DBMS cont. #
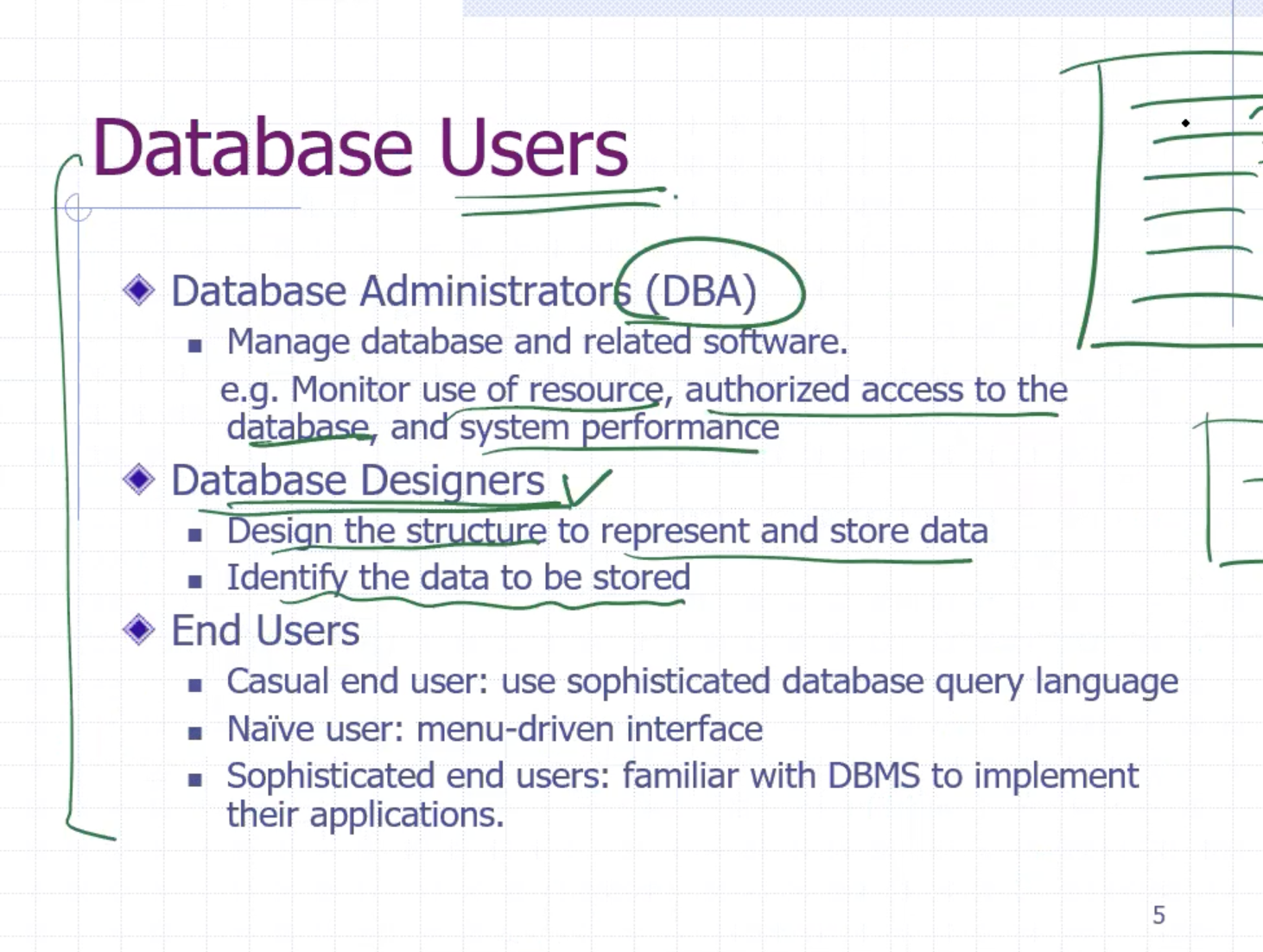
Database users #
If we’re storing student information in a database, we’ll have fields such as
- age
- birthdate
If we want to store one in the database, which should we pick? Why only one?
We should choose the birthdate because
- we can derive the age
- birthdate is also more accurate of a measure of age
- we won’t need to increment the age in the database every year
What is the disadvantage of saving both?
- we don’t want to waste space when we can derive the age from the birthdate.
- if we save both we have to make sure they are consistent. In other words: we would have to increment the age on the birthdate.
For end users:
