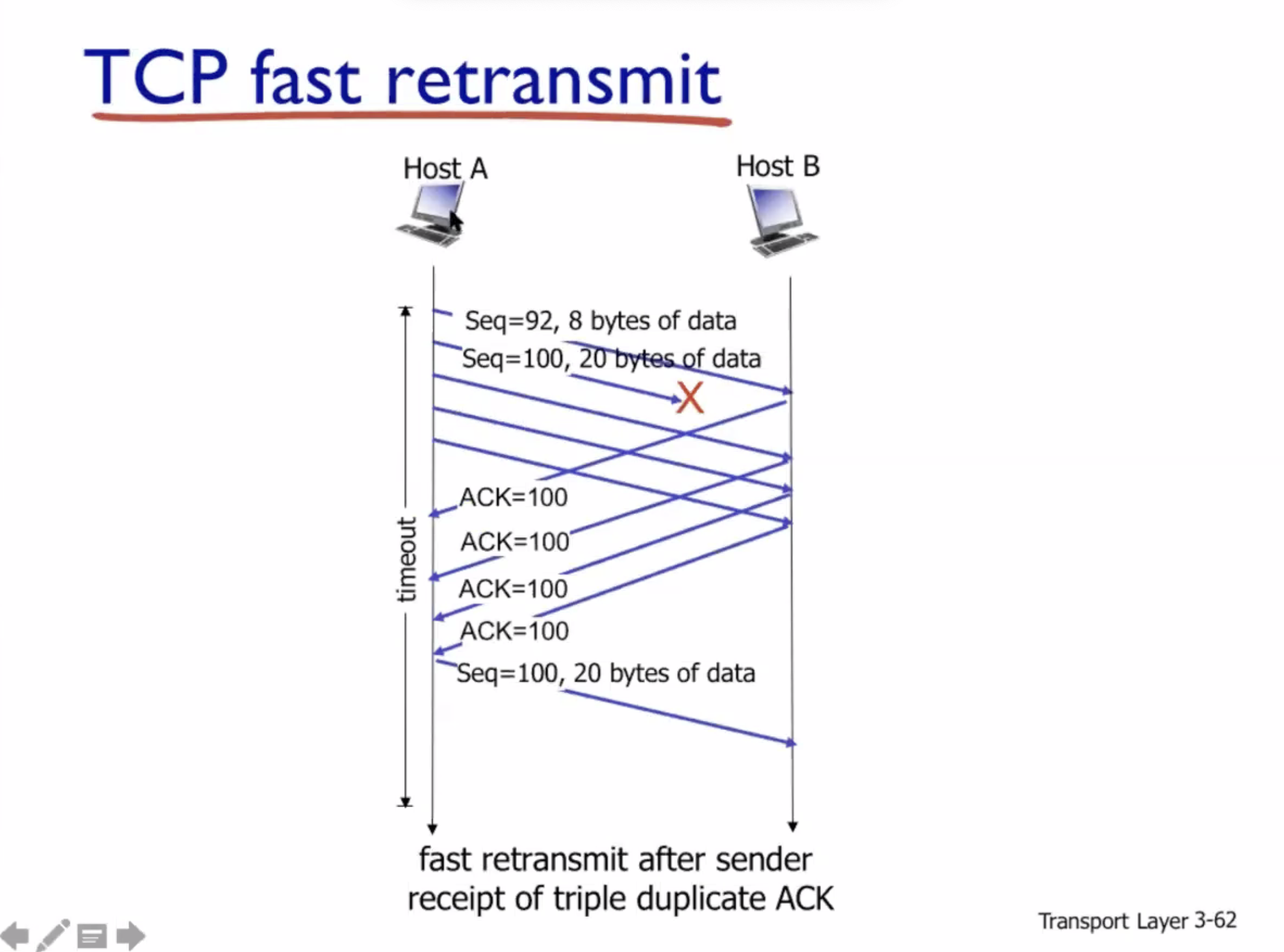
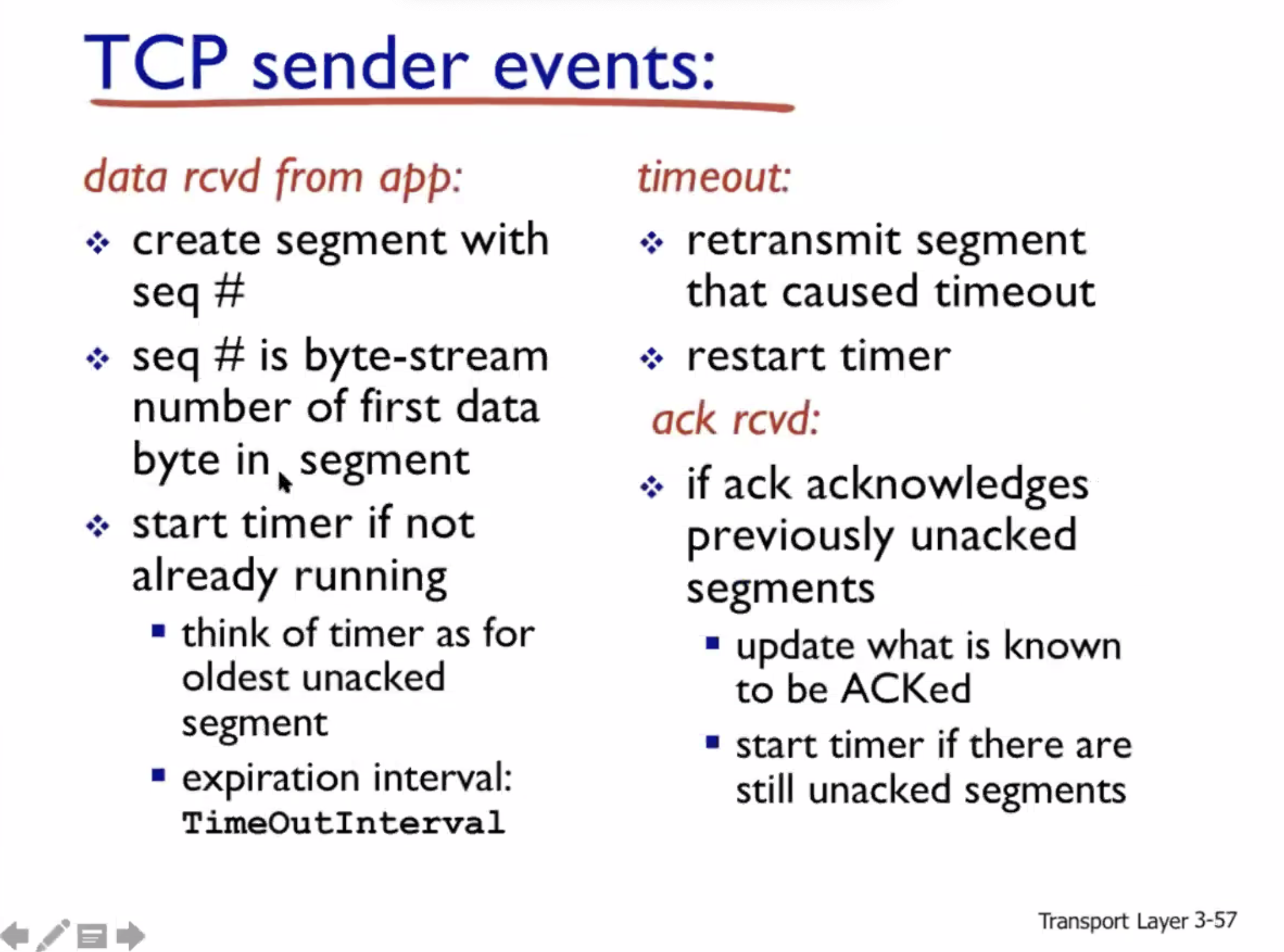
