Review for exam #
Example question set for Ch 1-2 #
-
What are the layers in TCP/IP protocol stack?
Application, transport, network, link, physical
-
What are layers in OSI reference model?
Extra 2 layers are presentation and
-
What is the major difference between packet switching and circuit switching?
Circuit reserves some resources, packet switchings allows sharing
-
What is the difference between routing and forwarding?
Router is global, forwarding is local
-
What is the relationship between routing and forwarding?
Interplay
-
How many types of packet delay does a network have?
4, nodal processing, packet transmission, propagation delay, queueing delay
-
Which tool/utility/program can be used to find out the IP address of the routers on the path from one source and destination?
traceroute -
Which tool/utility/program can be used to intercept and analyze network packets?
Wireshark
-
On which layer is SSL/TLS implemented for network security?
Application layer
-
What does DDoS mean?
Distributed denial of service
-
Among HTTP, FTP, SMTP, DNS, which protocols use TCP?
HTTP, FTP, SMTP
-
What are the service port numbers for HTTP, FTP, SMTP, DNS respectively?
80, 21/20, 25, 53
-
What is the major difference between persistent and non-persistent modes of HTTP?
Persistent allows one connection to be shared by multiple object transmissions. Non-persistent must have a connectino for each object transmission.
-
What is the major difference between Client/Server model and P2P model?
Client/server has an always on server, P2P doesn’t have a server (everyone is a peer)
-
Where is URL specified in HTTP request format?
In the first line (the request line) of request format
-
Where is the status code specified in HTTP response format?
In the first line, the status line
-
Is web cache a client or server for the original browser who sent the request to get one object?
Server
-
What benefits come from the conditional get technology? (at least 2 examples)
No object transmission delay, lower link utilization
-
What is the major difference between SMTP and POP/IMAP?
Push versus pull
-
What is the format for DNS resource records? (RR)
Name, value, type, TTL
-
Among the socket library functions, what are used by TCP and what are used by UDP?
TCP: UDP:
-
What is the major difference between TCP and UDP?
TCP has a handshake, and is reliable. UDP is non-reliable
True or false questions #
- Internet is a single network? (F)
- DNS runs on routers as it’s a network core function. (F)
- A network alyer does not need to rely on any service from its below layer. (F)
- TCP is a protocol on Application layer. (F)
- FDM/TDM is a pcket switching protocol (F)
- It’s impossible to have packet loss as the network is supposed to guarantee reliability (F)
- All the packet headers are added to data at application layer when the data leaves the application program (F)
- Routers support all seven layers of the OSI reference model (F)
- SMTP is a P2P protocol and there is no client in its communications (F)
- SMTP is a pull protocol (F)
Long answer questions #
- Cookie scenario in slides of ch. 1. How many components to make cookie system function? What are they respectively? What are their functionalities respectively? Especially, what cookie header lines in the first HTTP response message and next HTTP request messages?
There are four functions. Cookie on client, database on server, header line with cookie ID, header line from server. Database on server side contains all the info, cookie contains the ID, all future client/server messages have ID in headers.
- To insert resource records into DNS, what steps are needed? What RRs are inserted? Refer to the slides in Ch. 2

- What are the functions related to TCP and UDP socket programming?