- casual end users: need to use a sophisticated database query language, like SQL
- naive users: use a menu-driven interface
- sophisticated end users: familiar with DBMS to implement their applications
Data models #
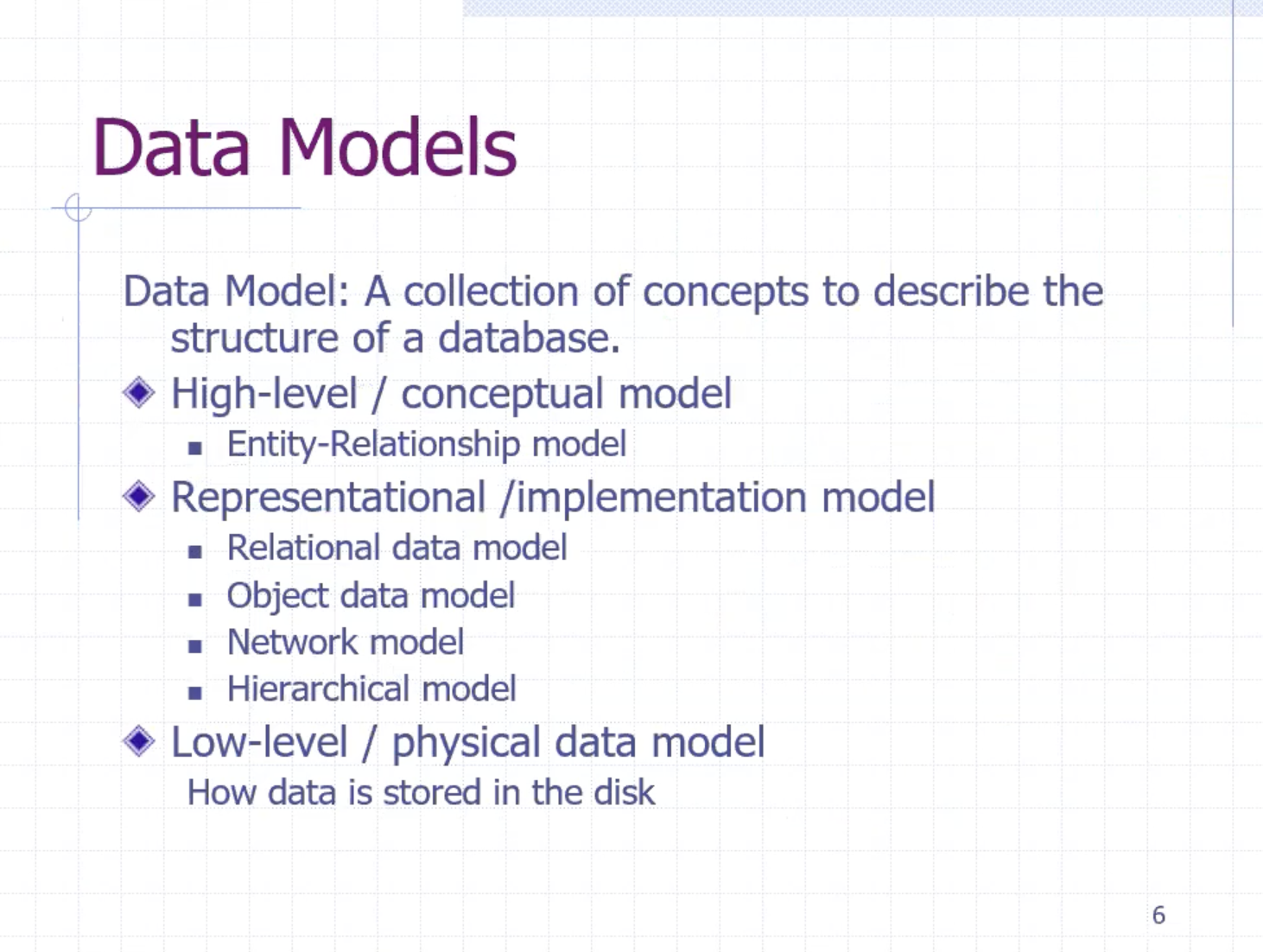
High level models
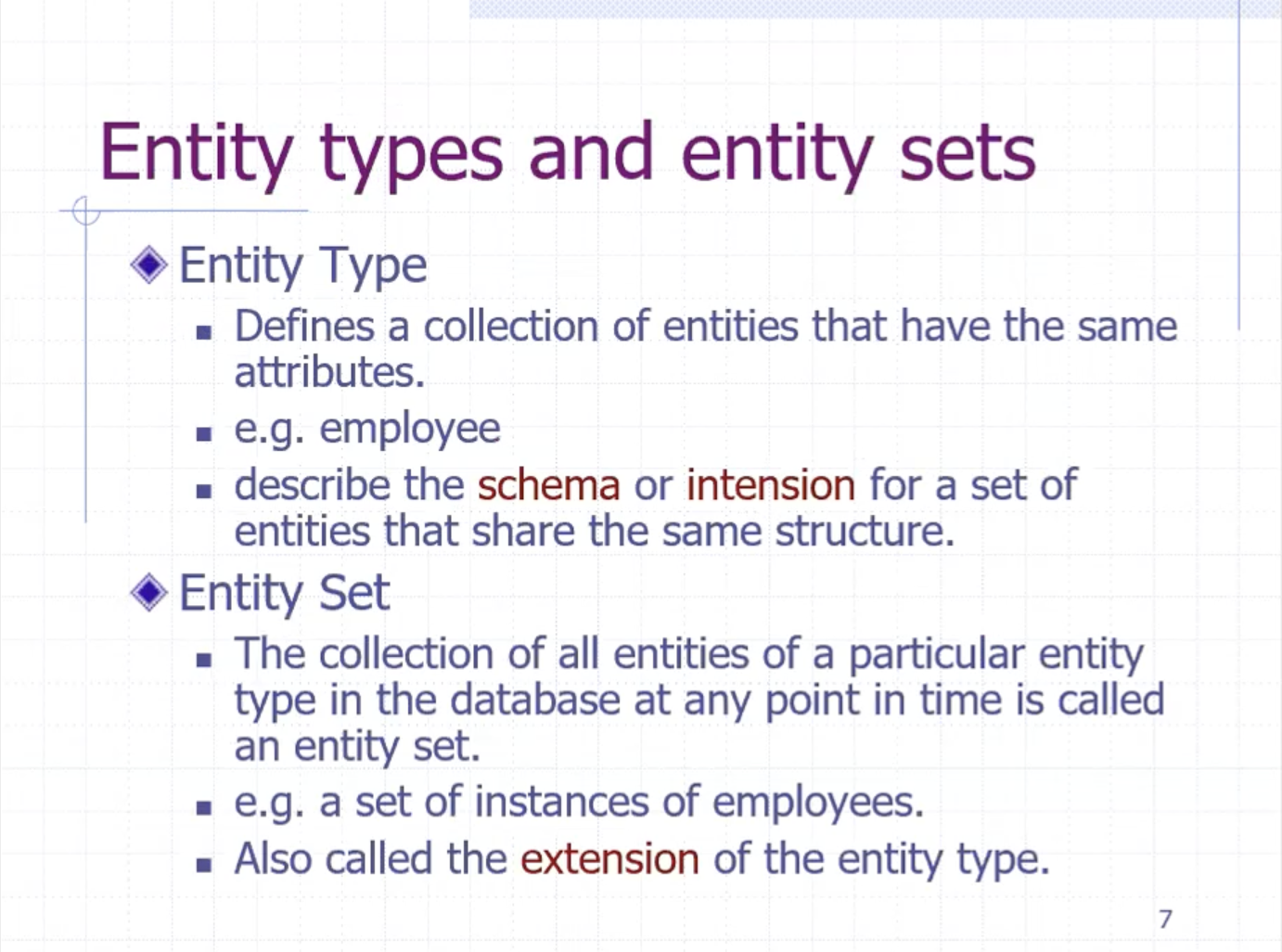
- ER, entity-relationship model, best for relational database
- UML
Representational / implementation model
- relational data model, uses relational database
- object data model, O-O, O-R
- network and hierarchical model, uses graph model
DBMS architecture and data independency #
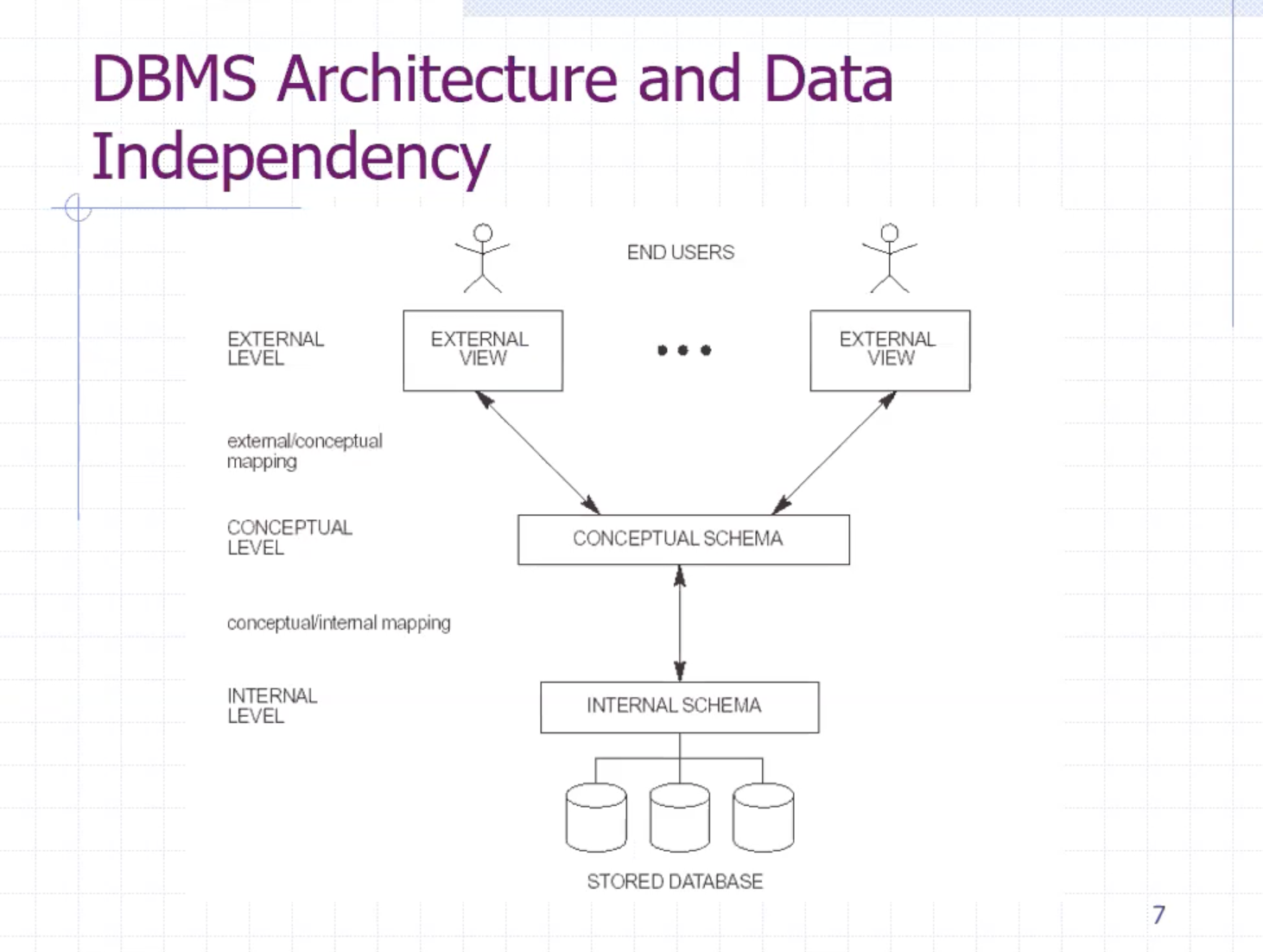
At the conceptual schema level, the user doesn’t necessarily know the exact implementation of the internal schema level.