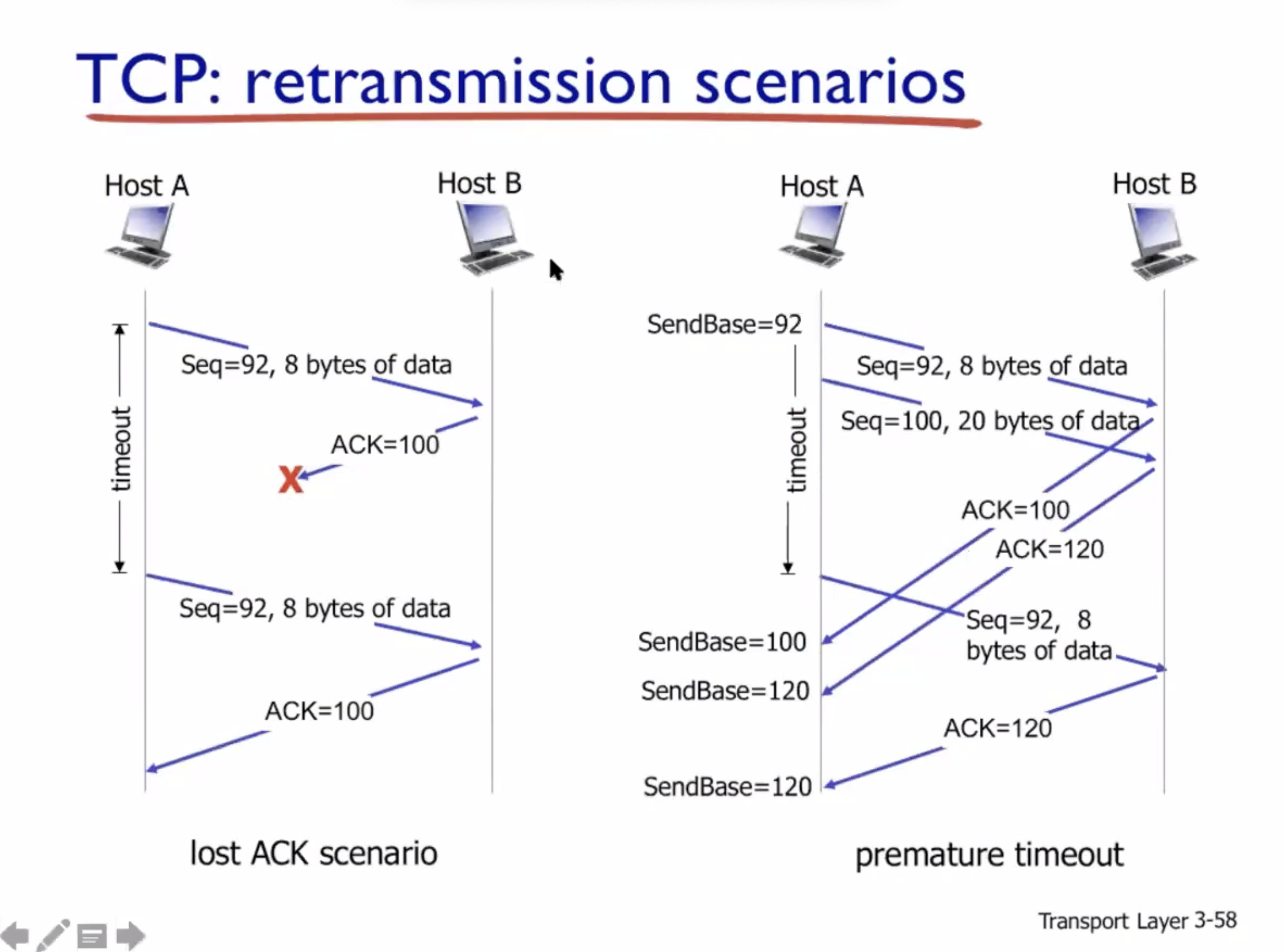
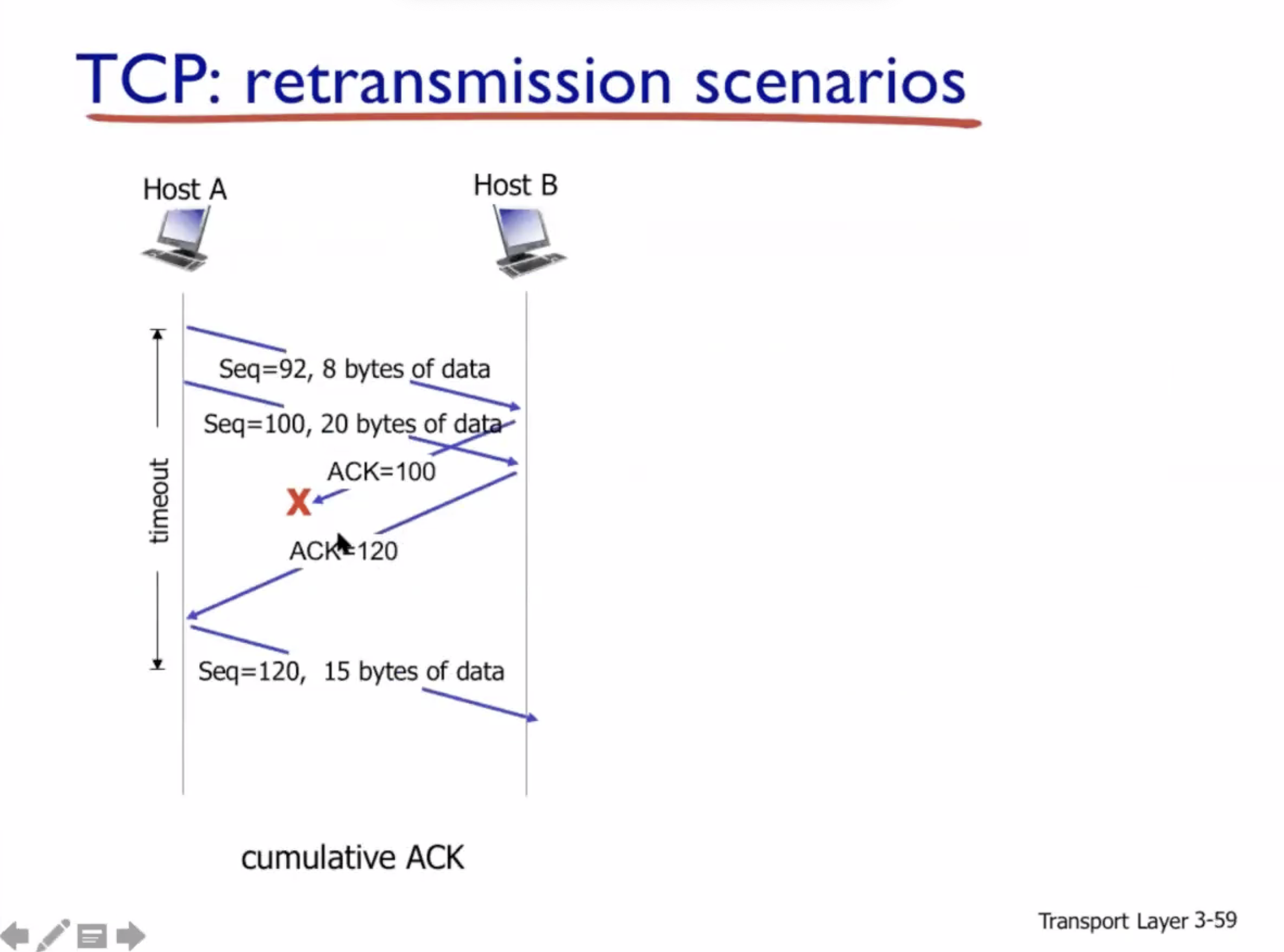