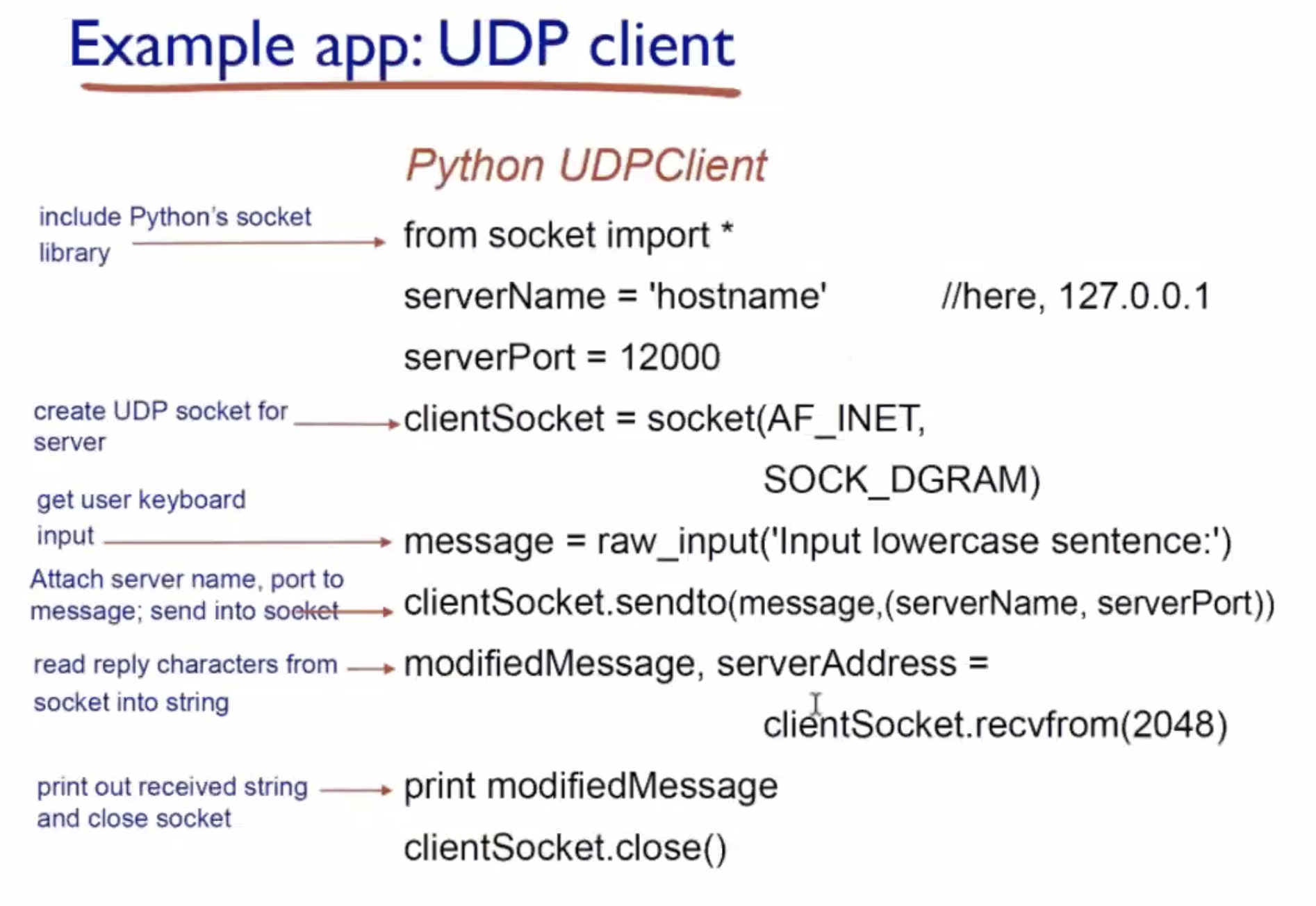
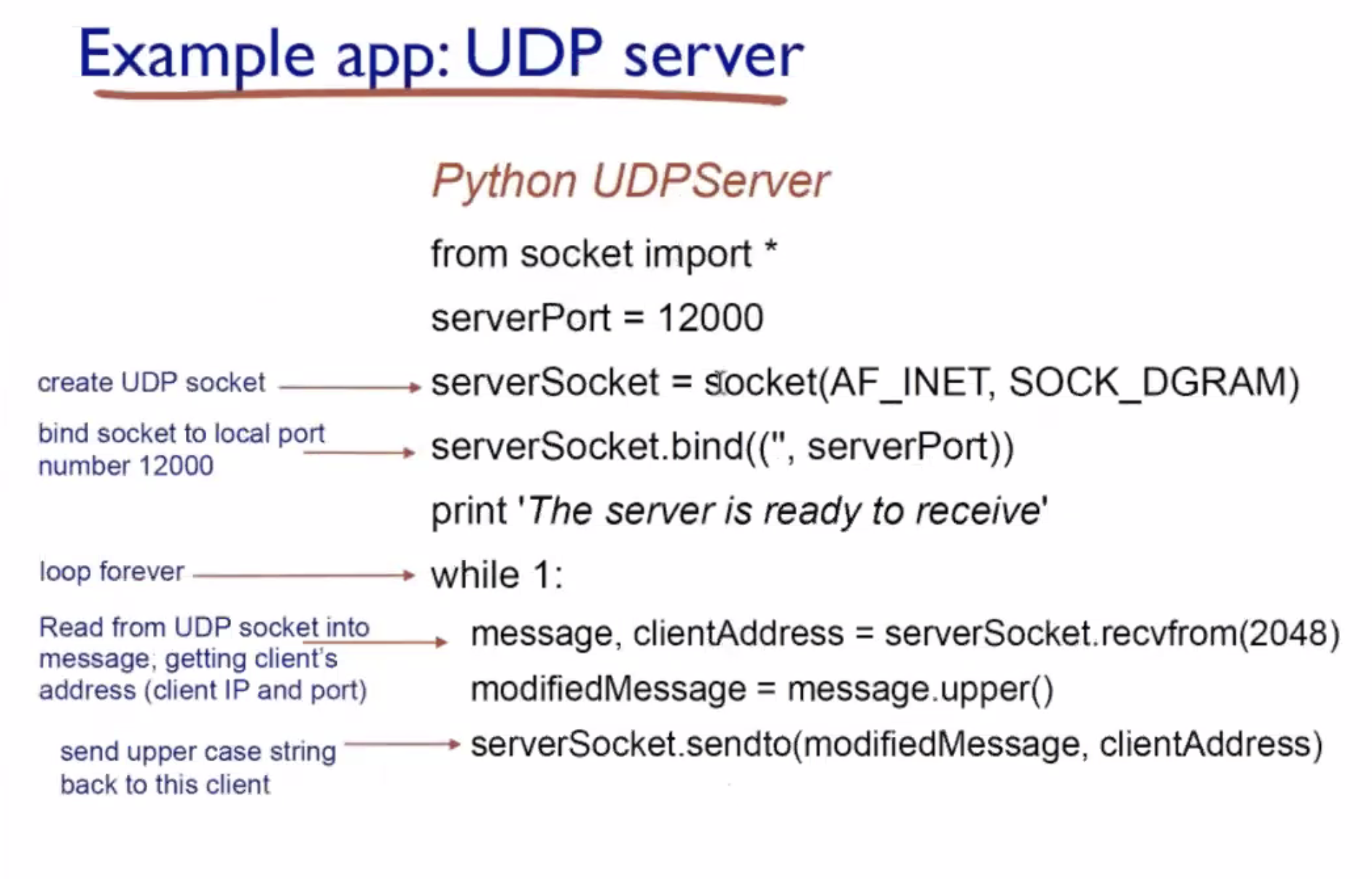
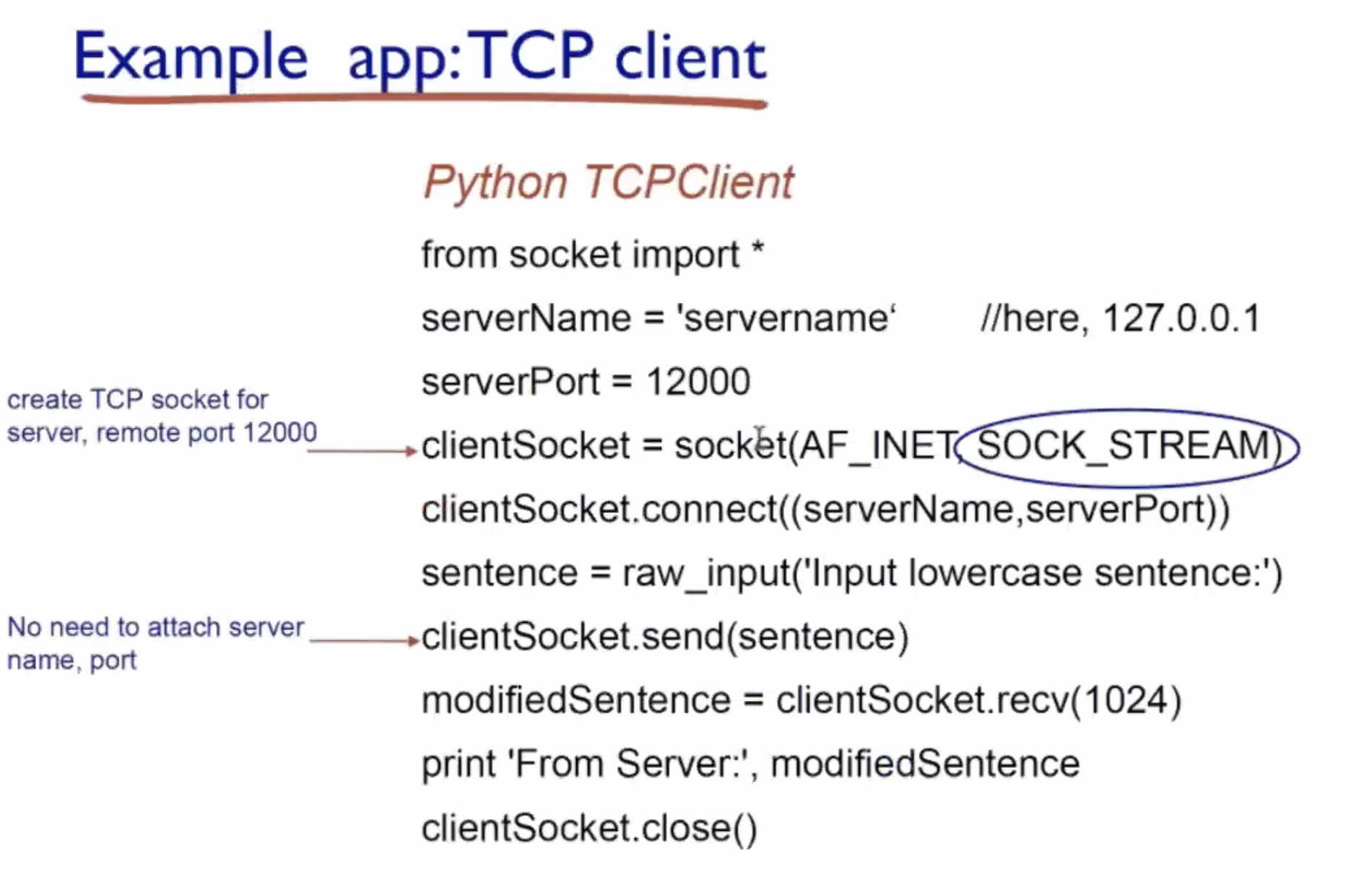