Database languages #
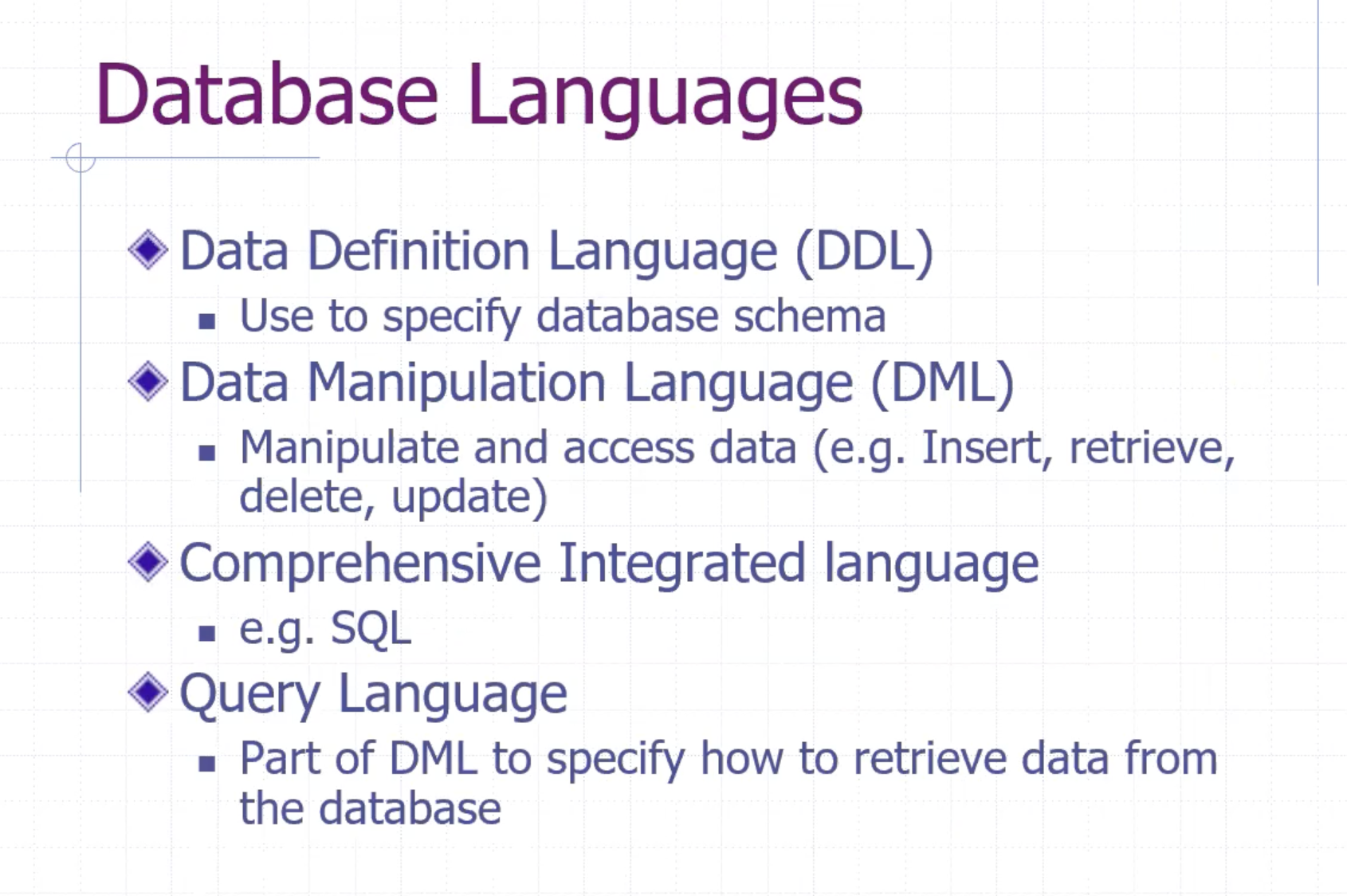
SQL is a comprehensive integrated language of DDL and DML for relational databases.
Entity-relationship model #
Note: ER diagram notation can change based on different textbooks. We will use the original notation that is used in our text book.
Entity and attributes #

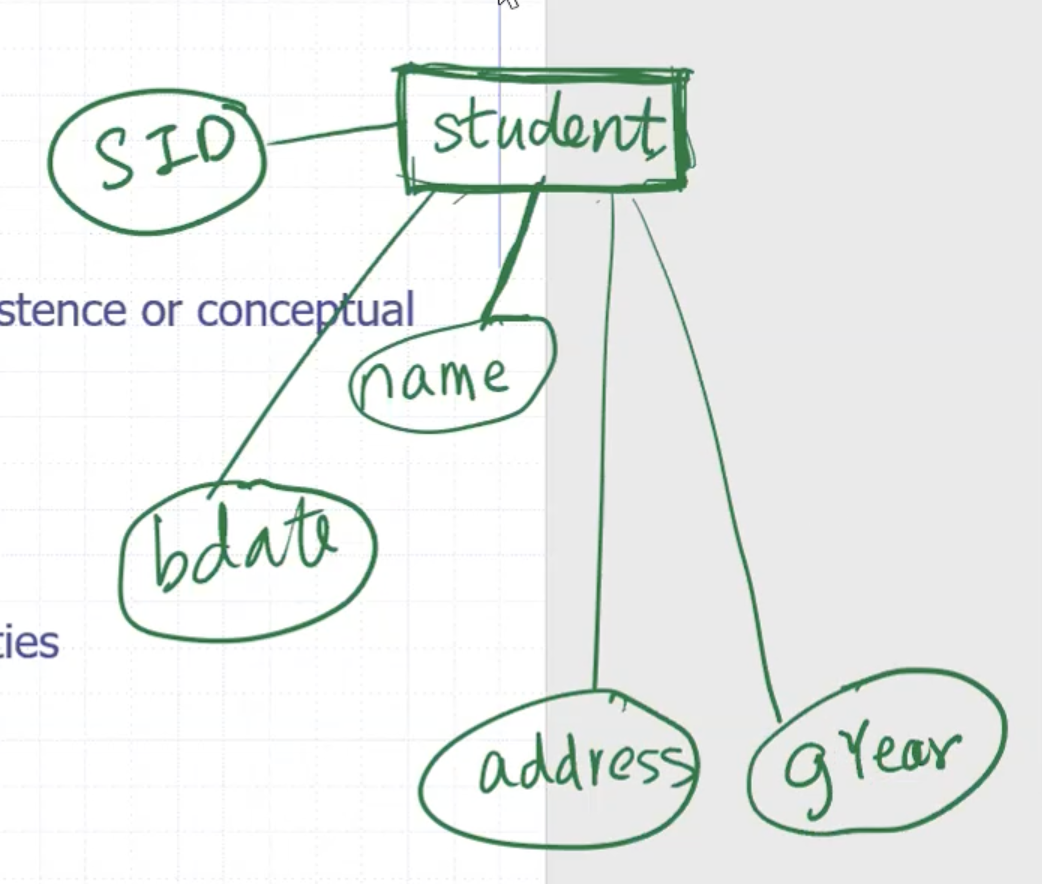
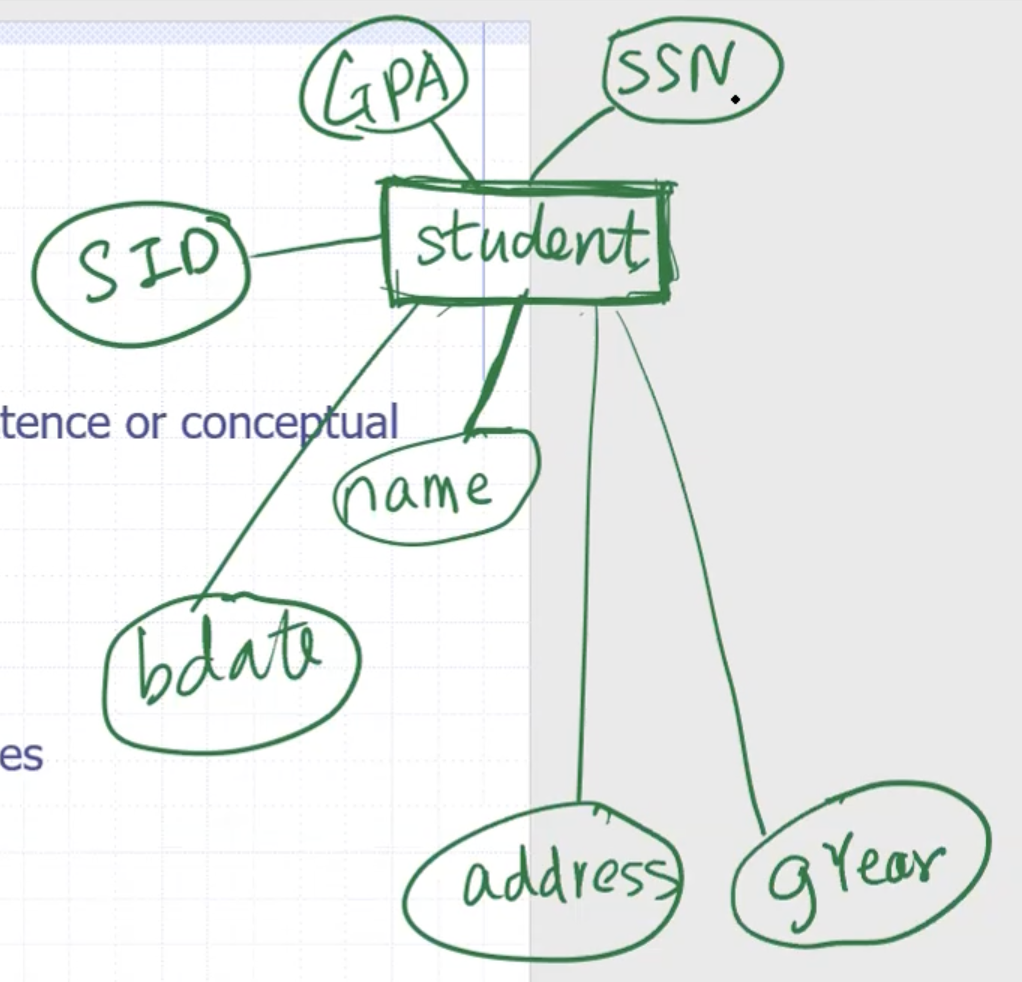
