Visitor pattern #
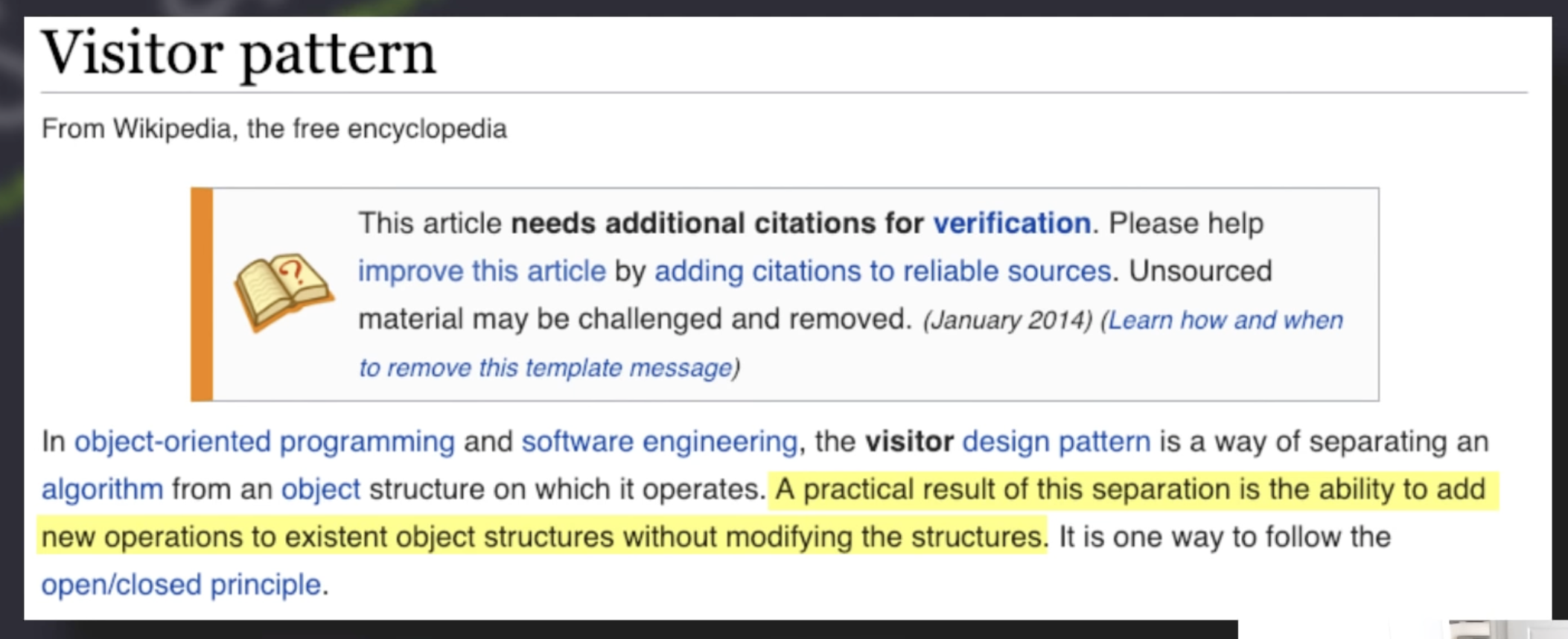
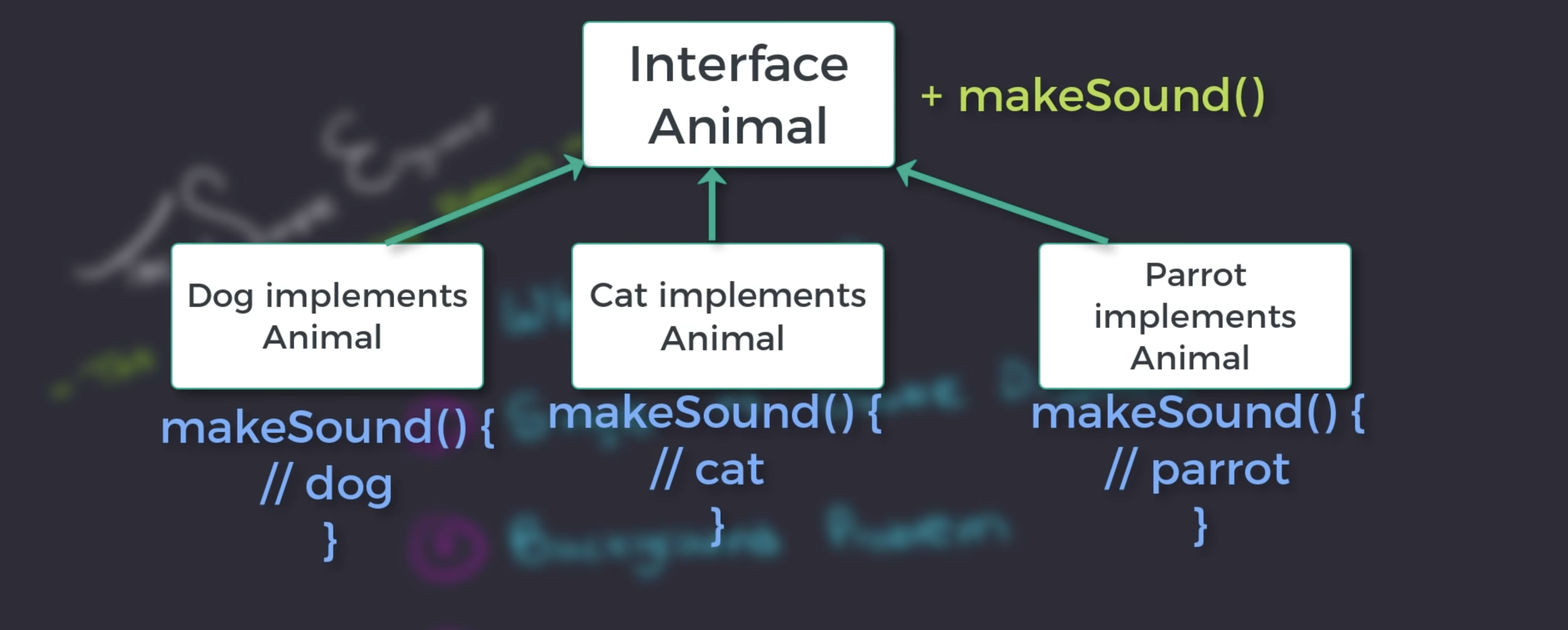
This becomes hard to maintain, and violates the open closed principle.
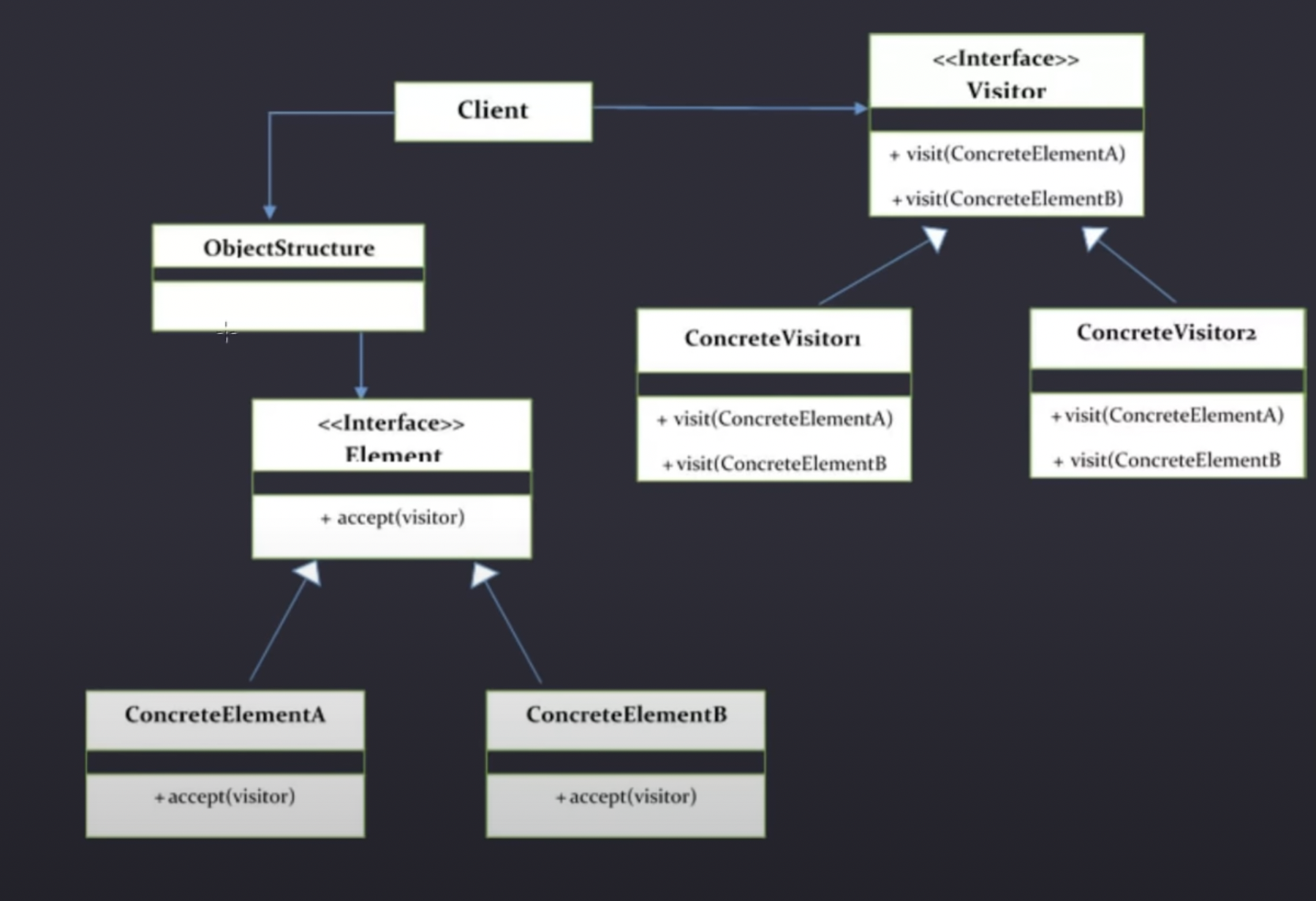
The concrete visitors are the extensible operations we can perform to add more features to the concrete elements.
Why the visitor pattern? #
Single vs double dispatch (polymorphism). Java supports single dispatch out of the box, but double isn’t supported out of the box.
Animal dog = new Dog();
Animal cat = new Cat();
Double dispatch is not openly supported, in other words you can’t have unique interactions between 2 different classes dynamically.
Something like
dog.makeSound(cat);
Gives a compilation because they are of Animal type.
Functional programming languages like scheme can support double (and multi) dispatch.