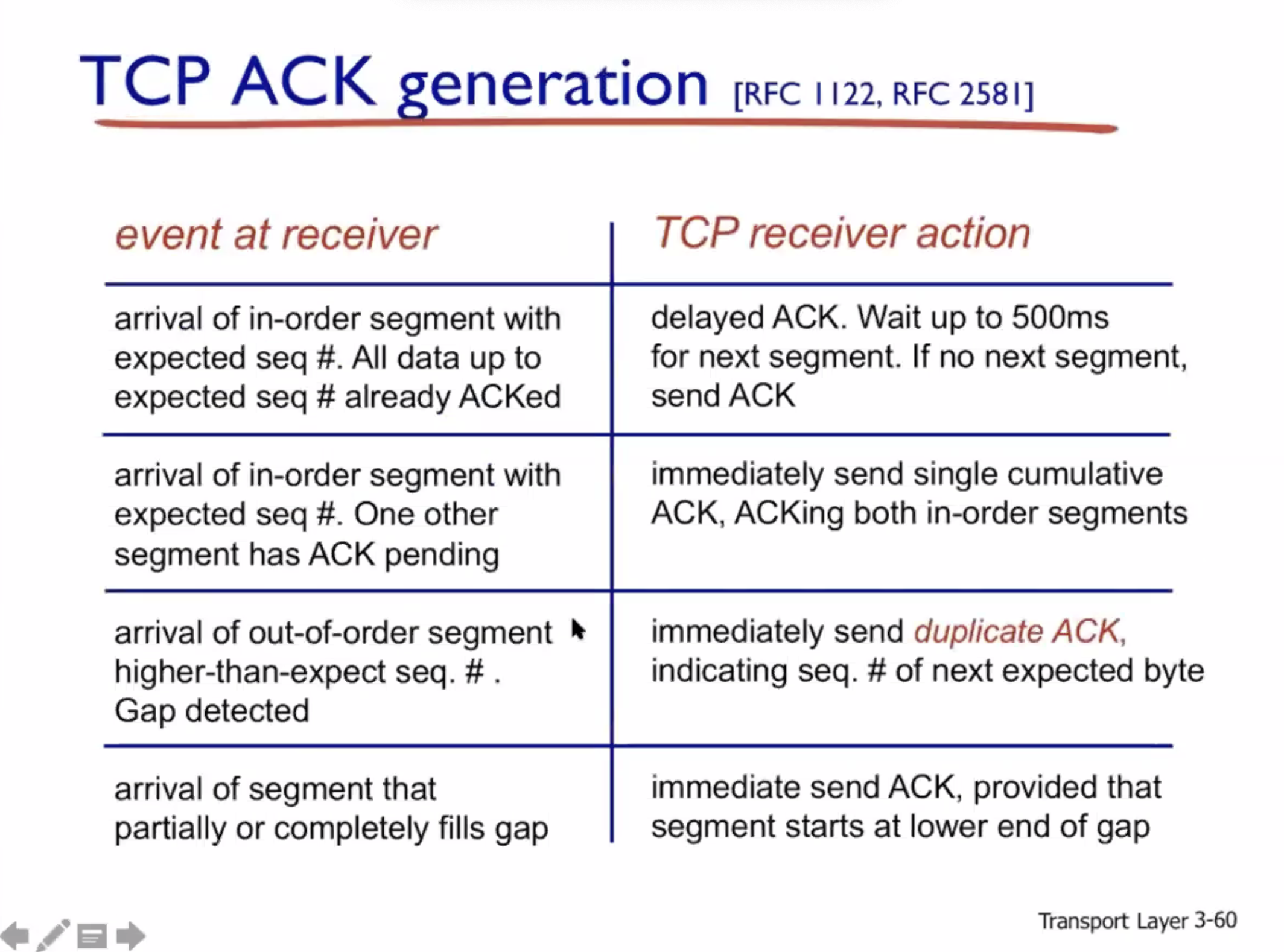
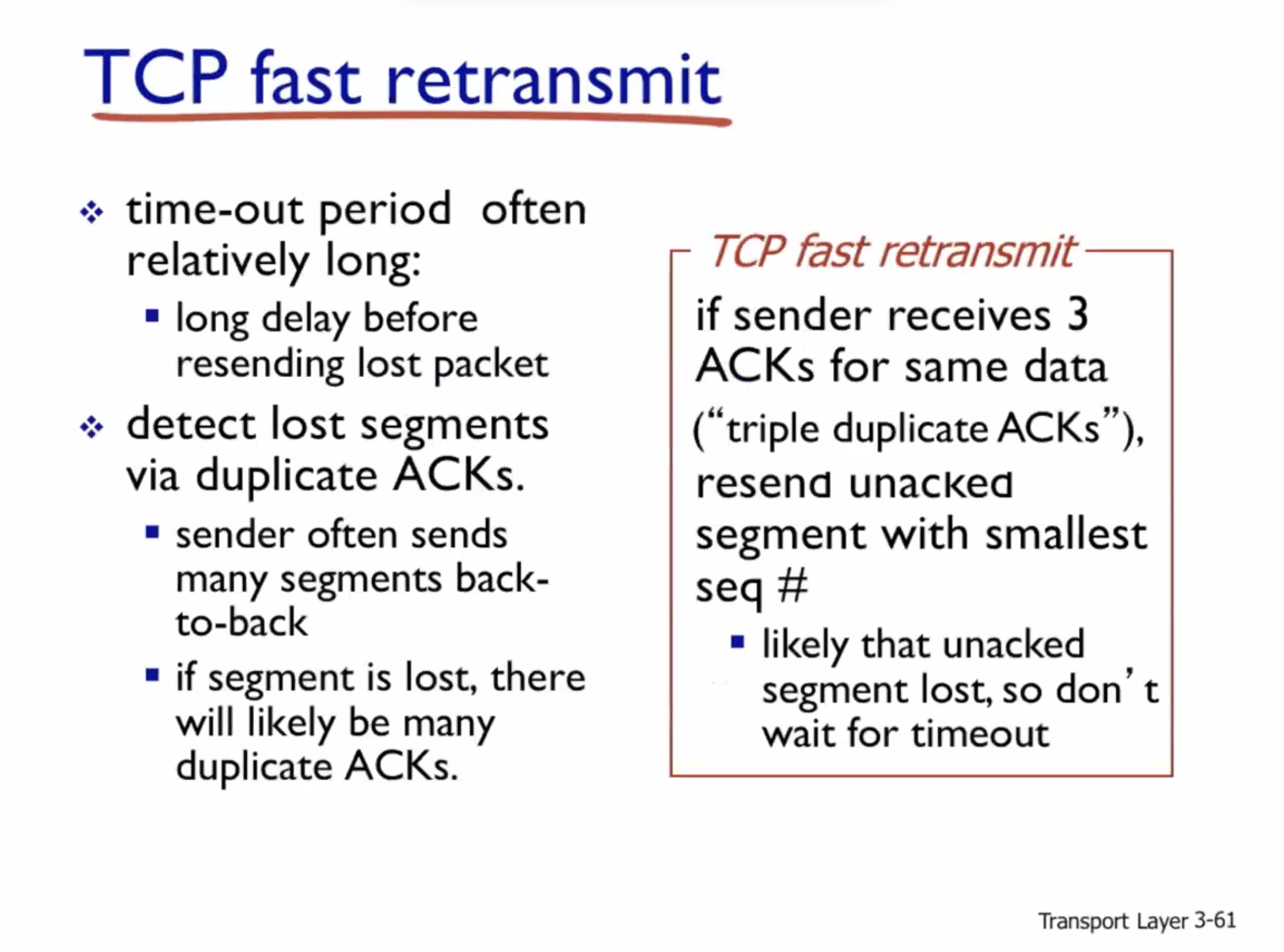