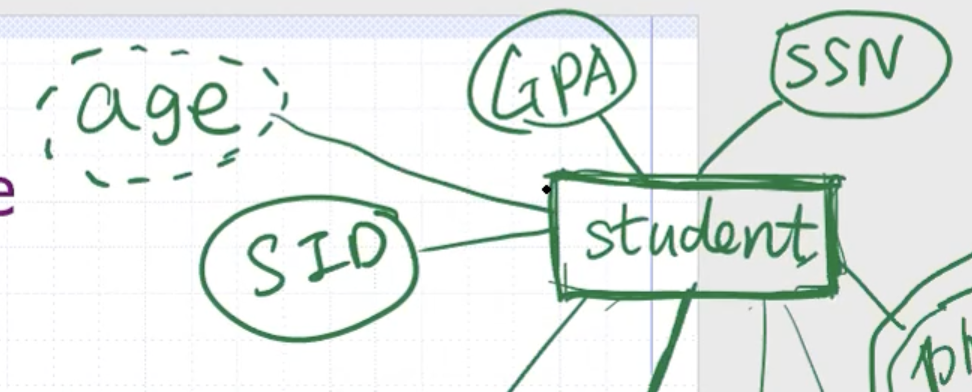
Properties can be used to describe the entity. For example for a student:
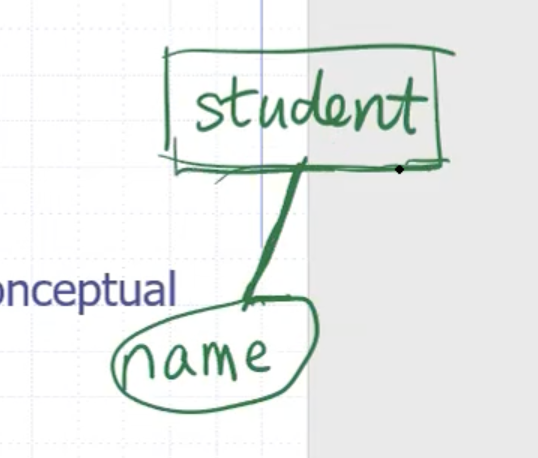
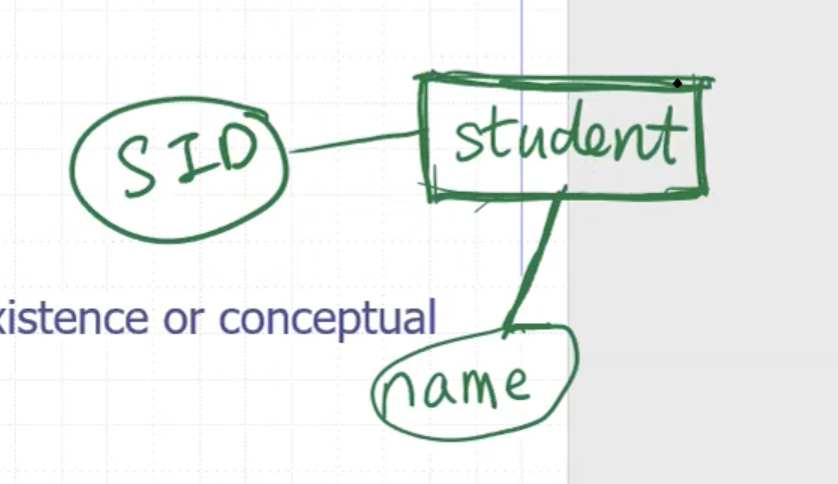
On notation:
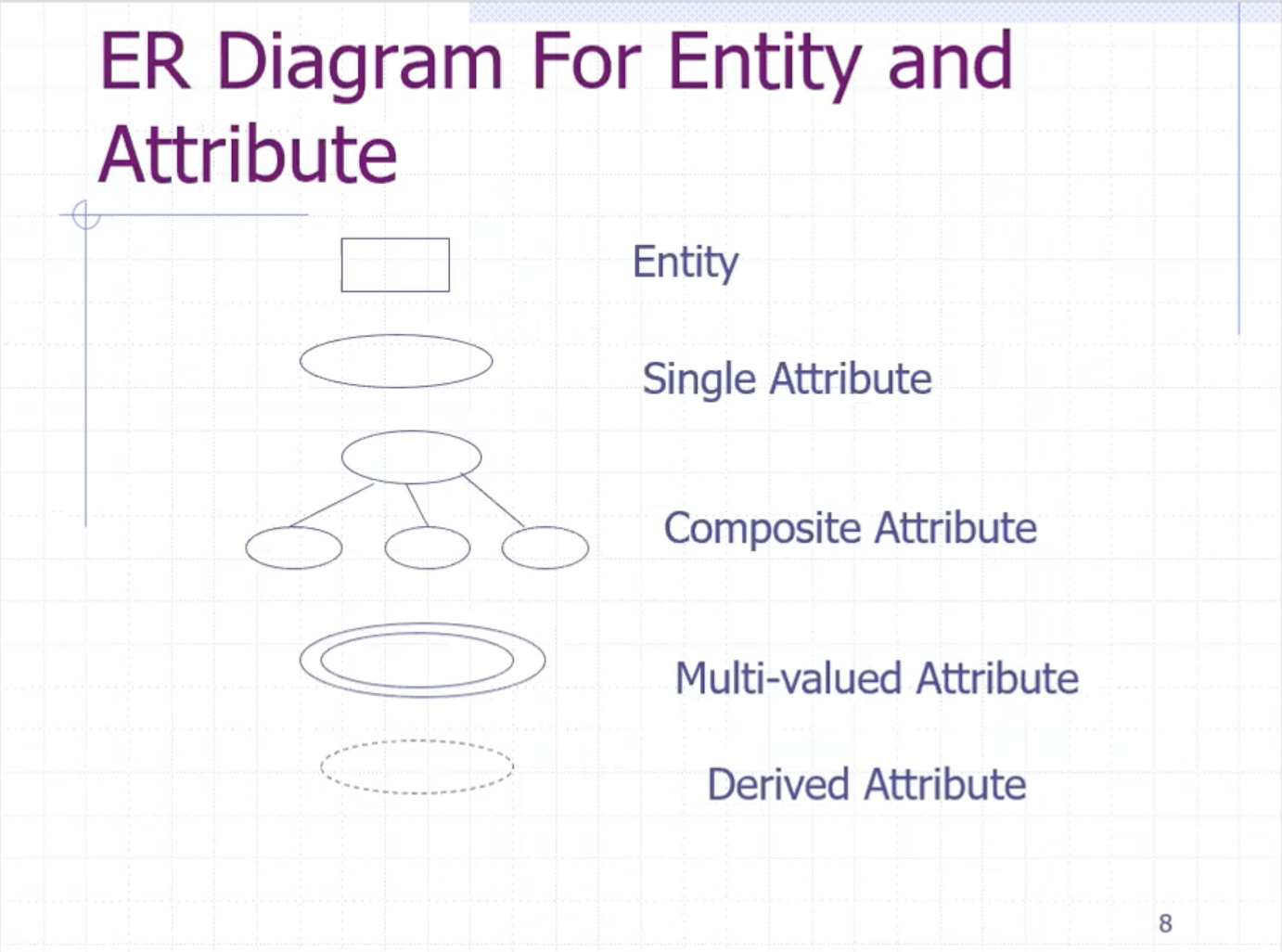
- entities are in rectangles
- attributes are circled and connected to the entity
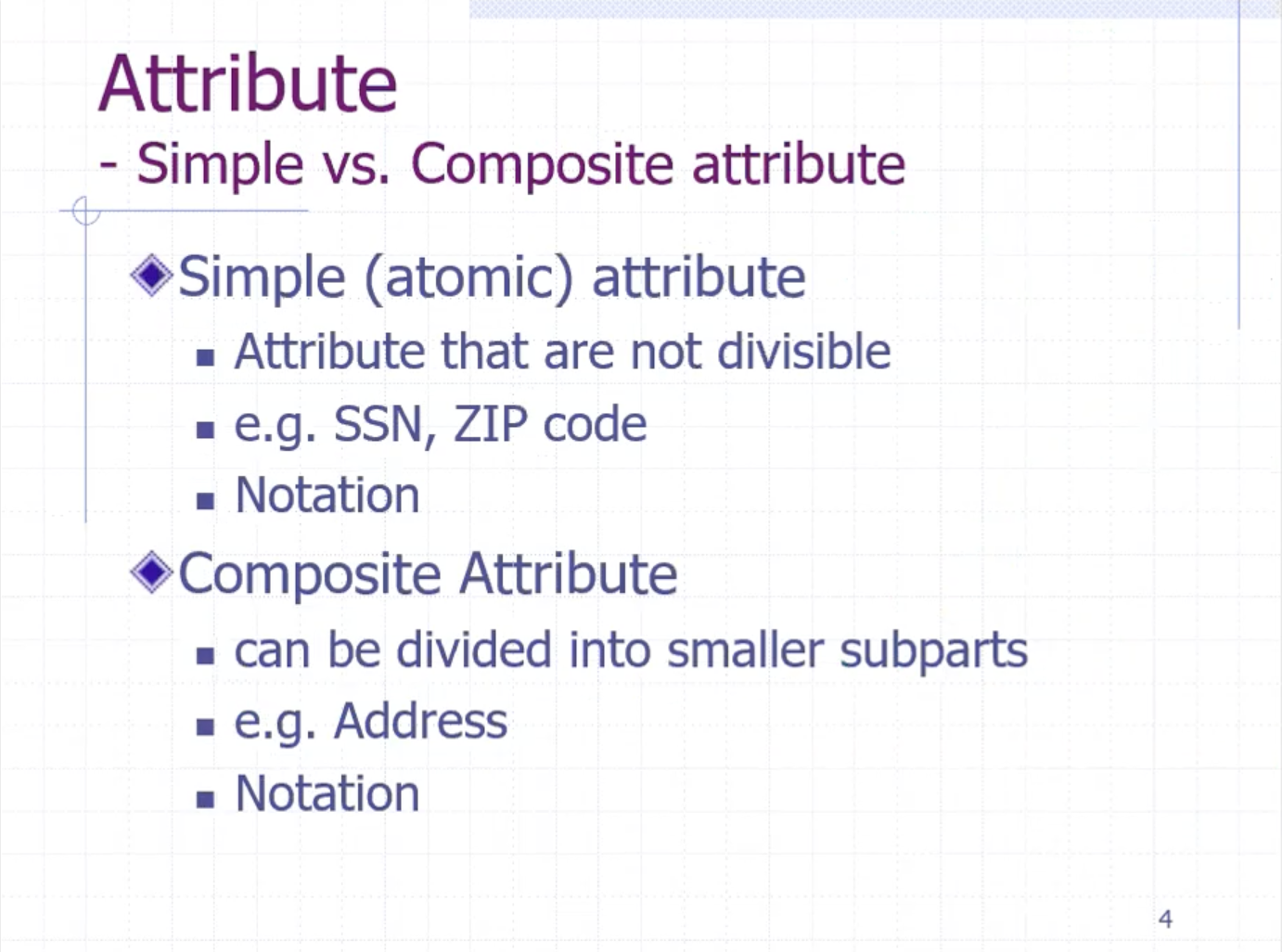