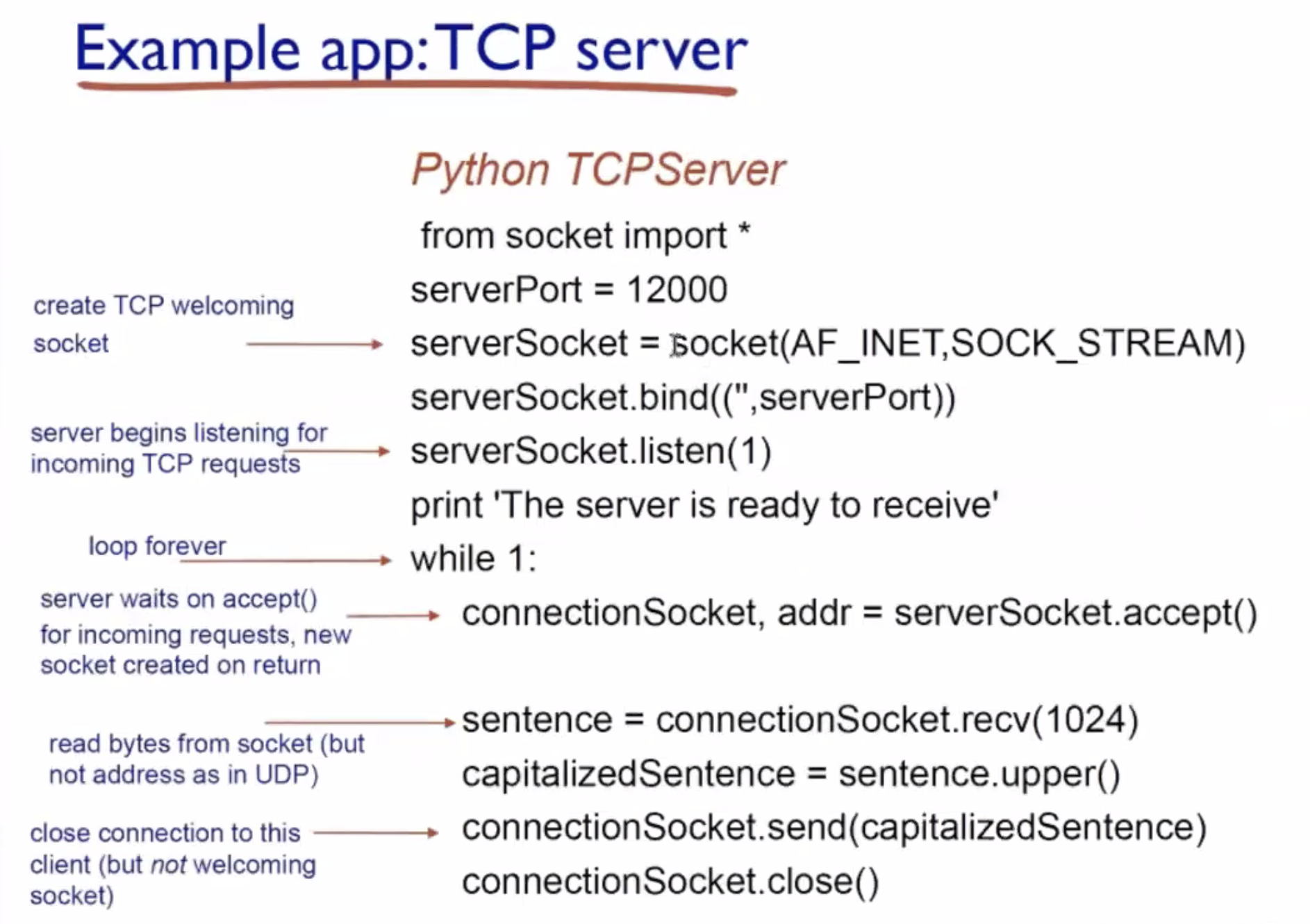
UDP cont. #


If packet isn’t lost:
sequenceDiagram participant S