An example with credit cards #
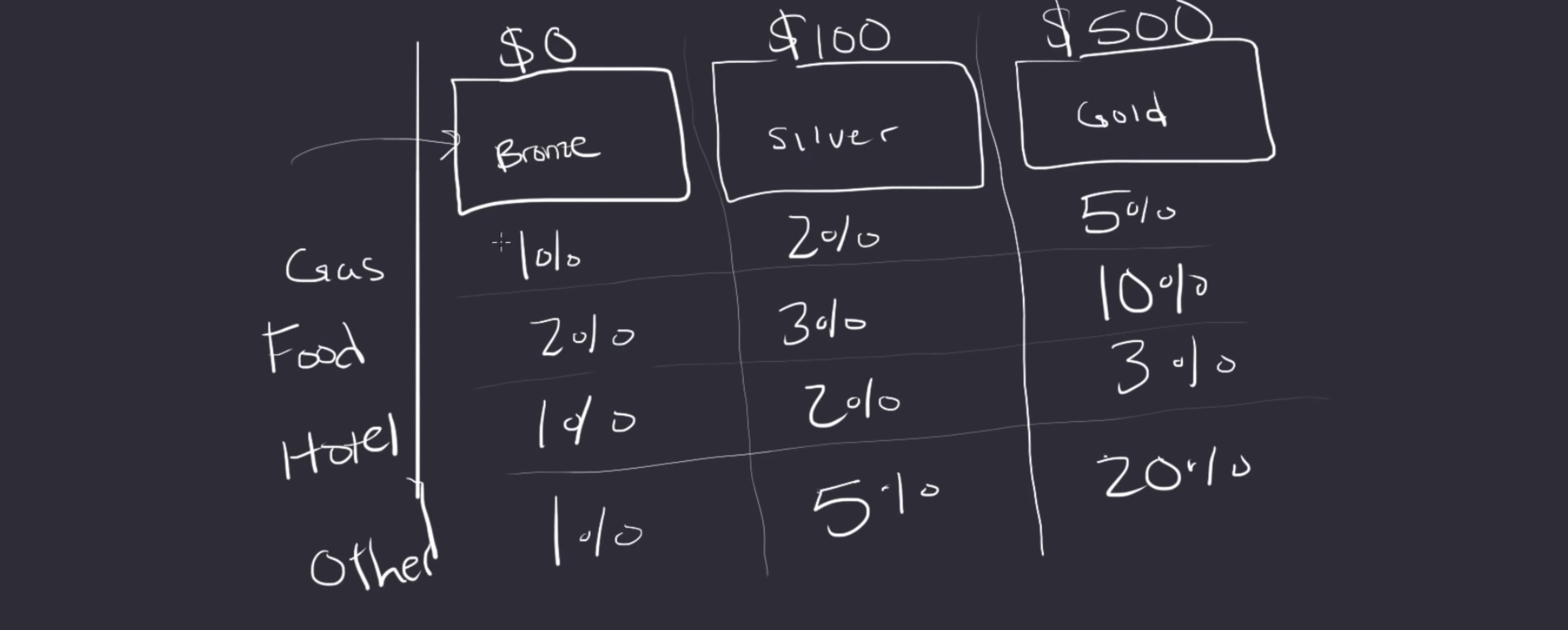
This table displays the interaction between 2 objects, the credit card and the offer type.
public interface CreditCard
{
String getName();
accept(OfferVisitor v);
}
public class BronzeCreditCard implements CreditCard
{
getName() {return "Bronze";}
void accept(OfferVisitor v)
{
v.visitBronzeCreditCard(this);
}
}
public interface OfferVisitor
{
void visitBronzeCreditCard(BronzeCreditCard bronze);
}
public class GasOfferVisitor implements OfferVisitor
{
void visitBronzeCreditCard(BronzeCreditCard bronze)
{
// code to compute cashback for a bronze card buying gas
}
}
public class HotelOfferVisitor implements OfferVisitor
{
void visitBronzeCreditCard(BronzeCreditCard bronze)
{
// code to compute cashback for a bronze card paying for a hotel
}
}
We can continue to add more offers without having to rewrite anything in our card classes.
So this is how its used:
BronzeCreditCard bronze = new BronzeCreditCard();
HotelOfferVisitor hotelVisitor = new HotelOfferVisitor();
GasOfferVisitor gasVisitor = new GasOfferVisitor();
// the interaction between a bronze card and a hotel offer
bronze.accept(hotelVisitor);
// the interaction between a bronze card and a gas offer
bronze.accept(gasVisitor);
The visitor pattern is usually going to be used if your class structure isn’t changed often, but the operations performed on the structure change quite a bit. Can be used when traversing a structure of items and needing to perform different operations on each node (compilers).