The divisibility of an attribute depends on application. We can divide address into subparts:
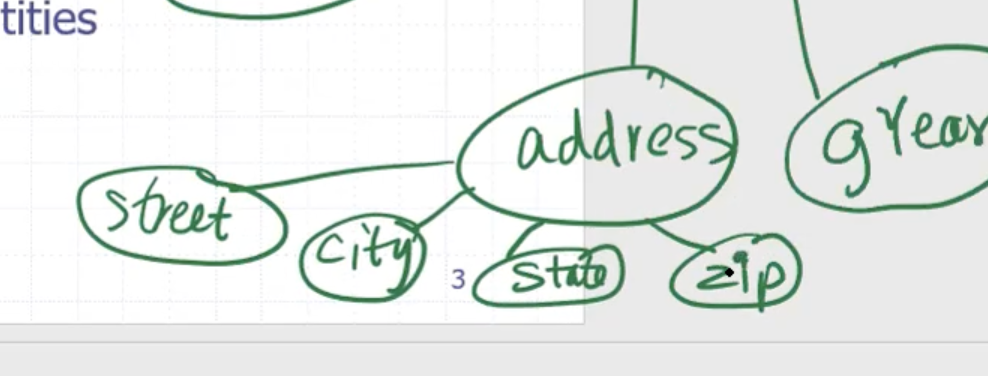
Here, address is the composite attribute. Name can also be composite.
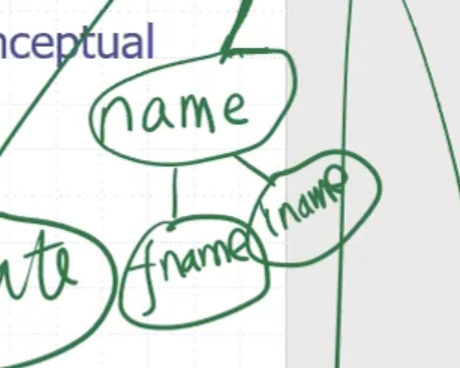
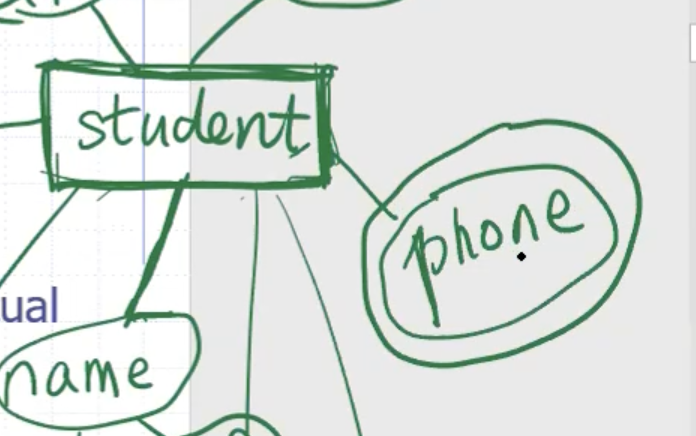
Students can only have 1 birthdate, but they can have multiple phone numbers. We can indicate that by a double circle.