as Sender participant R as Receiver S ->> R: send pkt 0 R ->> S: ack 0 S ->> R: pkt 1 R ->> S: ack 1 S ->> R: pkt 0
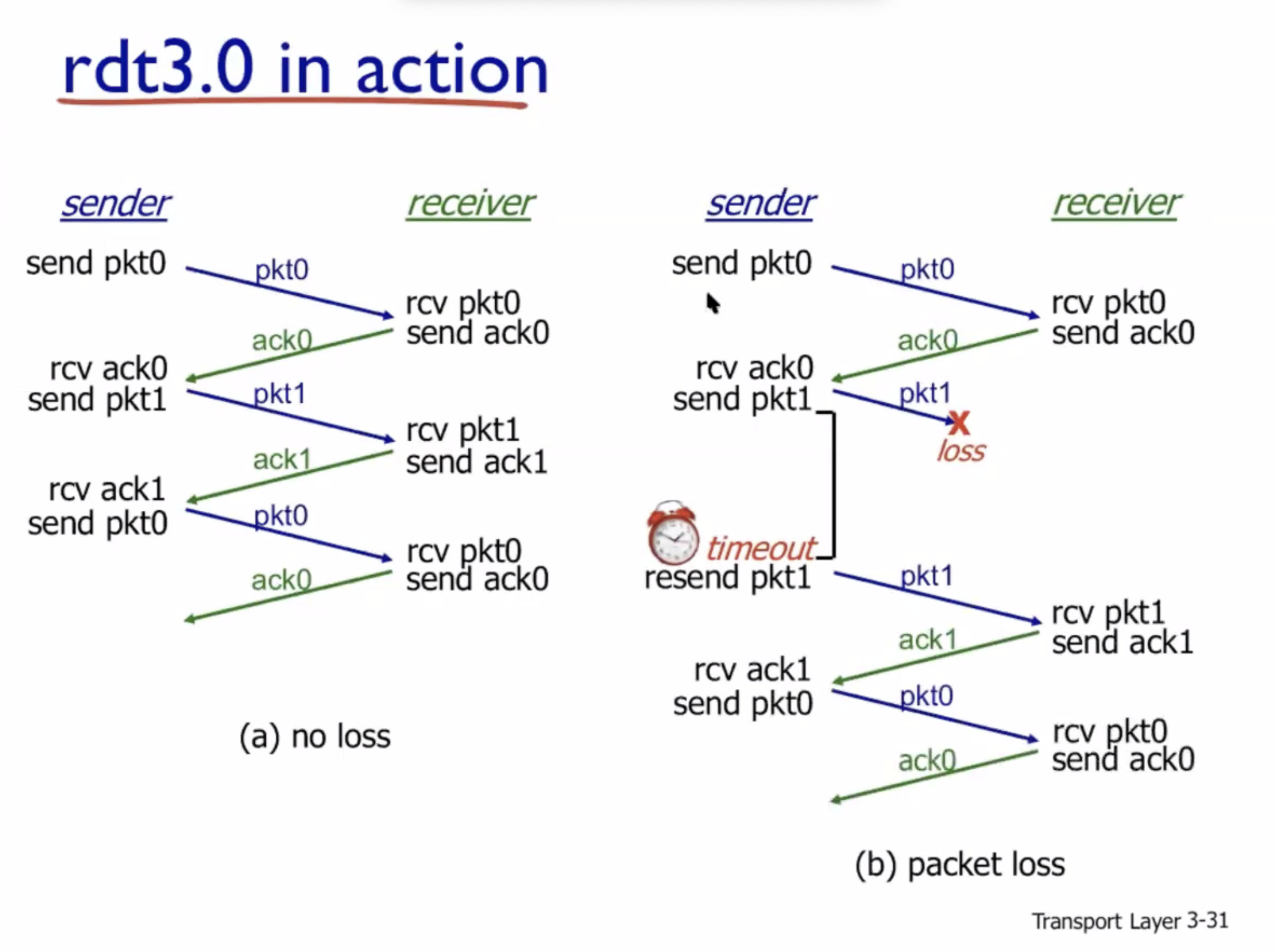
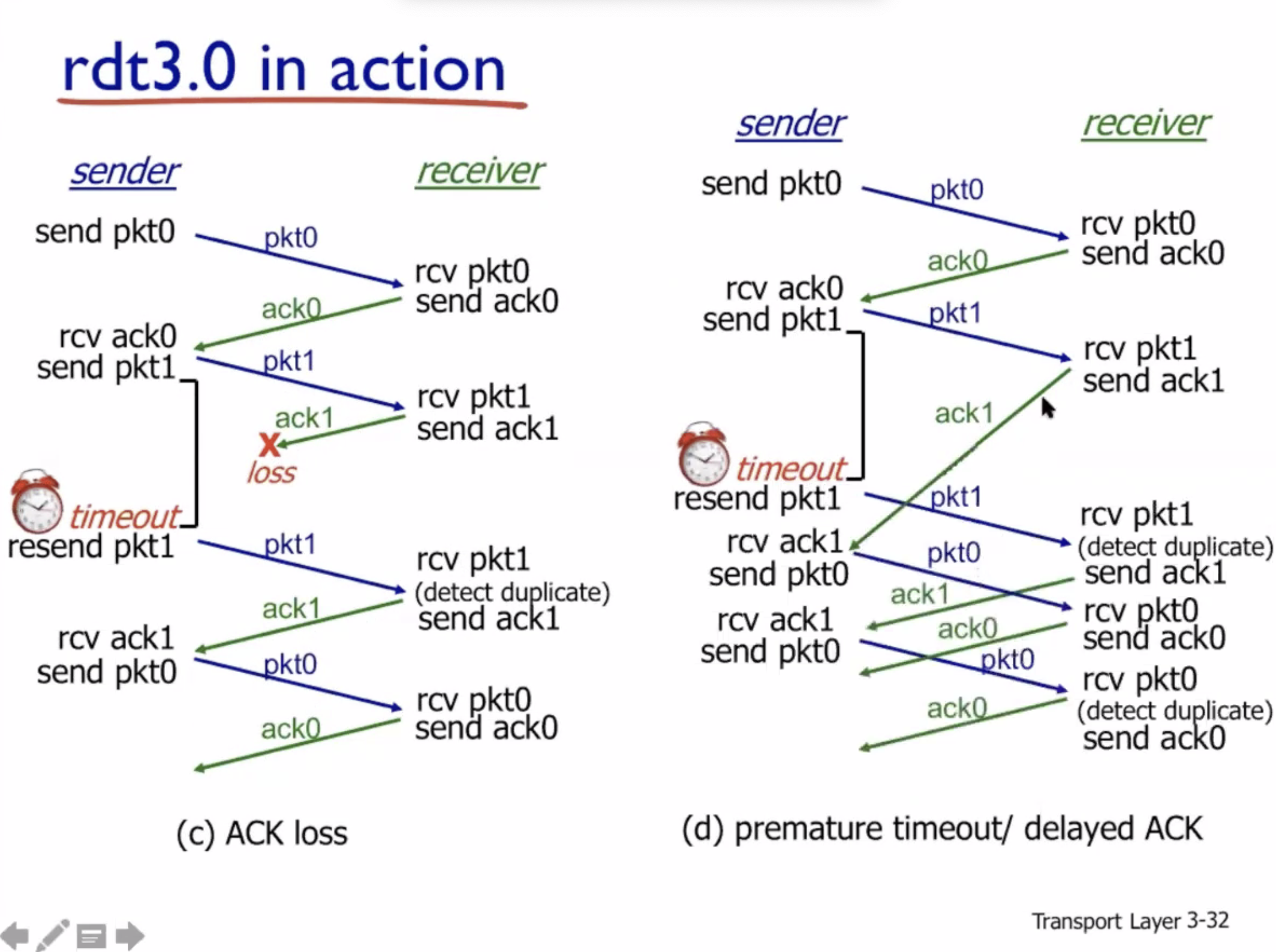
In case d, the functionality still works but the performance is poor, because each packet is transmitted twice after the first premature timeout.