Reliable data transfer #
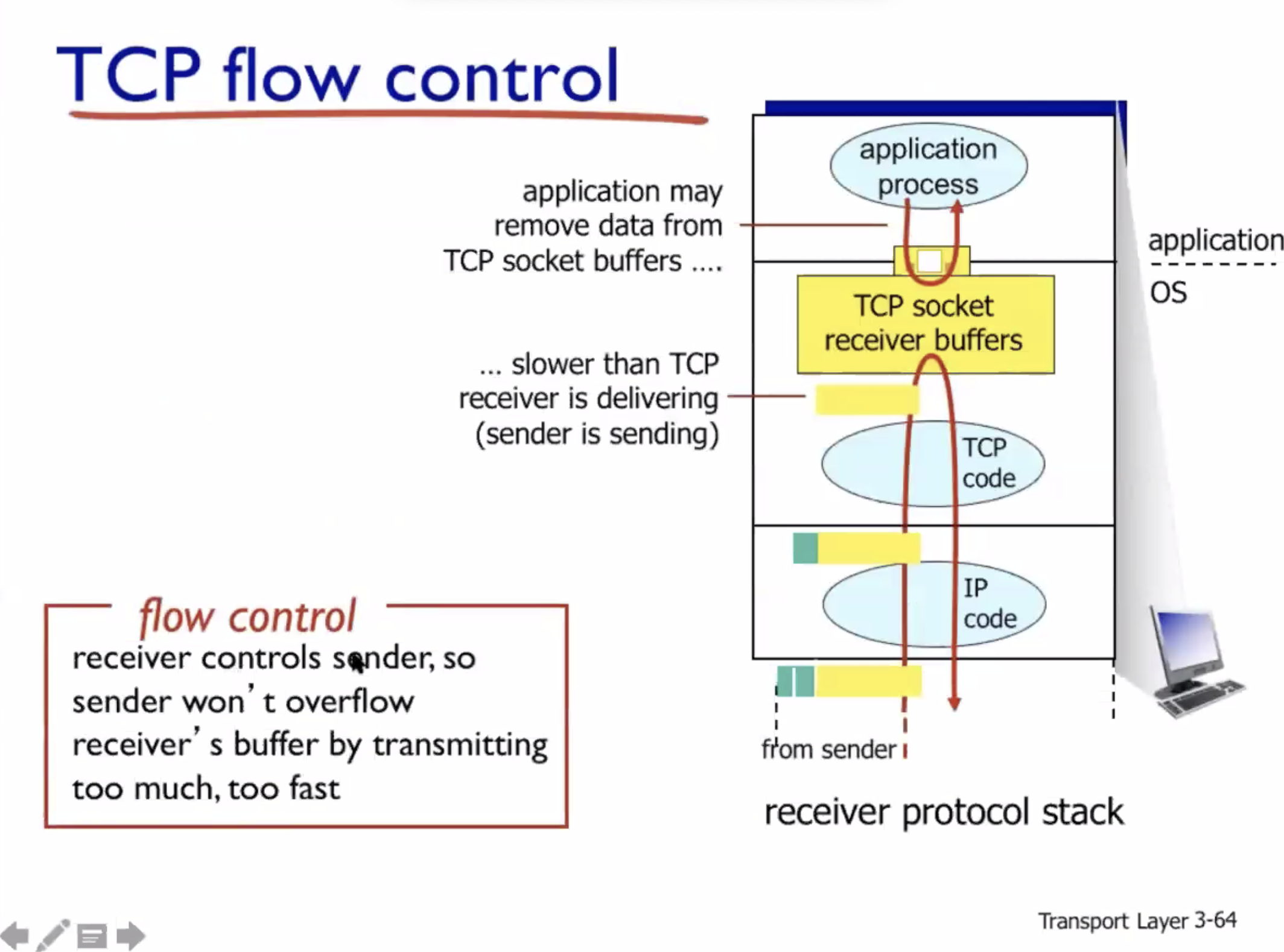
Flow control #
The difference between flow control and congestion control:
- Flow control is to make sure the receiver is not overwhelmed
- Congestion control is to make sure that the road (routers, other resources) is not overwhelmed