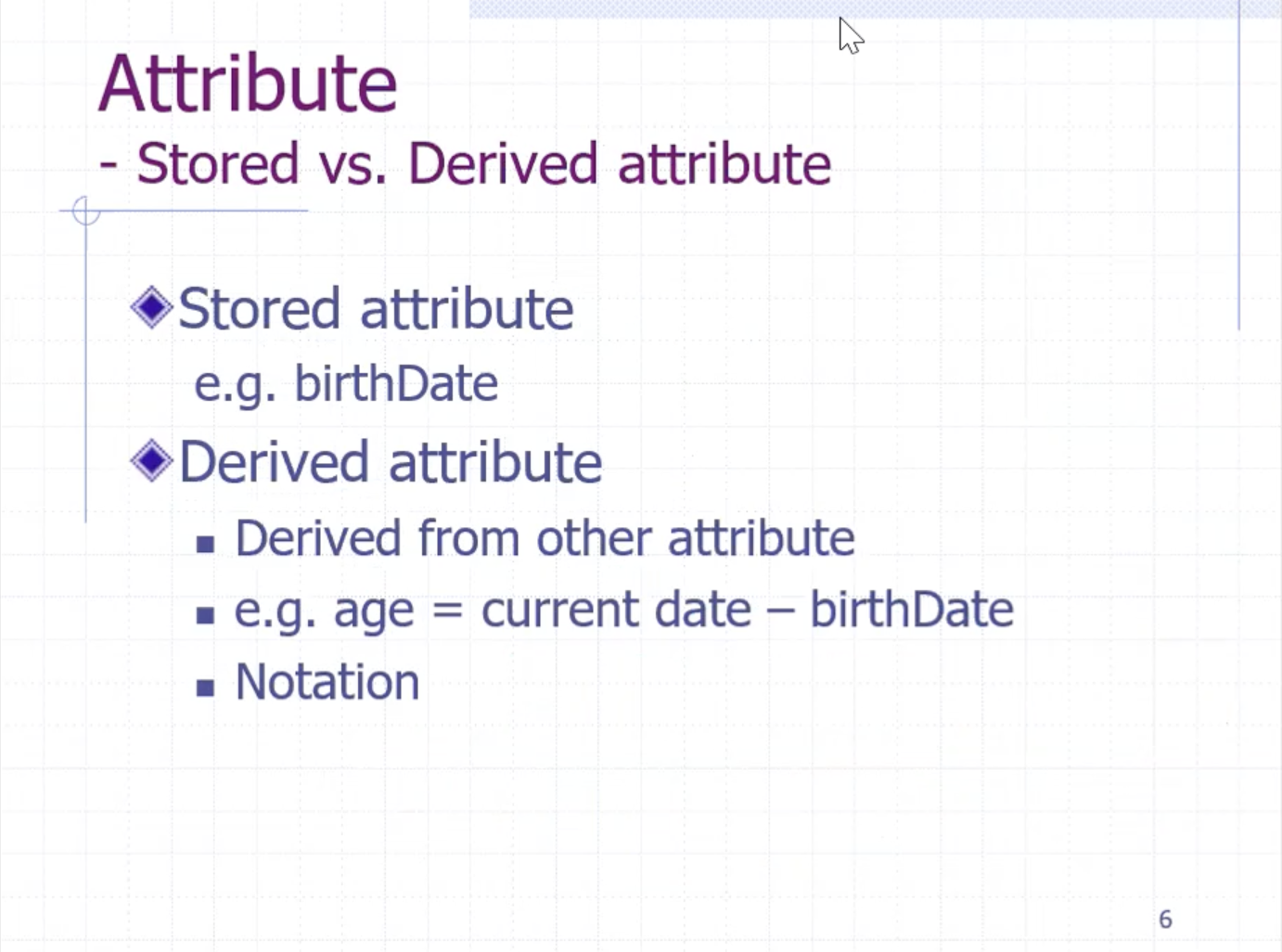
Since age can be calculated from the birthdate, we can put the age attribute in the ER diagram, but we indicate it can be derived with a dashed line.
ER diagram notation #
Keys #

- must be a unique identifier
We underline the attribute name to indicate that it is the key

If we have an entity called classroom:
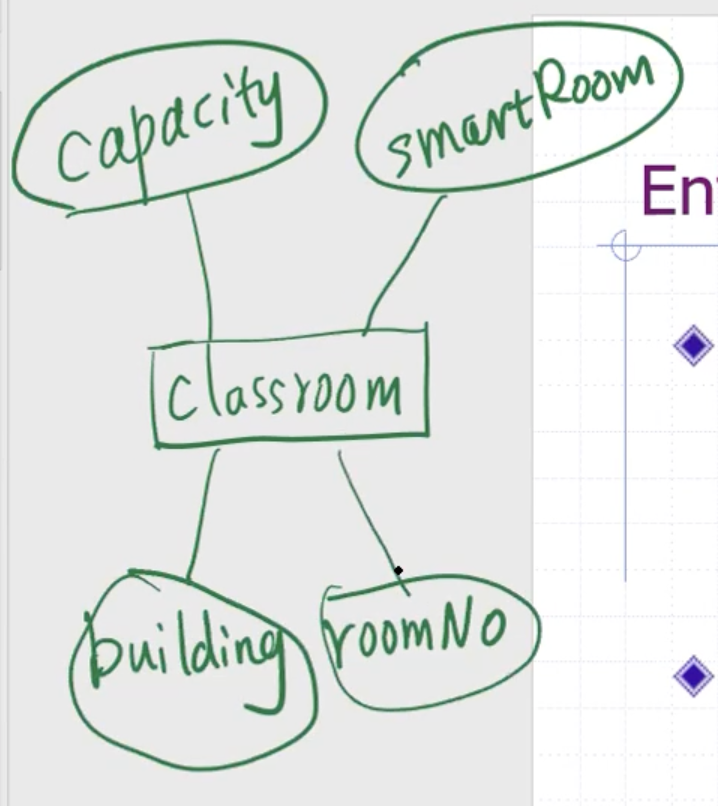
We can use a composite key of the attributes building and roomNo.
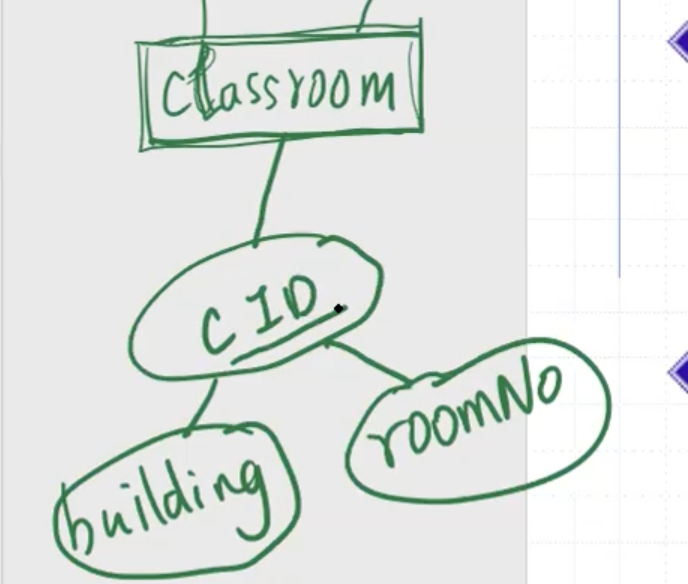
Keys must be minimal. In other words: adding capacity to the composite key for the classroom model wouldn’t add anything beneficial.