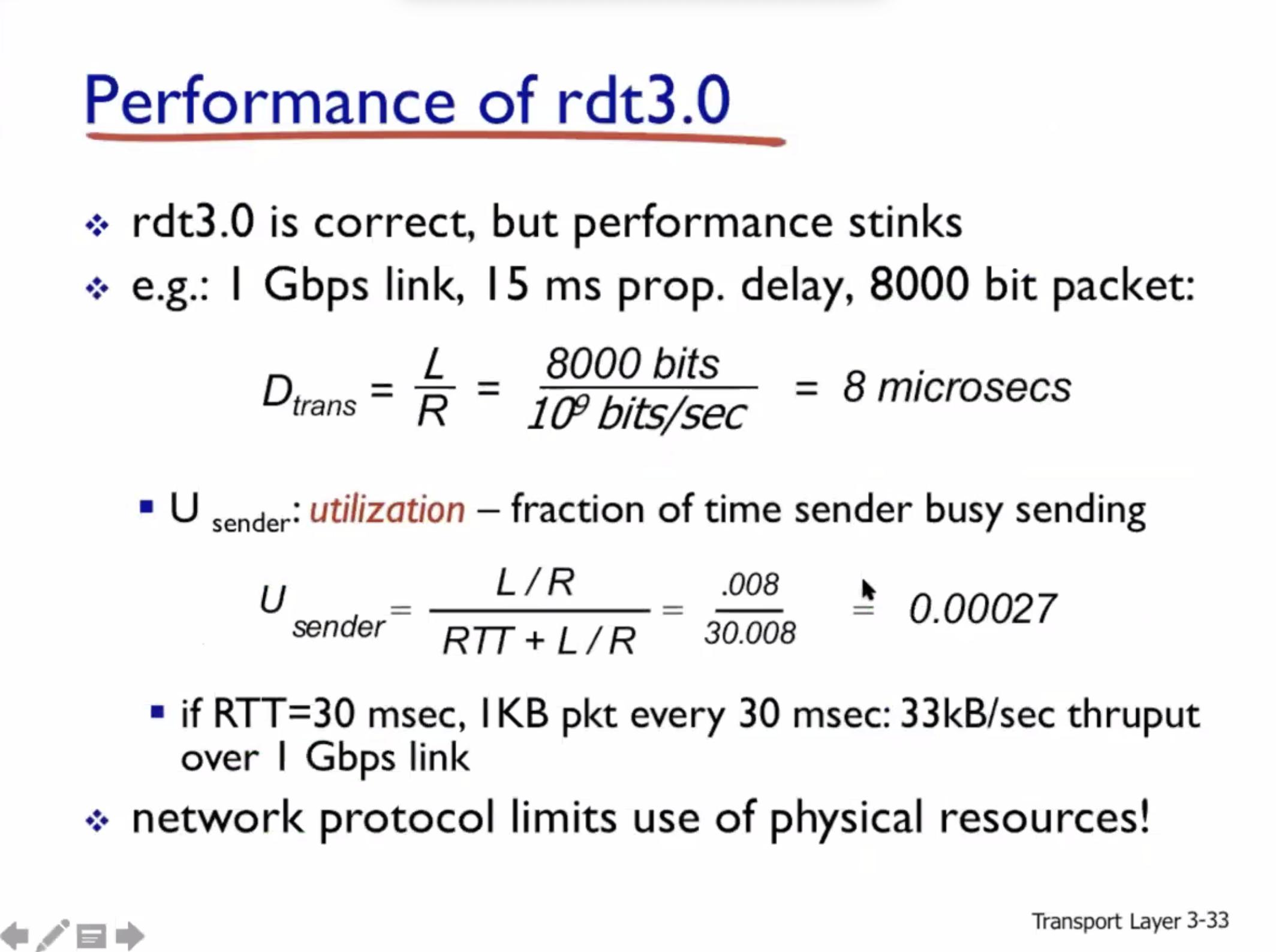
