Sequential Circuits #
In combinational circuits, the outputs are only dependent on the inputs. In sequential circuits, the outputs depend on the inputs, and the previous state of the circuit.
Core modules #
S-R Latches
- Latches are basic building blocks of flip-flops (basic memory unit)
- A 1 bit latch will store 1 bit, 4 bit latch stores 4 bits, and so forth …
- Two types of memory elements based on the type of trigger that is suitable to operate
- Latches, asynchronous
- Latches operate with an enable signal, which is level sensitive
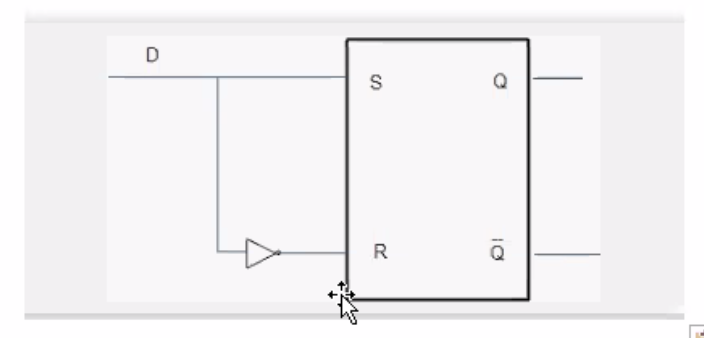
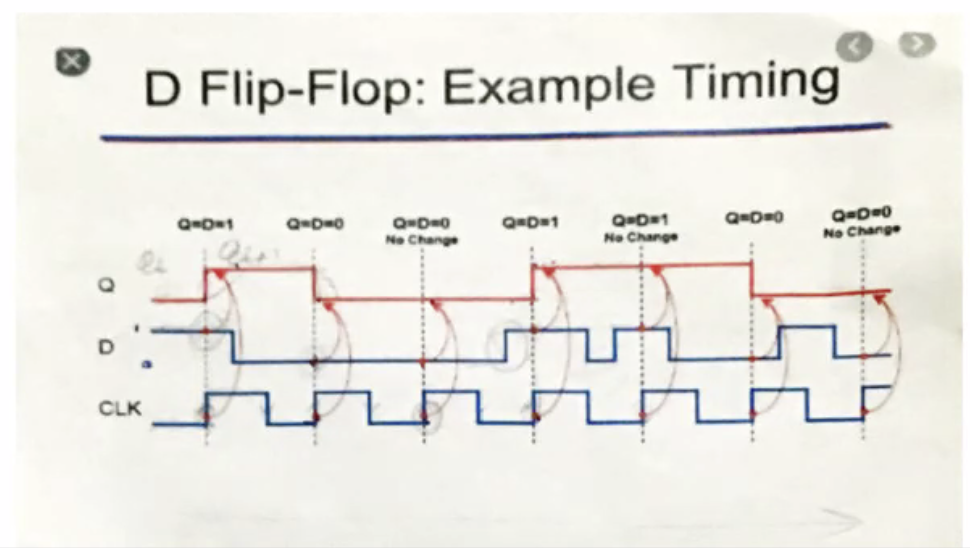
D flip-flop
- Basic memory storage device
- Block diagram of a D flip flop
- Flip flops, synchronous (the device samples its input based on a common clock)
- Flip flops are edge sensitive
- Doesn’t sample an input unless a clock comes in, clock signal needed to change states
- D flip flops is designed using S-R latches
- Similar to S-R latch, only we use set and reset function. (Ties D input to S and NOT D to R).
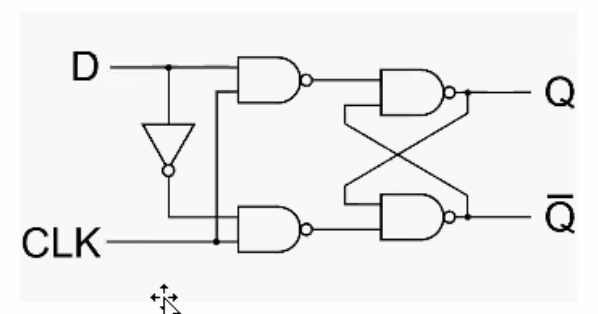
S-R flip flop with NOR gates #
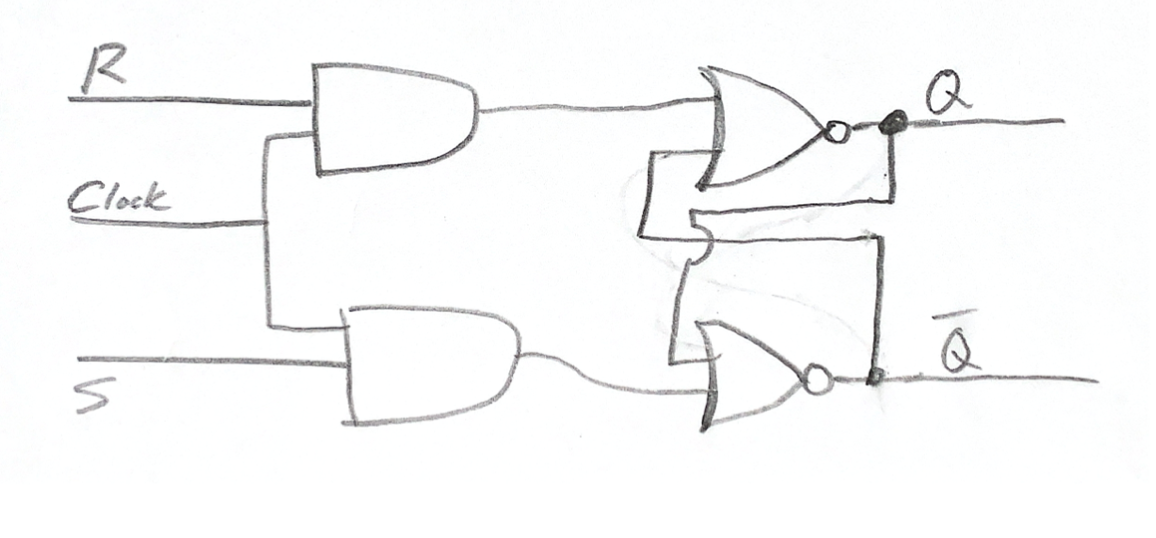
| \( S \) | \( R \) | \( Q_t \) | \( Q_{t+1} \) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | ||
| 0 | 1 | ||
| 1 | 0 | ||
| 1 | 1 | Undefined |
Finished in next lecture