Value sets #

ER diagram example #

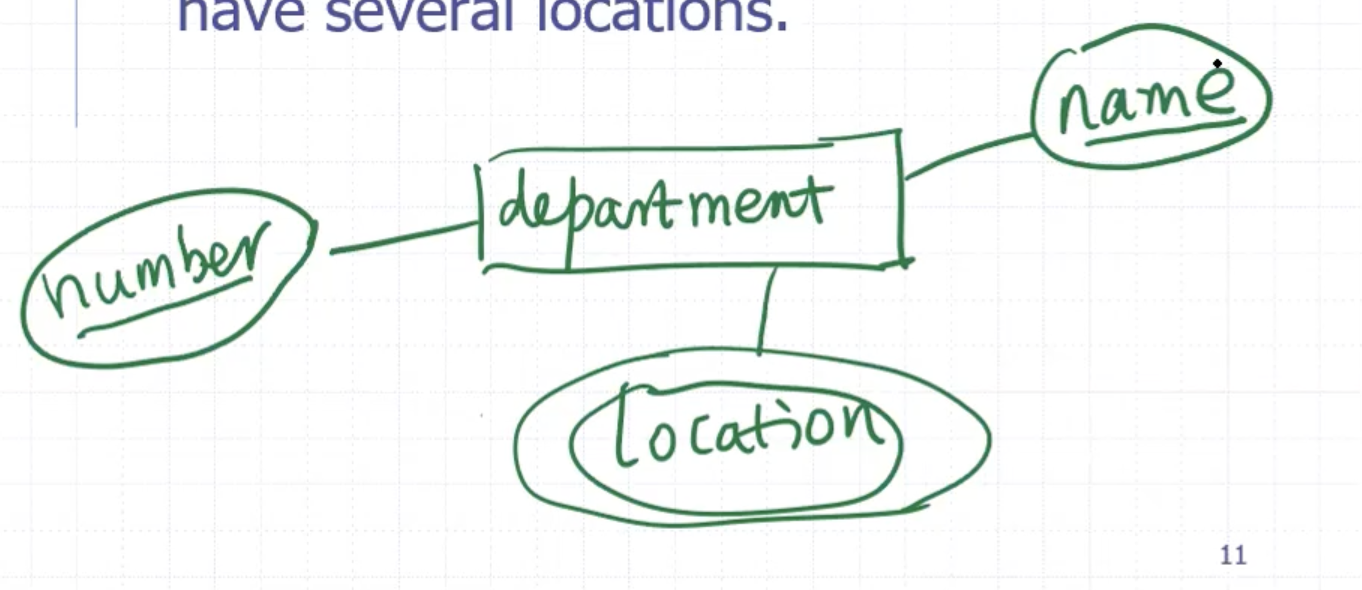
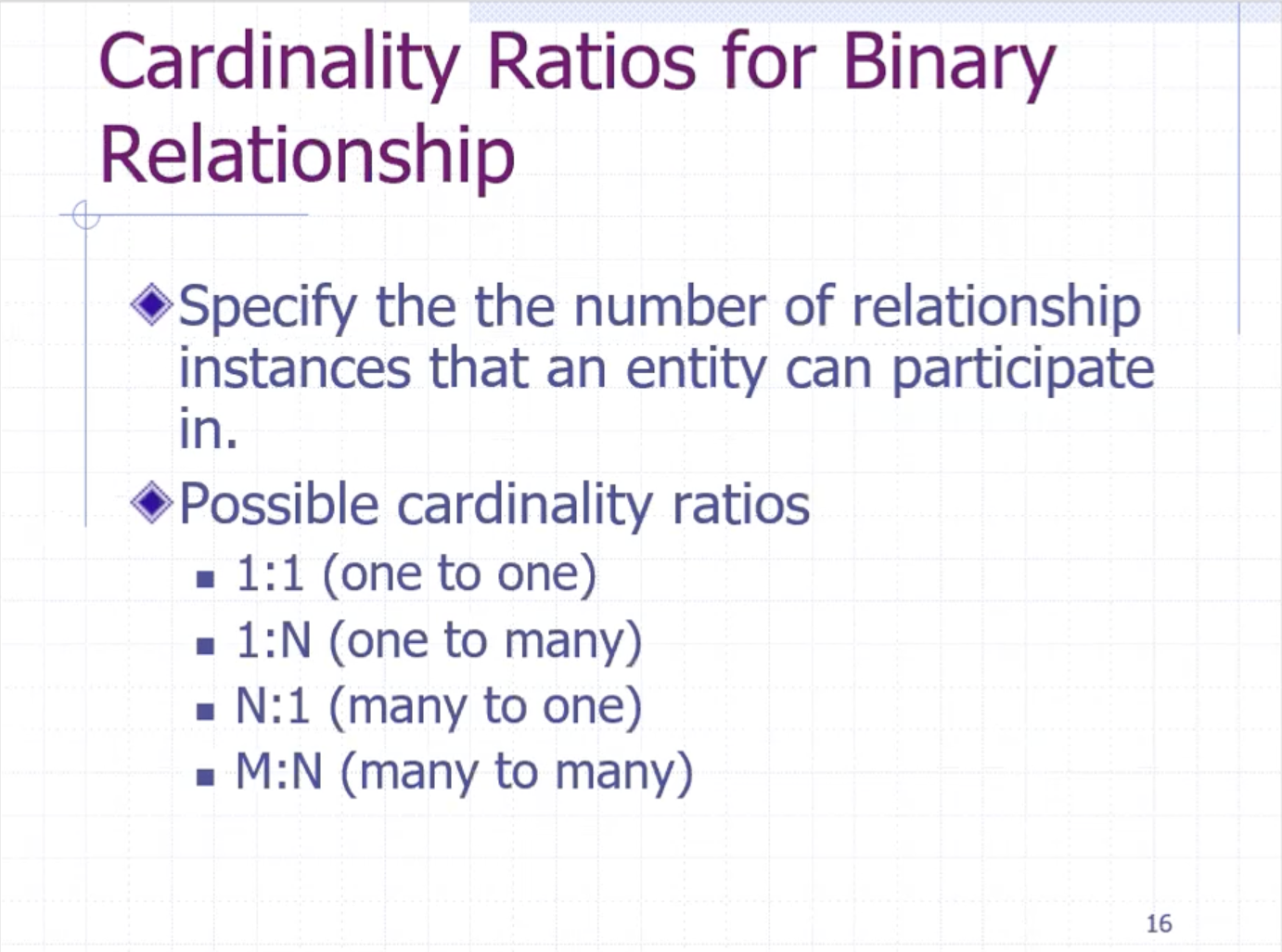
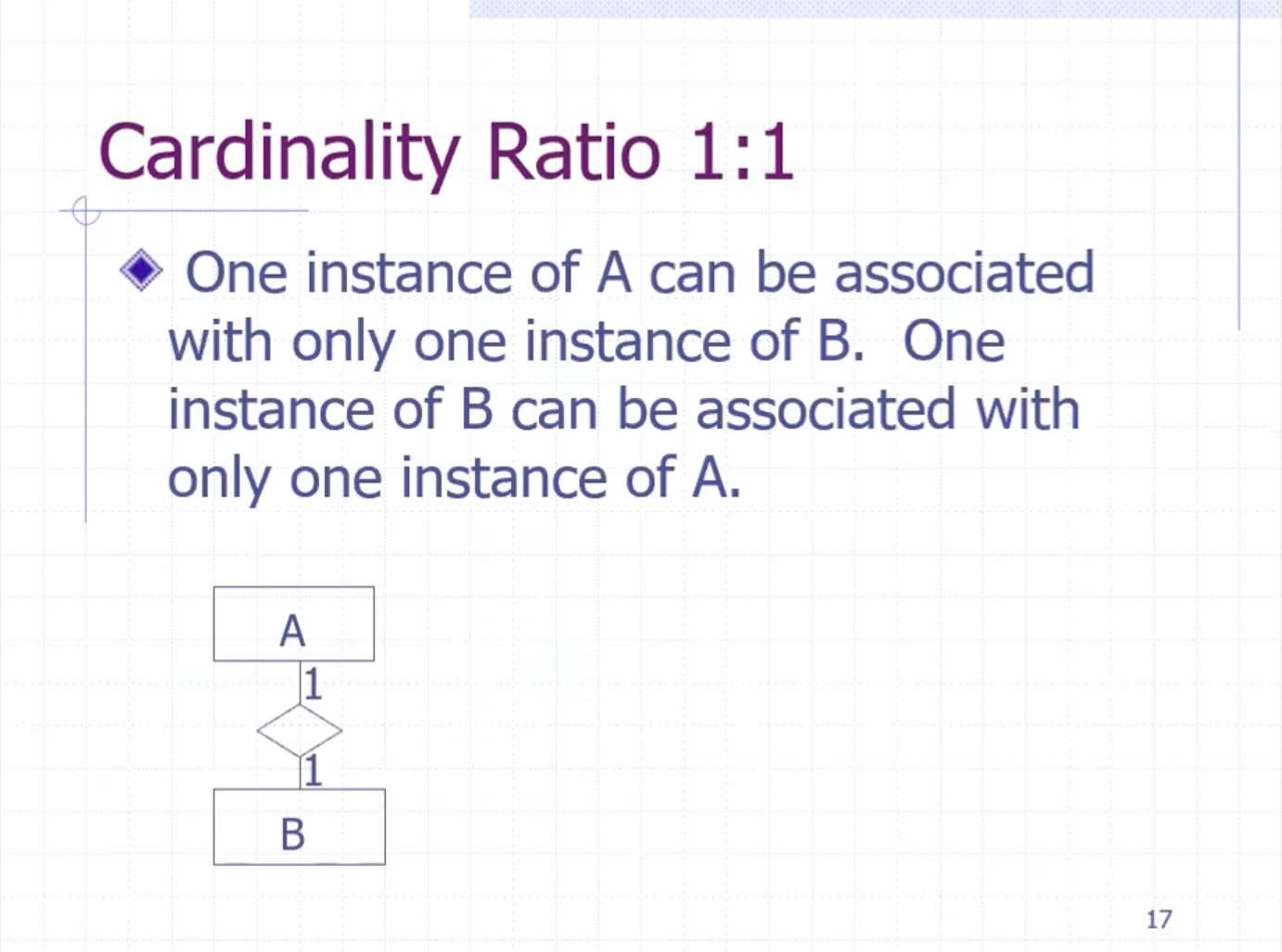
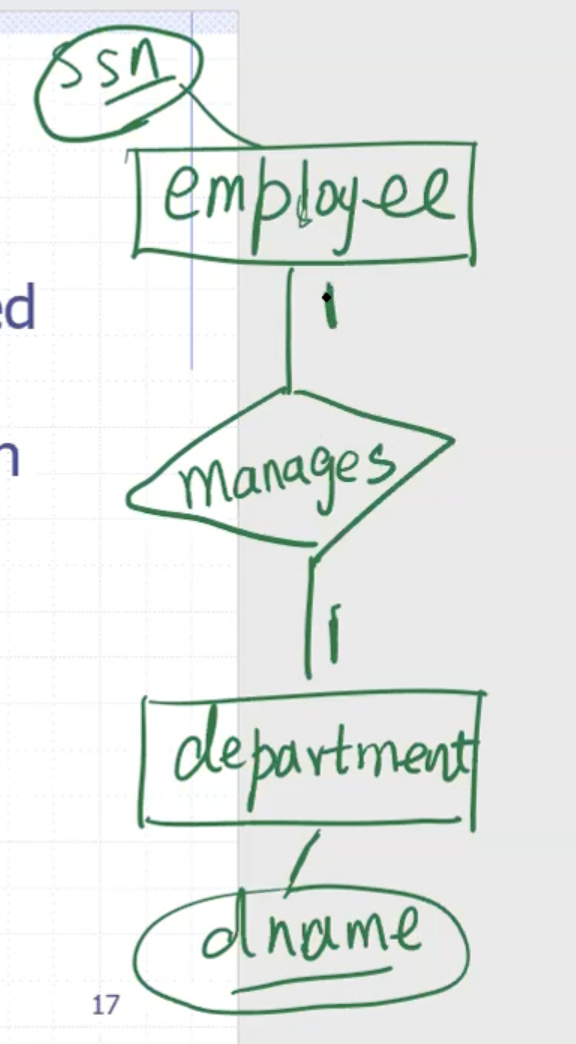