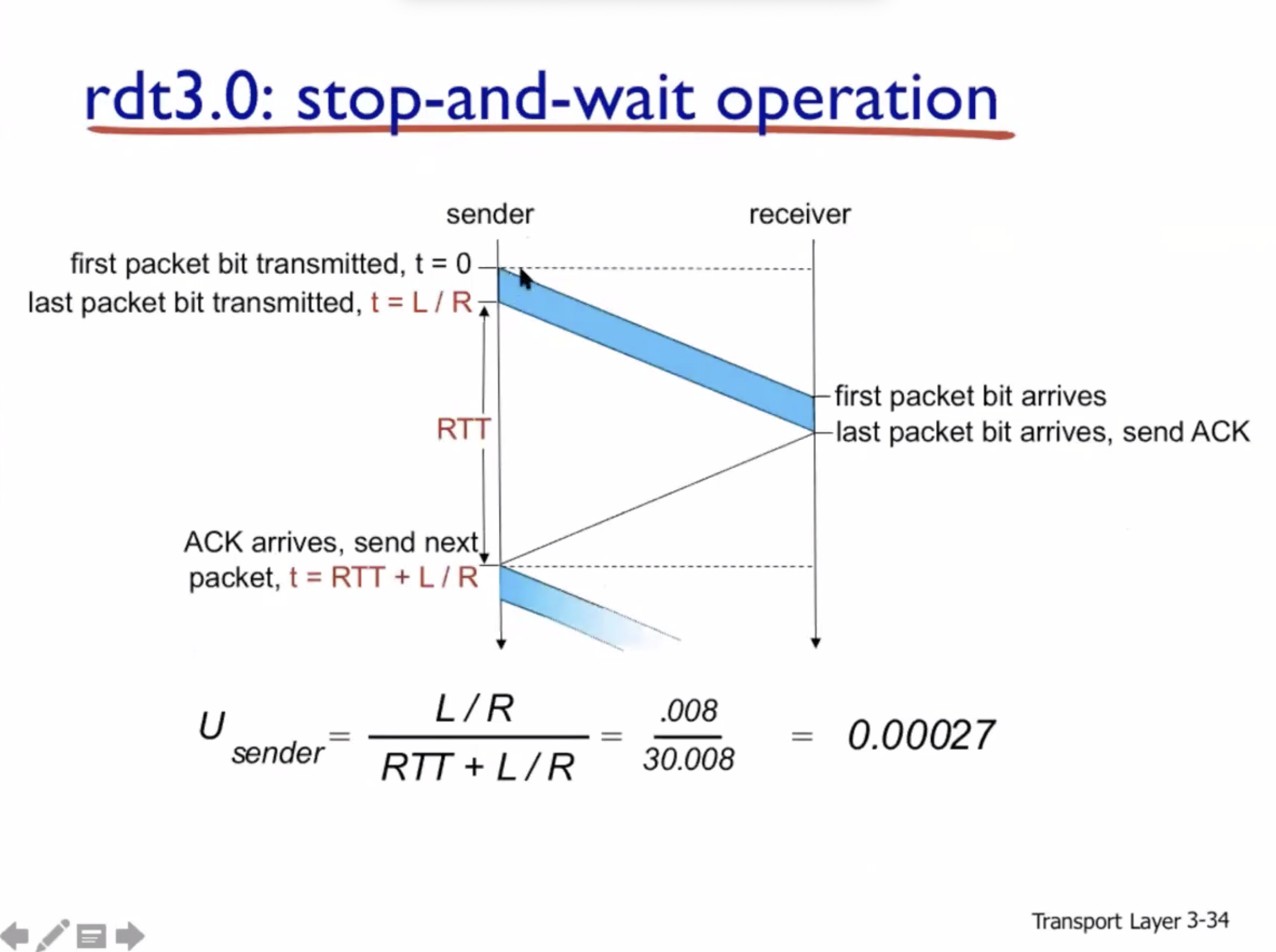
RTT = round trip time