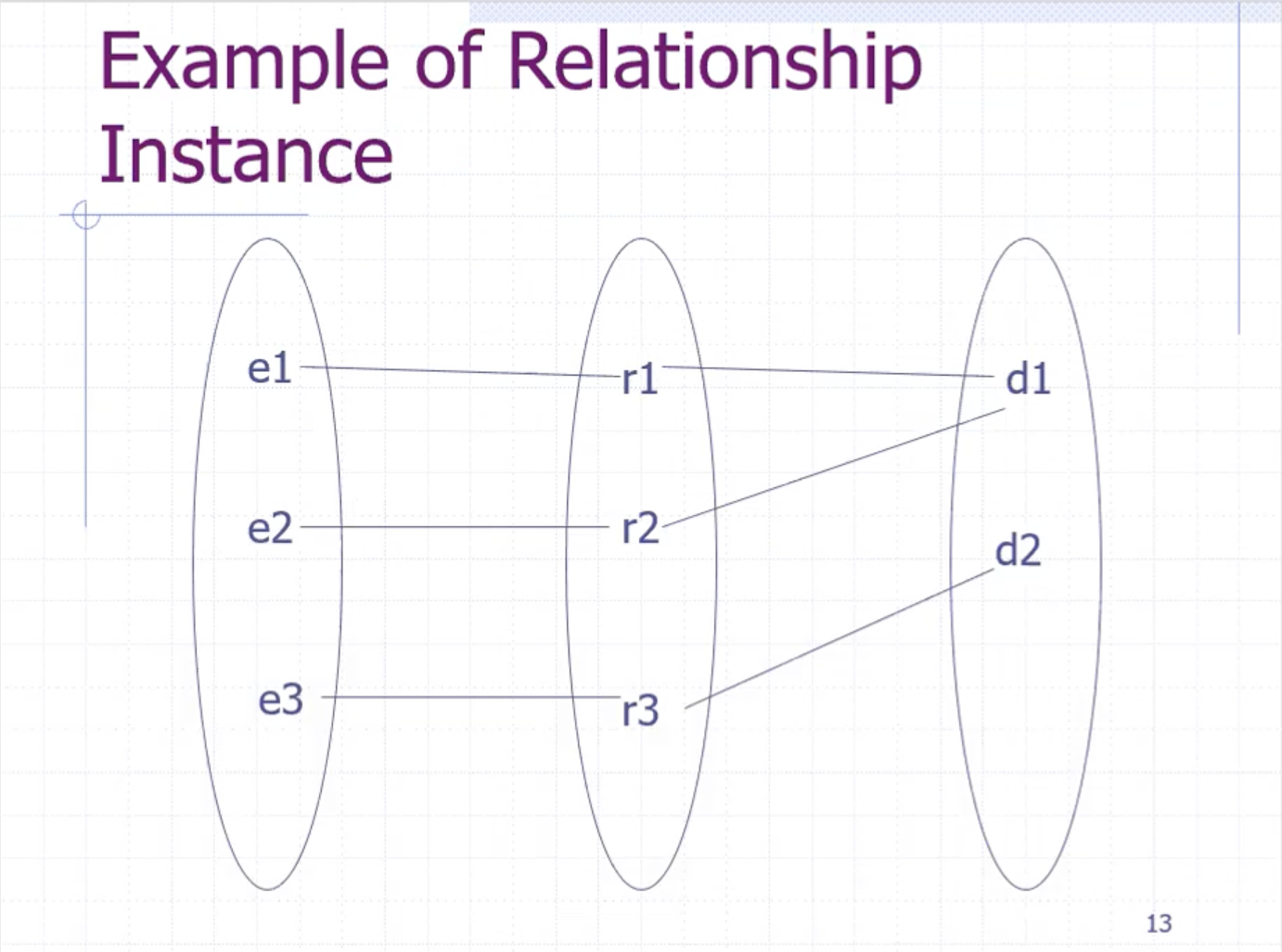
Relationship #

Relationships are drawn using a diamond.

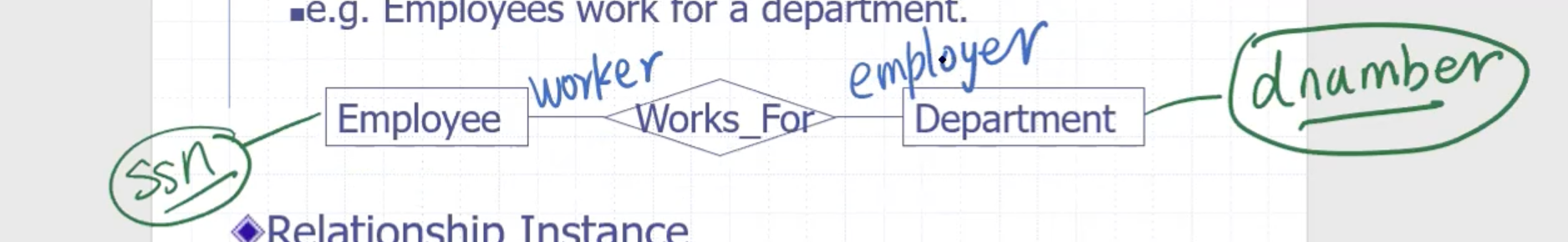
Structure constraint #